Antennae Band7 - Calibration for CASA 3.3: Difference between revisions
| Line 260: | Line 260: | ||
==Creating Tsys== | ==Creating Tsys== | ||
Next we do the Tsys calibration. Tsys measurements correct for the atmospheric opacity (to first-order) and allow the calibration sources to be measured at elevations that differ from the science target. The Tsys tables for these datasets were provided with the downloadable data, and have been obtained as follows: | |||
<source lang="python"> | <source lang="python"> | ||
| Line 295: | Line 298: | ||
plotcal(caltable=asdm+'.tsys.cal.fdm', xaxis="freq",yaxis="amp",overplot=False,plotrange=[0, 0, 0, 0],plotsymbol=".",figfile=asdm+'.tsys-spec-fdm.cal.png',timerange='<400000') | plotcal(caltable=asdm+'.tsys.cal.fdm', xaxis="freq",yaxis="amp",overplot=False,plotrange=[0, 0, 0, 0],plotsymbol=".",figfile=asdm+'.tsys-spec-fdm.cal.png',timerange='<400000') | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
We inspect them with the task {{plotcal}}: | |||
[[File:Cal-tsys_per_spw_7_uid___A002_X1d54a1_X174.png|200px|thumb|right|Example Tsys plot]] | |||
Aside from the large amplitudes in the edge channels (which we will handle below), the plots look acceptable. Note that in the lowest spectral window ID (spw 1), Tsys rises toward higher frequencies. This is due to a spectral line from O2 at XX GHz. | |||
==Applying calibration tables for WVR and Tsys== | ==Applying calibration tables for WVR and Tsys== | ||
Revision as of 06:33, 13 July 2011
Overview
This portion of the AntennaeBand7 CASA Guide will cover the calibration of the raw visibility data. To skip to the imaging portion of the guide, see: Antennae Band7 - Imaging.
If you haven't already downloaded the raw data, you may do that now by clicking on the region closest to your location and downloading the file named 'Antennae_Band7_UnCalibratedMSandTablesForReduction.tgz':
Once the download has finished, unpack the file:
# In a terminal outside CASA
tar -xvzf Antennae_Band7_UnCalibratedMSandTablesForReduction.tgz
cd Antennae_Band7_UnCalibratedMSandTablesForReduction
# Start CASA
casapy
The data have already been converted to CASA Measurement Set (MS) format using the CASA task importasdm. Accompanying the data are some basic calibration tables you will need for the following reduction, as well as the *.ms.flagversions files that are automatically generated by importasdm.
Initial Inspection and A priori Flagging
We will eventually concatenate the nine datasets used here into one large dataset. However, we will keep them separate for now, as some of the steps to follow require individual datasets (specifically, the application of the Tsys and WVR tables). We therefore start by defining an array "basename" that includes the names of the six files in chronological order. This will simplify the following steps by allowing us to loop through the files using a simple for-loop in python. Remember that if you log out of CASA, you will have to re-issue this command. We will remind you of this in the relevant sections by repeating the command at the start.
# In CASA
basename=['uid___A002_X1d54a1_X5','uid___A002_X1d54a1_X174','uid___A002_X1d54a1_X2e3',
'uid___A002_X1d5a20_X5','uid___A002_X1d5a20_X174','uid___A002_X1d5a20_X330']
The usual first step is then to get some basic information about the data. We do this using the task listobs, which will output a detailed summary of each dataset supplied.
# In CASA
for name in basename:
listobs(vis=name+'.ms')
Note that after cutting and pasting a for-loop you often have to press return several times to execute. The output will be sent to the CASA logger. You will have to scroll up to see the individual output for each of the datasets. Here is an example of the most relevant output for the first file in the list.
