Imaging an EVLA OSRO HI data set: Difference between revisions
| Line 175: | Line 175: | ||
|} | |} | ||
After getting a good look at the image cube in [[viewer]], it's time to start setting clean boxes. For this, we'll use the [[Image:drawingSelector.png|35px|Rectangle Drawing Button.]] and [[Image:viewer_polygon.png|35px|Polygon Drawing Button.]] | After getting a good look at the image cube in [[viewer]], it's time to start setting clean boxes. For this, we'll use the [[Image:drawingSelector.png|35px|Rectangle Drawing Button.]] and [[Image:viewer_polygon.png|35px|Polygon Drawing Button.]] buttons. Make sure '''Add'' (and not '''Erase''') is selected near the top of the [[viewer]] window in the menu that looks like this: [[Image:viewer_add_erase.png|55px|Add or erase clean boxes?.]] | ||
Find some flux that you would like to clean, and click the [[Image:drawingSelector.png|35px|Rectangle Drawing Button.]] icon with the mouse button you would like to use for setting clean boxes. Click and drag with this mouse button to create a green square, which will be | |||
[[Main Page | ↵ '''CASA Guides''']] | [[Main Page | ↵ '''CASA Guides''']] | ||
Revision as of 22:02, 12 March 2010
This article is under construction. Watch this space!
Overview
This tutorial explains how to image an HI dataset acquired with the WIDAR0 correlator. It assumes that you've already calibrated your data as described in the calibration tutorial, and that you now have a split dataset with a single source of interest in it. In this example, the source is called 'Leo-2'; see the calibration tutorial for more details on this data set.
Flag Your Split Data
Load the split dataset into plotms and/or viewer and flag any bad data.
For a spectral line dataset like this one, you'll probably want to average in various ways to spot bad data. Averaging channels together can make bad baselines pop up!
Doppler Tracking
Presently, doppler tracking is not performed online by the EVLA, so we have to correct for any velocity shifts now, in post-processing, with cvel.
# cvel :: regrid an MS to a new spectral window / channel structure or frame
vis = 'leo2.ms' # Name of input measurement set
outputvis = 'leo2_cvel.ms' # Name of output measurement set
passall = False # Pass through (write to output MS) non-selected data with no change
field = '' # Select field using field id(s) or field name(s)
spw = '0' # Select spectral window/channels
selectdata = False # Other data selection parameters
mode = 'channel' # Regridding mode
nchan = -1 # Number of channels in output spw (-1=all)
start = 0 # first input channel to use
width = 1 # Number of input channels to average
interpolation = 'linear' # Spectral interpolation method
phasecenter = '' # Image phase center: position or field index
restfreq = '1420405751.786Hz' # rest frequency (see help)
outframe = 'BARY' # Output frame (''=keep input frame)
veltype = 'radio' # velocity definition
hanning = False # Turn on Hanning smoothing of spectral channels
async = False # If true the taskname must be started using cvel(...)
Cvel creates a new measurement set (outputvis= 'leo2_cvel.ms') for which, at each time, the spectrum has been shifted and channels regridded to keep the spectral line centered in the frame of your choice (here, we choose barycentric; outframe= 'BARY'). You'll also want to give cvel the rest frequency of your spectral line (restfreq= '1420405751.786Hz' for HI).
