Sunspot Band6 Imaging for CASA 4.7
Overview
This portion of the Sunspot Band6 CASA Guide for CASA 4.7 will cover the image synthesis of a sunspot. It begins where Sunspot_Band6_Calibration_for_CASA_4.7 is completed. In the case, we assume that you are working on the working directory ‘Sunspot_Band6_UncalibratedData’.
If you did not complete the Calibration portion of the guide, the you can download the calibrated visibility data by click on the region closed to your location:
Once the download has finished, unpack the file:
# In a terminal outside CASA
tar -xvzf Sunspot_Band6_CalibratedData.tgz
cd Sunspot_Band6_CalibratedData
#Start CASA
casa
From next, we will show all commands for solar image synthesis. If you do not want to cut-&-past the commands, you can use the script as described in #Alternative way of Imaging.
Confirm your version of CASA
This guide has been written for CASA release 4.7. Please confirm your version before proceeding.
# In Casa
version = casadef.casa_version
print "You are using " + version
if (version < '4.7.0'):
print "YOUR VERSION OF CASA IS TOO OLD FOR THIS GUIDE."
print "PLEASE UPDATE IT BEFORE PROCEEDING."
else:
print "Your version of CASA is appropriate for this guide."Flagging of the surplus scans
<figure id="fieldid">
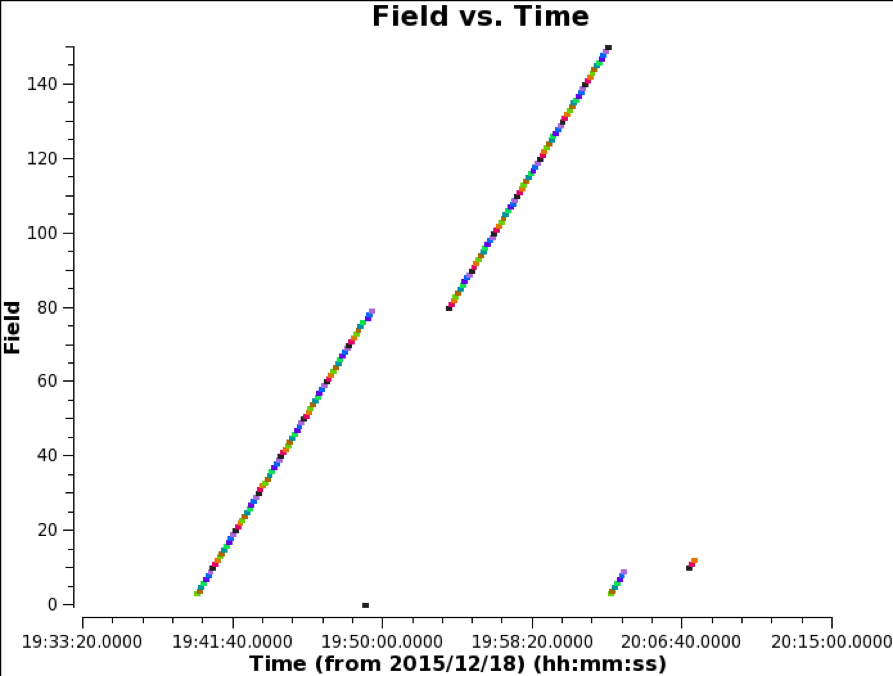
</figure>
The actual duration of the observations does not exactly equal to the required duration of the 149-poinitng MOSAIC. Hence, some fields were observed twice, as shown in <xr id="fieldid"/>. Although the visibility data of the surplus scans are valid, it is better that they are not used for the image synthesis, considering the uniformity of the sensitivity in a map. For the reason, we flagged the surplus scans by the following command.
# In Casa
msc = ‘uid___A002_Xae00c5_X2a8d_split.ms.cal’
flagdata(vis = msc, mode = 'manual', timerange = '2015/12/18/20:02:35~20:08:20', flagbackup = False)
Continuum imaging
Now we are ready to synthesize a sunspot image from the visibilities. For the image synthesis, we execute the following command.
# In Casa
clean(vis = msc, spw = '0,1,2,3', stokes = 'I', field='0,3~150',phasecenter='0', imagename='AR12470_B6AllSpw_I', cell = '0.15 arcsec', imsize = [2048, 2048], interactive = False,mask = 'box[[555pix,565pix],[1505pix,1490pix]]', weighting = 'briggs', robust = 1., niter = 5000000000, sfmode = 'clark', imagermode='mosaic', mosweight = True, minpb=0.3, pbcor=F, threshold='1.0Jy', gain=0.1)
To obtain good SNR of the image, we synthesize an image from the data of all spectrum windows. From here, we will comment only about the options that are the special measures for solar image synthesis.
<figure id="mos2">
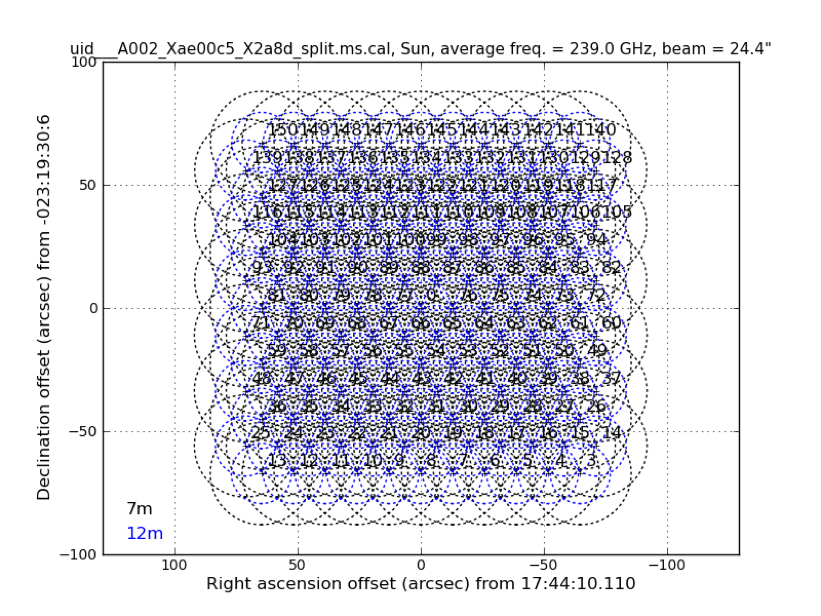
</figure>
mask = 'box[[555pix,565pix],[1505pix,1490pix]]
In most cases of solar observations, the field of view (FoV) of the map is filled up with solar structures. Therefore, ideally, the CLEAN box for the solar image synthesis is the same as the FoV. Since the observation was done with the 7m + 12m heterogeneous array, the FoV of the 7m-array is not the same as that of the 12m-array, and the area near the outer edge of the FoV is observed only with 7m-array, as shown in Figure2. If the CLEAN box includes the area, the synthesized map will include remarkable artificial structures. To avoid the artificial structure, we need to make a CLEAN box that is smaller than the FoV of the 12m-array. In the tutorial, the CLEAN box covers the area that the effective response is larger than 0.6, as shown in Figure 3.