2011-07-13 03:09:07 INFO PlotMS::summary+ MeasurementSet Name: /Users/despada/Desktop/Imaging/Antennae/Datasets/band7/uid___A002_X207fe4_X3a.ms MS Version 2 2011-07-13 03:09:07 INFO PlotMS::summary+ ================================================================================ 2011-07-13 03:09:07 INFO PlotMS::summary+ Observer: Unknown Project: T.B.D. 2011-07-13 03:09:07 INFO PlotMS::summary+ Observation: ALMA(12 antennas) 2011-07-13 03:09:07 INFO PlotMS::summary Data records: 211116 Total integration time = 4997.38 seconds 2011-07-13 03:09:07 INFO PlotMS::summary+ Observed from 03-Jun-2011/21:08:39.6 to 03-Jun-2011/22:31:56.9 (UTC) 2011-07-13 03:09:07 INFO PlotMS::summary Fields: 26 2011-07-13 03:09:07 INFO PlotMS::summary+ ID Code Name RA Decl Epoch SrcId 2011-07-13 03:09:07 INFO PlotMS::summary+ 0 none 3c279 12:56:11.1666 -05.47.21.5247 J2000 0 2011-07-13 03:09:07 INFO PlotMS::summary+ 1 none Titan 12:42:08.4083 -01.42.40.8166 J2000 1 2011-07-13 03:09:07 INFO PlotMS::summary+ 2 none NGC4038 - A* 12:01:53.1701 -18.52.37.9200 J2000 2 2011-07-13 03:09:07 INFO PlotMS::summary+ 3 none NGC4038 - A* 12:01:51.9030 -18.51.49.9437 J2000 2 2011-07-13 03:09:07 INFO PlotMS::summary+ 4 none NGC4038 - A* 12:01:52.4309 -18.51.49.9437 J2000 2 2011-07-13 03:09:07 INFO PlotMS::summary+ 5 none NGC4038 - A* 12:01:52.9587 -18.51.49.9437 J2000 2 2011-07-13 03:09:07 INFO PlotMS::summary+ 6 none NGC4038 - A* 12:01:53.4866 -18.51.49.9436 J2000 2 2011-07-13 03:09:07 INFO PlotMS::summary+ 7 none NGC4038 - A* 12:01:54.0144 -18.51.49.9436 J2000 2 2011-07-13 03:09:07 INFO PlotMS::summary+ 8 none NGC4038 - A* 12:01:52.1669 -18.51.56.4319 J2000 2 2011-07-13 03:09:07 INFO PlotMS::summary+ 9 none NGC4038 - A* 12:01:52.6948 -18.51.56.4318 J2000 2 2011-07-13 03:09:07 INFO PlotMS::summary+ 10 none NGC4038 - A* 12:01:53.2226 -18.51.56.4318 J2000 2 2011-07-13 03:09:07 INFO PlotMS::summary+ 11 none NGC4038 - A* 12:01:53.7505 -18.51.56.4318 J2000 2 2011-07-13 03:09:07 INFO PlotMS::summary+ 12 none NGC4038 - A* 12:01:51.9030 -18.52.02.9201 J2000 2 2011-07-13 03:09:07 INFO PlotMS::summary+ 13 none NGC4038 - A* 12:01:52.4309 -18.52.02.9200 J2000 2 2011-07-13 03:09:07 INFO PlotMS::summary+ 14 none NGC4038 - A* 12:01:52.9587 -18.52.02.9200 J2000 2 2011-07-13 03:09:07 INFO PlotMS::summary+ 15 none NGC4038 - A* 12:01:53.4866 -18.52.02.9200 J2000 2 2011-07-13 03:09:07 INFO PlotMS::summary+ 16 none NGC4038 - A* 12:01:54.0144 -18.52.02.9199 J2000 2 2011-07-13 03:09:07 INFO PlotMS::summary+ 17 none NGC4038 - A* 12:01:52.1669 -18.52.09.4082 J2000 2 2011-07-13 03:09:07 INFO PlotMS::summary+ 18 none NGC4038 - A* 12:01:52.6948 -18.52.09.4082 J2000 2 2011-07-13 03:09:07 INFO PlotMS::summary+ 19 none NGC4038 - A* 12:01:53.2226 -18.52.09.4082 J2000 2 2011-07-13 03:09:07 INFO PlotMS::summary+ 20 none NGC4038 - A* 12:01:53.7505 -18.52.09.4081 J2000 2 2011-07-13 03:09:07 INFO PlotMS::summary+ 21 none NGC4038 - A* 12:01:51.9030 -18.52.15.8964 J2000 2 2011-07-13 03:09:07 INFO PlotMS::summary+ 22 none NGC4038 - A* 12:01:52.4309 -18.52.15.8964 J2000 2 2011-07-13 03:09:07 