Continuum Subtraction
|
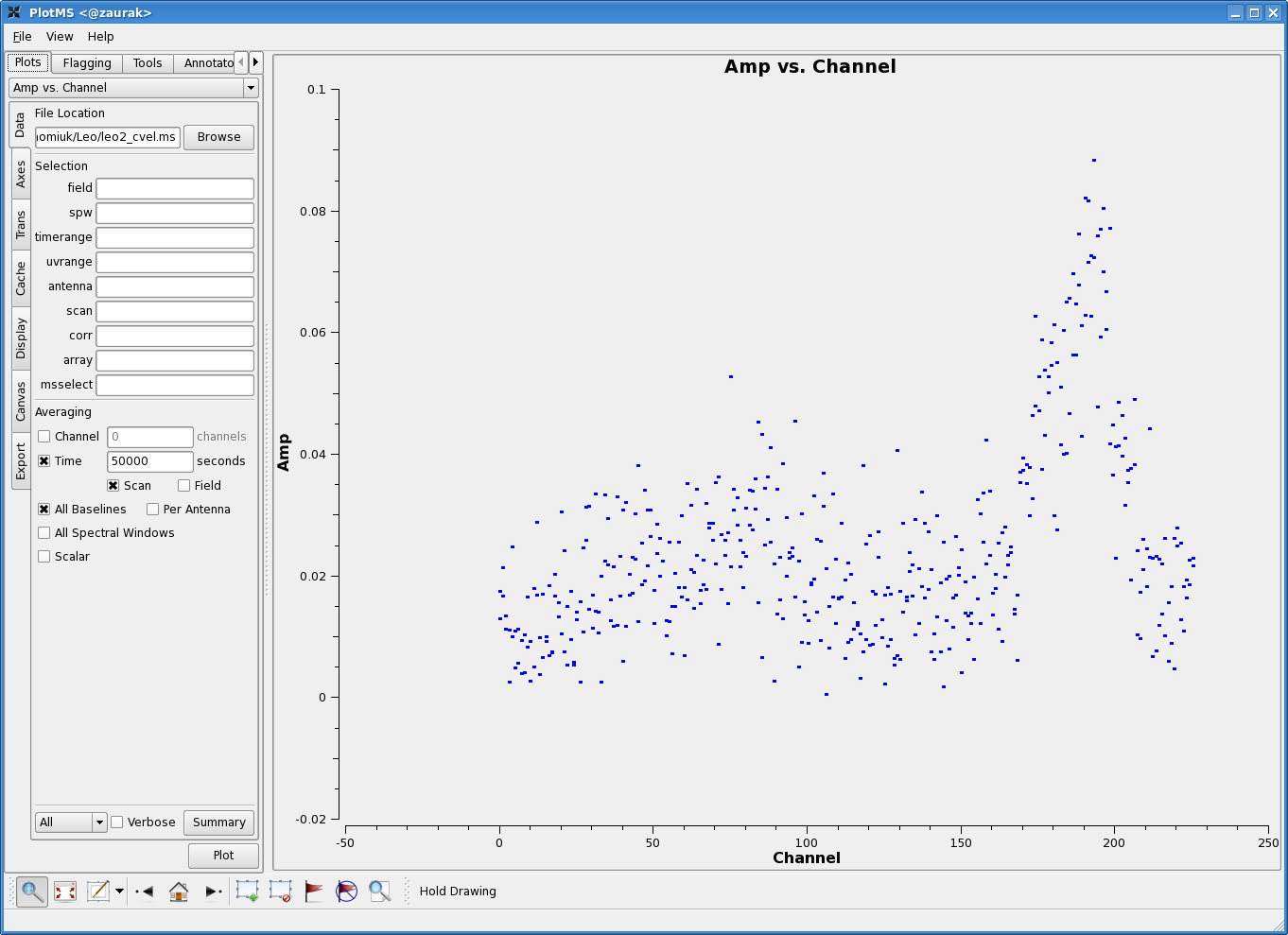
In preparation for subtracting the continuum, let us plot up the combined spectrum on our science field and identify some line-free channels. Open up a plotms GUI window and load the doppler-tracked measurement set containing your science target. You'll want to average over both time and baselines to get as much signal-to-noise as possible, hopefully revealing a nice 21 cm profile. In the Data tab of plotms, set the below averaging options:
(See Averaging data in plotms for more details on averaging options). You'll also want to click on the Axes tab in the plotms window, and change the axes settings to:
The figure to the right shows the resulting plot in plotms. There is clearly some line emission around channel 190, and possibly some faint emission around channel 88. Let's use channels 10--55 and 120--155 to fit the continuum. |
Next, use uvcontsub to subtract the continuum from your data set. Here are the parameters we used:
# uvcontsub :: Continuum fitting and subtraction in the uv plane vis = 'leo2.ms' # Name of input visibility file field = '' # Select field using field id(s) or field name(s) fitspw = '0:10~55;120~155' # Spectral window/channel selection for fitting the continuum spw = '0' # Spectral window selection for subtraction/export solint = '60s' # Continuum fit timescale fitorder = 0 # Polynomial order for the fit fitmode = 'subtract' # Use of continuum fit (subtract,replace,model) splitdata = True # Split out continuum, continuum-subtracted data async = False # If true the taskname must be started using uvcontsub(...)
Here, we are fitting the continuum to channels 10--55 and 120--155 of spectral window 0 (the only spectral window). We're averaging over one minute intervals (solint= '60s') before fitting the continuum; note that the default will fit each integration (so, every one second for un-averaged EVLA data). We're fitting a simple mean to the continuum (fitorder= 0), although higher-order fits are certainly possible.