INFO PlotMS::summary+ 23 none NGC4038 - A* 12:01:52.9587 -18.52.15.8963 J2000 2 2011-07-13 03:09:07 INFO PlotMS::summary+ 24 none NGC4038 - A* 12:01:53.4866 -18.52.15.8963 J2000 2 2011-07-13 03:09:07 INFO PlotMS::summary+ 25 none NGC4038 - A* 12:01:54.0144 -18.52.15.8963 J2000 2 2011-07-13 03:09:07 INFO PlotMS::summary+ (nVis = Total number of time/baseline visibilities per field) 2011-07-13 03:09:08 INFO PlotMS::summary Spectral Windows: (9 unique spectral windows and 2 unique polarization setups) 2011-07-13 03:09:08 INFO PlotMS::summary+ SpwID #Chans Frame Ch1(MHz) ChanWid(kHz)TotBW(kHz) Ref(MHz) Corrs 2011-07-13 03:09:08 INFO PlotMS::summary+ 0 4 TOPO 184550 1500000 7500000 183300 I 2011-07-13 03:09:08 INFO PlotMS::summary+ 1 3840 TOPO 344845.586 488.28125 1875000 344908.33 XX YY 2011-07-13 03:09:08 INFO PlotMS::summary+ 2 1 TOPO 343908.086 1875000 1875000 344908.33 XX YY 2011-07-13 03:09:08 INFO PlotMS::summary+ 3 3840 TOPO 354971.074 488.28125 1875000 344908.33 XX YY 2011-07-13 03:09:08 INFO PlotMS::summary+ 4 1 TOPO 343908.086 1875000 1875000 344908.33 XX YY 2011-07-13 03:09:08 INFO PlotMS::summary+ 5 128 TOPO 344900.518 15625 2000000 344908.33 XX YY 2011-07-13 03:09:08 INFO PlotMS::summary+ 6 1 TOPO 343892.705 1796875 1796875 344908.33 XX YY 2011-07-13 03:09:08 INFO PlotMS::summary+ 7 128 TOPO 354916.143 15625 2000000 344908.33 XX YY 2011-07-13 03:09:08 INFO PlotMS::summary+ 8 1 TOPO 343892.705 1796875 1796875 344908.33 XX YY 2011-07-13 03:09:08 INFO PlotMS::summary Sources: 63 2011-07-13 03:09:08 INFO PlotMS::summary+ ID Name SpwId RestFreq(MHz) SysVel(km/s) 2011-07-13 03:09:08 INFO PlotMS::summary+ 0 3c279 0 - - 2011-07-13 03:09:08 INFO PlotMS::summary+ 0 3c279 9 - - 2011-07-13 03:09:08 INFO PlotMS::summary+ 0 3c279 10 - - 2011-07-13 03:09:08 INFO PlotMS::summary+ 0 3c279 11 - - 2011-07-13 03:09:08 INFO PlotMS::summary+ 0 3c279 12 - - 2011-07-13 03:09:08 INFO PlotMS::summary+ 0 3c279 13 - - 2011-07-13 03:09:08 INFO PlotMS::summary+ 0 3c279 14 - - 2011-07-13 03:09:08 INFO PlotMS::summary+ 0 3c279 15 - - 2011-07-13 03:09:08 INFO PlotMS::summary+ 0 3c279 16 - - 2011-07-13 03:09:08 INFO PlotMS::summary+ 0 3c279 17 - - 2011-07-13 03:09:08 INFO PlotMS::summary+ 0 3c279 18 - - 2011-07-13 03:09:08 INFO PlotMS::summary+ 0 3c279 19 - - 2011-07-13 03:09:08 INFO PlotMS::summary+ 0 3c279 20 - - 2011-07-13 03:09:08 INFO PlotMS::summary+ 0 3c279 1 - - 2011-07-13 03:09:08 INFO PlotMS::summary+ 0 3c279 2 - - 2011-07-13 03:09:08 INFO PlotMS::summary+ 0 3c279 3 - - 2011-07-13 03:09:08 INFO PlotMS::summary+ 0 3c279 4 - - 2011-07-13 03:09:08 INFO PlotMS::summary+ 1 Titan 0 - - 2011-07-13 03:09:08 INFO PlotMS::summary+ 1 Titan 9 - - 2011-07-13 03:09:08 INFO PlotMS::summary+ 1 Titan 10 - - 2011-07-13 03:09:08 INFO PlotMS::summary+ 1 Titan 11 - - 2011-07-13 03:09:08 INFO PlotMS::summary+ 1 Titan 12 - - 2011-07-13 03:09:08 INFO PlotMS::summary+ 1 Titan 13 - - 2011-07-13 03:09:08 INFO PlotMS::summary+ 1 Titan 14 - - 2011-07-13 03:09:08 INFO PlotMS::summary+ 1 Titan 15 - - 2011-07-13 03:09:08 INFO PlotMS::summary+ 1 Titan 16 - - 2011-07-13 03:09:08 INFO PlotMS::summary+ 1 Titan 17 - - 2011-07-13 03:09:08 INFO PlotMS::summary+ 1 Titan 18 - - 2011-07-13 03:09:08 INFO PlotMS::summary+ 1 Titan 19 - - 2011-07-13 03:09:08 INFO PlotMS::summary+ 1 Titan 20 - - 2011-07-13 03:09:08 INFO PlotMS::summary+ 1 Titan 1 - - 2011-07-13 03:09:08 INFO PlotMS::summary+ 1 Titan 2 - - 2011-07-13 03:09:08 INFO PlotMS::summary+ 1 Titan 3 - - 2011-07-13 03:09:08 INFO PlotMS::summary+ 1 Titan 4 - - 2011-07-13 03:09:08 INFO PlotMS::summary+ 0 Titan 5 - - 2011-07-13 03:09:08 INFO PlotMS::summary+ 0 Titan 6 - - 2011-07-13 03:09:08 INFO PlotMS::summary+ 0 Titan 7 - - 2011-07-13 03:09:08 INFO PlotMS::summary+ 0 Titan 8 - - 2011-07-13 03:09:08 INFO PlotMS::summary+ 1 3c279 5 - - 2011-07-13 03:09:08 INFO PlotMS::summary+ 1 3c279 6 - - 2011-07-13 03:09:08 INFO PlotMS::summary+ 1 3c279 7 - - 2011-07-13 03:09:08 INFO PlotMS::summary+ 1 3c279 8 - - 2011-07-13 03:09:08 INFO PlotMS::summary+ 2 NGC4038 - A* 0 - - 2011-07-13 03:09:08 INFO PlotMS::summary+ 2 NGC4038 - A* 9 - - 2011-07-13 03:09:08 INFO PlotMS::summary+ 2 NGC4038 - A* 10 - - 2011-07-13 03:09:08 INFO PlotMS::summary+ 2 NGC4038 - A* 11 - - 2011-07-13 03:09:08 INFO PlotMS::summary+ 2 NGC4038 - A* 12 - - 2011-07-13 03:09:08 INFO PlotMS::summary+ 2 NGC4038 - A* 13 - - 2011-07-13 03:09:08 INFO PlotMS::summary+ 2 NGC4038 - A* 14 - - 2011-07-13 03:09:08 INFO PlotMS::summary+ 2 NGC4038 - A* 15 - - 2011-07-13 03:09:08 INFO PlotMS::summary+ 2 NGC4038 - A* 16 - - 2011-07-13 03:09:08 INFO PlotMS::summary+ 2 NGC4038 - A* 17 - - 2011-07-13 03:09:08 INFO PlotMS::summary+ 2 NGC4038 - A* 18 - - 2011-07-13 03:09:08 INFO PlotMS::summary+ 2 NGC4038 - A* 19 - - 2011-07-13 03:09:08 INFO PlotMS::summary+ 2 NGC4038 - A* 20 - - 2011-07-13 03:09:08 INFO PlotMS::summary+ 2 NGC4038 - A* 1 - - 2011-07-13 03:09:08 INFO PlotMS::summary+ 2 NGC4038 - A* 2 - - 2011-07-13 03:09:08 INFO PlotMS::summary+ 2 NGC4038 - A* 3 - - 2011-07-13 03:09:08 INFO PlotMS::summary+ 2 NGC4038 - A* 4 - - 2011-07-13 03:09:08 INFO PlotMS::summary+ 2 NGC4038 - A* 5 - - 2011-07-13 03:09:08 INFO PlotMS::summary+ 2 NGC4038 - A* 6 - - 2011-07-13 03:09:08 INFO PlotMS::summary+ 2 NGC4038 - A* 7 - - 2011-07-13 03:09:08 INFO PlotMS::summary+ 2 NGC4038 - A* 8 - - 2011-07-13 03:09:08 INFO PlotMS::summary Antennas: 12 'name'='station' 2011-07-13 03:09:08 INFO PlotMS::summary+ ID= 0-3: 'DV02'='A015', 'DV04'='J505', 'DV05'='A067', 'DV06'='T704', 2011-07-13 03:09:08 INFO PlotMS::summary+ ID= 4-7: 'DV07'='A004', 'DV08'='A072', 'DV09'='A008', 'DV10'='A009', 2011-07-13 03:09:08 INFO PlotMS::summary+ ID= 8-11: 'DV11'='A016', 'DV12'='A011', 'PM01'='T702', 'PM03'='J504' 2011-07-13 03:09:42 INFO PlotMS::summary ================================================================================
This output shows that three fields were observed: 3c279, Titan, and the different pointing of the Antennae mosaic. Field 0 (3c279) will serve as the gain calibrator and bandpass calibrator; field 1 (Titan) will serve as the flux calibrator; and field 2 (Antennae) is, of course, the science target.