Note that the form of the output from uvcontsub can be a bit confusing, and depends on your choice of the fitmode and splitdata parameters. If splitdata= True, two new measurement sets will be created: one with the fitted continuum data ('leo2.ms.cont') and one with the continuum-subtracted data ('leo2.ms.contsub'). Uvcontsub will also alter your 'corrected' and 'model' data columns---exactly how depends on your choice of fitmode. We have set fitmode= 'subtract', which means the fitted continuum values are placed in the 'model' column, and the continuum-subtracted data are placed in the 'corrected' column.
If you have previously applied a calibration to the measurement set that you now want to continuum-subtract (with applycal, so that the 'data' and 'corrected' columns are different), note that uvcontsub will overwrite the 'corrected' data column. In this case, it is best to first create a new calibrated measurement set using split (datacolumn= 'corrected'), and then run uvcontsub on that newly-split data set.
Make an Image Cube
|
It's finally time to make an image! Pretty much all imaging in CASA should be done with clean, including mosaicing. Here, we discuss interactive imaging/deconvolution, but see the NGC 5921 tutorial for an example of non-interactive imaging.
# clean :: Invert and deconvolve images with selected algorithm
vis = 'leo2.ms.contsub' # Name of input visibility file
imagename = 'leo2_cube0' # Pre-name of output images
outlierfile = '' # Text file with image names, sizes, centers for outliers
field = '' # Field Name or id
spw = '' # Spectral windows e.g. '0~3', '' is all
selectdata = False # Other data selection parameters
mode = 'channel' # Spectral gridding type (mfs, channel, velocity, frequency)
nchan = -1 # Number of channels (planes) in output image; -1 = all
start = 0 # First channel to use (0=first channel specified in spw)
width = 1 # Number of input channels to average
interpolation = 'nearest' # Spectral interpolation (nearest, linear, cubic)
outframe = '' # velocity frame of output image
gridmode = '' # Gridding kernel for FFT-based transforms, default='' None
niter = 10000 # Maximum number of iterations
gain = 0.1 # Loop gain for cleaning
threshold = '0.0mJy' # Flux level to stop cleaning, must include units: '1.0mJy'
psfmode = 'clark' # Method of PSF calculation to use during minor cycles
imagermode = '' # Options: 'csclean' or 'mosaic', '', uses psfmode
multiscale = [] # Deconvolution scales (pixels); [] = standard clean
interactive = True # Use interactive clean (with GUI viewer)
npercycle = 500 # Clean iterations before interactive prompt (can be changed)
chaniter = False # Clean each channel to completion (True), or all channels each cycle (False)
mask = [] # Cleanbox(es), mask image(s), and/or mask region(s)
imsize = [512, 512] # x and y image size in pixels. Single value: same for both
cell = ['12.0arcsec', '12.0arcsec'] # x & y cell size(s). Default unit arcsec.
phasecenter = '' # Image center: direction or field index
restfreq = '' # Rest frequency to assign to image (see help)
stokes = 'I' # Stokes params to image (eg I,IV, QU,IQUV)
weighting = 'briggs' # Weighting of uv (natural, uniform, briggs, ...)
robust = 0.0 # Briggs robustness parameter
npixels = 0 # number of pixels to determine uv-cell size 0=> field of view
uvtaper = False # Apply additional uv tapering of visibilities
modelimage = '' # Name of model image(s) to initialize cleaning
restoringbeam = [''] # Output Gaussian restoring beam for CLEAN image
pbcor = False # Output primary beam-corrected image
minpb = 0.2 # Minimum PB level to use
calready = True # True required for self-calibration
async = False # If true the taskname must be started using clean(...)