Note that there are more than two SpwIDs even though the observations were set up to have two spectral windows. The spectral line data themselves are found in spectral windows 1,3, which have 3840 channels each. The first one (spw 1) is centered on the CO(1-0) emission line in the Antennae. There is one additional spectral window (spw 3) in the Upper Side Band (USB). The additional spectral window is used to measure the continuum emission in the galaxy, and may contain other emission lines as well. There are two spectral windows (spw 5 and 7) fully covering spw 1 and 3 but in TDM mode (2 GHz bandwidth, 128 channels), which are used for tsys calibration.
Spectral windows 2,4,6,8 contain channel averages of the data in spectral windows 1,3,5,7, respectively. These are not useful for the offline data reduction. Spectral window 0 contains the WVR data. You may notice that there are additional SpwIDs listed in the "Sources" section which are not listed in the "Spectral Windows" section. These spectral windows are reserved for the WVRs of each antenna (seven in our case). At the moment, all WVRs point to spw 0, which contains nominal frequencies. The additional spectral windows (spw 9-15) are therefore not used and can be ignored.
Another important thing to note is that the position of Titan is listed as 00:00:00.0000 +00.00.00.0000. This is due to the fact that for ephemeris objects, the positions are currently not stored in the asdm. This will be handled correctly in the near future, but at present, we have to fix this offline. We will correct the coordinates below by running the procedure fixplanets, which takes the position from the pointing table.
The final column of the listobs output in the logger (not shown above) gives the scan intent. This information is used later to flag the pointing scans and the hot and ambient load calibration scans, using scan intent as a selection option. Also these intents will be used in the future for pipeline processing.
A total of 12 antennas were used for the dataset listed above. Note that numbering in python always begins with "0", so the antennas have IDs 0-11. To see what the antenna configuration looked like at the time of this observation, we will use the task plotants.
# In CASA
plotants(vis=basename[0]+'.ms', figfile=basename[0]+'_plotants.png')
This will plot the antenna configuration on your screen as well as save it under the specified filename for future reference. This will be important later on when we need to choose a reference antenna, since the reference antenna should be close to the center of the array (as well as stable and present for the entire observation).
You can check using plotants for the other datasets that the configuration stays relatively constant during the course of the observations.
As for Delay correction, no large delays are found in phase in any of the datasets, so bandpass calibration should remove the small phase delays (i.e., less than one wrap over the bandpass).
Flagging
The first editing we will do is some a priori flagging with flagdata and flagautocorr. We will start by flagging the shadowed data and the autocorrelation data. ALMA data contains both the cross correlation and autocorrelation data, but here we are only interested in the cross-correlation data. Additionally, for compact configurations of the array, one antenna can shadow another, blocking its view. These data also need to be flagged. Remember that you first need to redefine the "basename" array if you logged out of CASA prior to starting this section.
# In CASA
basename_all=["uid___A002_X1ff7b0_Xb","uid___A002_X1ff7b0_X1c8","uid___A002_X207fe4_X3a","uid___A002_X207fe4_X1f7","uid___A002_X207fe4_X3b9","uid___A002_X207fe4_X4d7","uid___A002_X215db8_X18","uid___A002_X215db8_X1d5","uid___A002_X215db8_X392","uid___A002_X2181fb_X49"]
Now we will loop over the datasets, running the two flagging commands:
# In CASA
for name in basename_all:
flagdata(vis=name+'.ms', flagbackup = F, mode = 'shadow')
flagautocorr(vis=name+'.ms')
There are a number of scans in the data that were used by the online system for pointing calibration. These scans are no longer needed, and we can flag them easily with flagdata by selecting on 'intent':
# In CASA
for name in basename_all:
flagdata(vis=name+'.ms', mode='manualflag', flagbackup = F, intent='*POINTING*')
Similarly, we can flag the scans corresponding to atmospheric calibration:
# In CASA
for name in basename_all:
flagdata(vis=name+'.ms', mode='manualflag', flagbackup = F, intent='*ATMOSPHERE*')
We will then store the current flagging state for each dataset using the flagmanager:
# In CASA
for name in basename:
flagmanager(vis = name+'.ms', mode = 'save', versionname = 'Apriori')
Fixing frequency labelling problem
Spectral window 3 and 7 (Upper Side Band) need to be fixed.
# In CASA
for i in basename_all:
ms1 = i+'.ms'
bbFreq = 355.90833
spwToCorrect = [3,7]
tb.open(ms1+'/SPECTRAL_WINDOW', nomodify=False)
for i in range(tb.nrows()):
if i in spwToCorrect:
numChan1 = tb.getcell(columnname='NUM_CHAN', rownr=i)
chanFreq1 = tb.getcell(columnname='CHAN_FREQ', rownr=i)
centerFreq1 = (max(chanFreq1) + min(chanFreq1)) / 2.0
print i, numChan1, centerFreq1, bbFreq, max(chanFreq1)-min(chanFreq1)
chanFreq1 = chanFreq1 + (bbFreq*1e9 - centerFreq1)
centerFreq1 = (max(chanFreq1) + min(chanFreq1)) / 2.0
print i, numChan1, centerFreq1, bbFreq, max(chanFreq1)-min(chanFreq1)
for j in range(numChan1):
chanFreq1[j] = centerFreq1 + (centerFreq1 - chanFreq1[j])
tb.putcell(columnname='CHAN_FREQ', rownr=i, thevalue=chanFreq1)
tb.close()
Creating Tsys
Next we do the Tsys calibration. Tsys measurements correct for the atmospheric opacity (to first-order) and allow the calibration sources to be measured at elevations that differ from the science target. The Tsys tables for these datasets were provided with the downloadable data, and have been obtained as follows:
numms=len(basename_all)
for msnumber in range (0,numms):
asdm=basename_all[msnumber]
#Gencal. This makes a gain table from the TDM mode (2GHz, 128 channels per baseband, XX and YY polarizations).
# Gencal needs to be executed on each ms individually. If it is done on
# the concatenated data set, only values for the first observation are generated.
#Don't worry about 'No scr col generation' message.
#band 5
os.system('rm -rf '+ asdm+'.tsys.cal')
gencal(vis=asdm+".ms", caltype='tsys', caltable=asdm+'.tsys.cal')
#Plot the tsys calibration tables:Time and Freq. domain
plotcal(caltable=asdm+'.tsys.cal', xaxis="time", iteration='antenna',yaxis="amp",overplot=False, plotrange=[0, 0, 0, 0],plotsymbol=".",figfile=asdm+'.tsys-time.cal.png',timerange='<400000')
plotcal(caltable=asdm+'.tsys.cal', xaxis="freq", yaxis="amp", subplot=111, overplot=False, plotrange=[0, 0, 0, 0],plotsymbol=".",figfile=asdm+'.tsys-spec-tdm.cal.png',timerange='<400000')
#at the end of the band there are high values.
#without the timerange< it does not work...
sleep(5)
#Instance for tsys interpolation band5
interpolatetsys=aU.InterpolateTsys(asdm+'.tsys.cal')
#Ignoring spectral window [0, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19] because it is WVR related
#Correcting time stamps
interpolatetsys.correctBadTimes()
# this sets the tsys when atmcal was actually observed.
interpolatetsys.assignFieldAndScanToSolution() # This associates the field and scan numbers to the table properly. This will allow you to use the field id to identify which tsys you want to map to which field source in the dataset.
#Plot the tsys calibration tables with corrected times: Time domain. spw 5 and 7 are TDM mode.
plotcal(caltable=asdm+'.tsys.cal', xaxis="time", iteration='antenna',yaxis="amp",overplot=False, plotrange=[0, 0, 0, 0],plotsymbol=".",figfile=asdm+'.tsys-time-correctbadtimes.cal.png',timerange='<400000')
#without the <number it does not work.