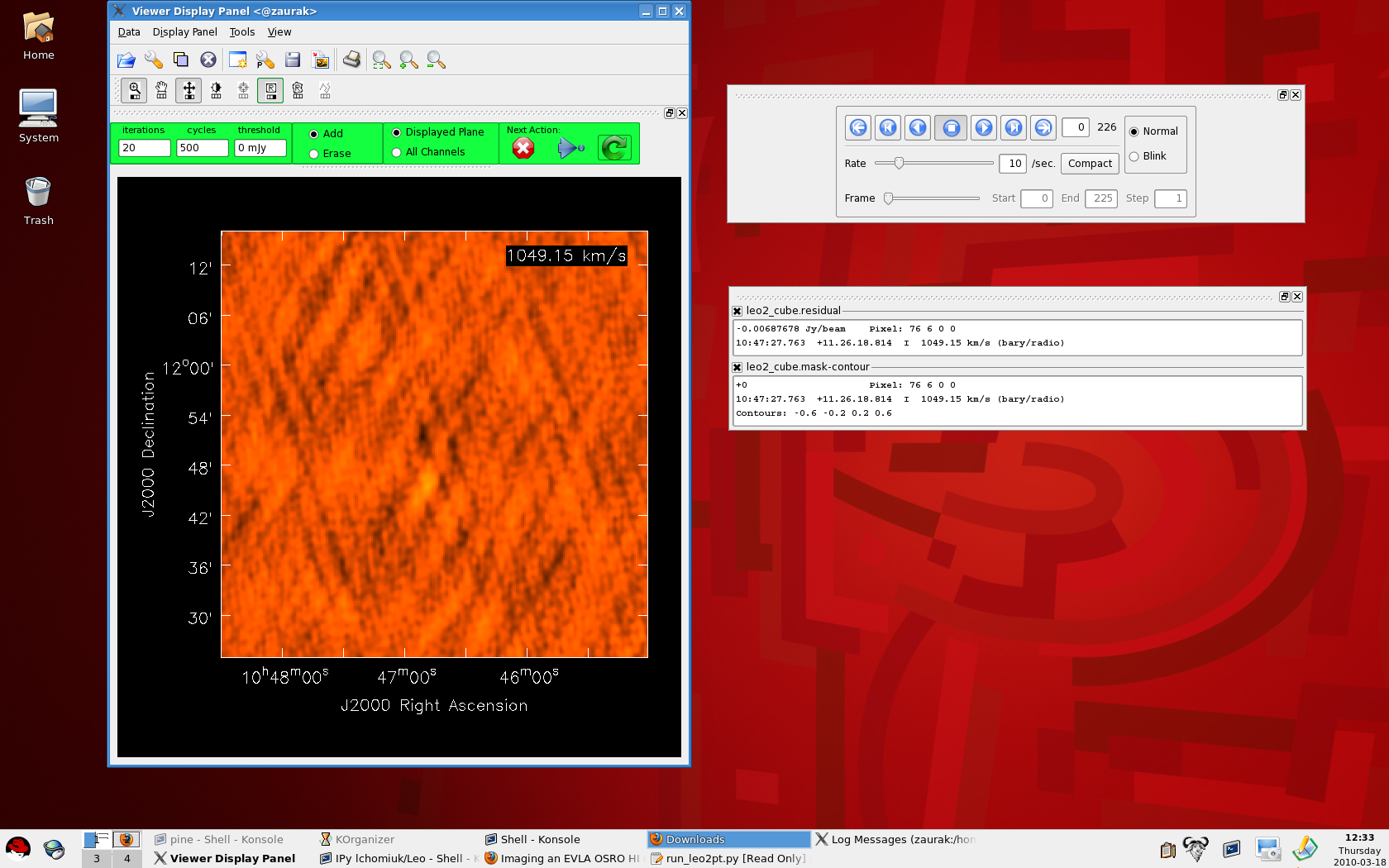
The viewer which pops up during interactive clean |
|
Wait while CASA processes your measurement set, producing output that looks like this on the command line: CASA <25>: go clean ---------> go(clean) Executing: clean() 0%....10....20....30....40....50....60....70....80....90....100% 0%....10....20....30....40....50....60....70....80....90....100% After the second '100%', a viewer window will pop up with your dirty image cube (like the figure above and to the right). You can make the image itself bigger in the viewer by clicking on the dashed line above the panel with the DVD-like control buttons and dragging it onto your desktop. Similarly, you can also drag the bottom-most panel which tracks your mouse and displays basic image information out of the viewer and on to the desktop (see the figure to the right). To view different channels, use the DVD-like control panel. The Drag panels out of the viewer and on to your desktop to enlarge the image |
After getting a good look at the image cube in viewer, it's time to start setting clean boxes. For this, we'll use the ![]() and
and ![]() buttons. Make sure Add (and not Erase') is selected near the top of the viewer window in the menu that looks like this:
buttons. Make sure Add (and not Erase') is selected near the top of the viewer window in the menu that looks like this: ![]()
Find some flux that you would like to clean, and click the ![]() icon with the mouse button you would like to use for setting clean boxes. Click and drag with this mouse button to create a green square, which will be
icon with the mouse button you would like to use for setting clean boxes. Click and drag with this mouse button to create a green square, which will be