sleep(5)
#TDM to FDM interpolation
interpolatetsys.getTdmFdmSpw()
interpolatetsys.interpolateTsys()
# many errors!!! but just means that some channels are missing.
plotcal(caltable=asdm+'.tsys.cal.fdm', xaxis="freq",yaxis="amp",overplot=False,plotrange=[0, 0, 0, 0],plotsymbol=".",figfile=asdm+'.tsys-spec-fdm.cal.png',timerange='<400000')
We inspect them with the task plotcal:
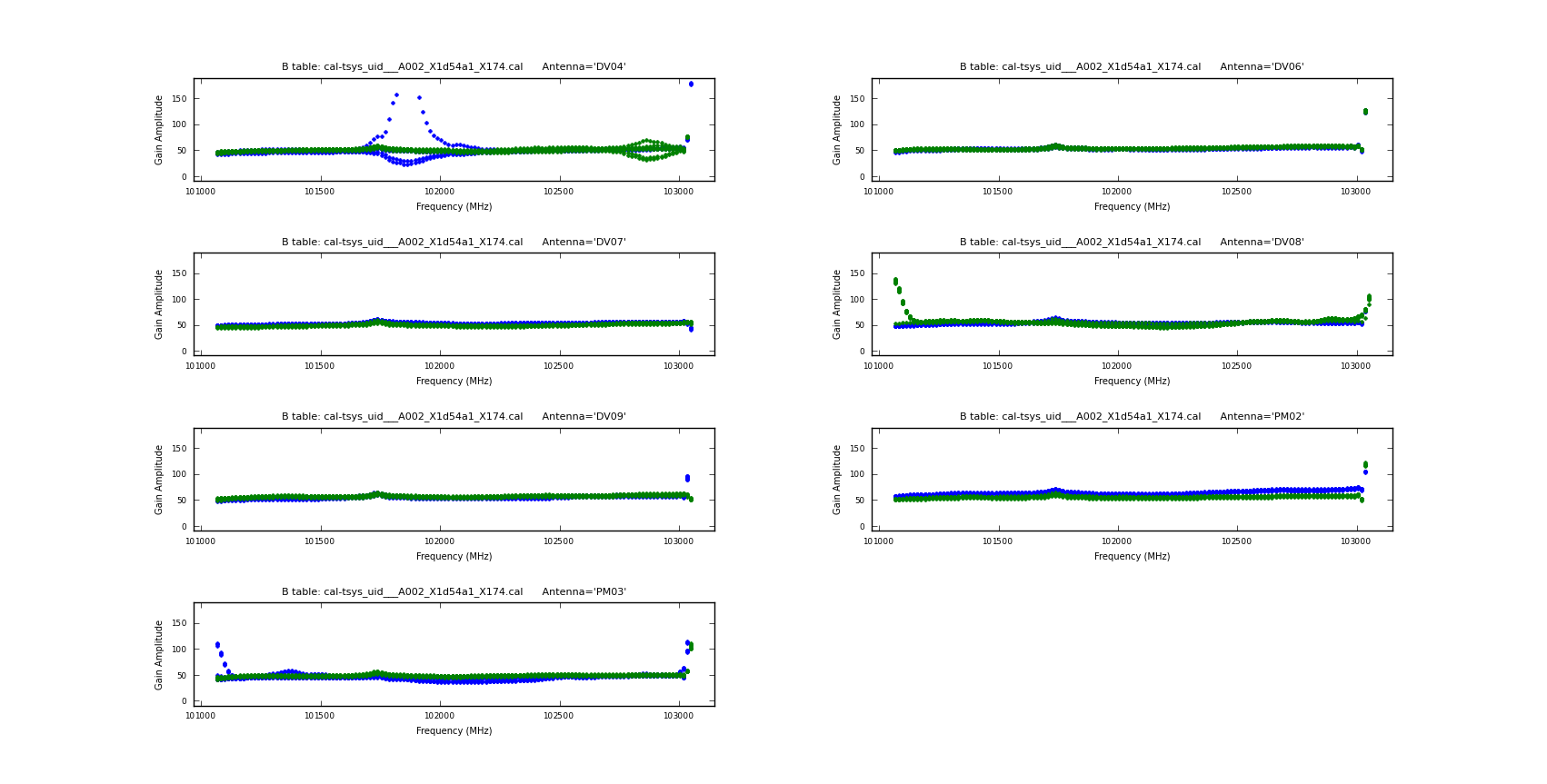
Aside from the large amplitudes in the edge channels (which we will handle below), the plots look acceptable. Note that in the lowest spectral window ID (spw 1), Tsys rises toward higher frequencies. This is due to a spectral line from O2 at XX GHz.
Applying calibration tables for WVR and Tsys
We will now apply the tsys and the WVR calibration tables to the data with the task applycal. We do this in two steps. First we will cycle over the three datasets from the first day of observations, because we have to correct the delay error for DV07 for those data. For the last three datasets (i.e. those taken during the second day), we do not need to correct the delays, so we just apply the WVR tables. In the call to applycal, we will specify interpolation="nearest". This is important for the WVR corrections, and it doesn't make a difference for the delay corrections because they have no time dependence.
First, remember to redefine the "basename_all" array if you've logged out of CASA at any point up until now.
# In CASA
basename_all=["uid___A002_X1ff7b0_Xb","uid___A002_X1ff7b0_X1c8","uid___A002_X207fe4_X3a","uid___A002_X207fe4_X1f7","uid___A002_X207fe4_X3b9","uid___A002_X207fe4_X4d7","uid___A002_X215db8_X18","uid___A002_X215db8_X1d5","uid___A002_X215db8_X392","uid___A002_X2181fb_X49"]
Now loop through the datasets as described above, applying the tsys and wvr calibration tables to all the datasets and sources:
# In CASA
for asdm in basename_all:
print asdm
#plotcal(caltable=directory+asdm+'.tsys.cal.fdm', xaxis="freq",yaxis="amp",overplot=False,plotrange=[0, 0, 0, 0],plotsymbol=".",timerange='<400000')
for fieldname in ['Titan','3c279','NGC4038*','Antenna*']:
applycal(vis=directory+asdm+".ms", spw='1,3', flagbackup=F, field=fieldname, gainfield=fieldname,interp=['nearest','nearest'], gaintable=[directory+asdm+".tsys.cal.fdm",directory+asdm+'.wvr.cal'])
Now you can use plotms to show some of the before-and-after effects of calibration. Just re-run the previous plotms command, repeated below, or if the window is still open, check 'force reload'. This will display the uncorrected phases across the band. To display the corrected phases, you will need to select the CORRECTED data column in the axes tab and replot.
# In CASA
plotms(vis=basename[0]+'.ms', xaxis='channel', yaxis='phase',
spw='1', antenna='', correlation='XX', avgtime='1e8',
coloraxis='baseline', avgscan=T, selectdata=T, field='1037*')
Now we split out the CORRECTED data column of the datasets with the task split. We give the resulting datasets the extension "_K_WVR" to indicate that the delay tables and WVR tables have been applied in the DATA column, and we specify spectral windows 0-8 to get rid of the "WVR placeholder" spectral windows. Since split will not overwrite existing files, we start by removing any previous versions of the split ms's before running the split command.
# In CASA
for asdm in basename_all:
os.system('rm -rf '+asdm+'.split.ms')
split(vis=directory+asdm+'.ms', outputvis=asdm+'.split.ms', datacolumn='corrected', spw='1,3')
We will apply the Tsys tables with applycal. We do this for each field separately so that the appropriate calibration data are applied to the right fields. The "field" parameter specifies the field to which we will apply the calibration, and the "gainfield" parameter specifies the field from which we wish to take the calibration solutions from the gaintable.
Without giving the full recipe here, we suggest at this point that you use plotms to plot channel-averaged amplitudes as a function of time, comparing the DATA and CORRECTED columns after applying the Tsys correction. This way you can check that calibration has done what was expected, which is put the data onto the Kelvin temperature scale.
We then once again split out the CORRECTED data column, this time only retaining spectral windows 1,3. This will get rid of the extraneous spectral windows, including the channel averaged spectral windows and spw 0, which is the one that contained the WVR data.
# In CASA
for name in basename:
os.system('rm -rf '+name+'_line.ms*')
split(vis=name+'_K_WVR.ms', outputvis=name+'_line.ms',
datacolumn='corrected', spw='1,3,5,7')
The WVR and Tsys tables are now applied in the DATA column of the new measurement sets. These datasets have the extension "_line" to indicate that they only contain the spectral line data and no longer the "channel average" spectral windows. These measurement sets therefore have four spectral windows, with IDs 0-3.
Now that we have applied the Tsys calibration and WVR corrections, we can concatenate the six individual data sets into one big measurement set. We define an array "comvis" that contains the names of the measurement sets we wish to concatenate, and then we run the task concat.
# In CASA
comvis=[]
for name in basename:
comvis.append(name+'_line.ms')
os.system('rm -rf ngc3256_line.ms*')
concat(vis=comvis, concatvis='ngc3256_line.ms')
We run a listobs on the resulting concatenated data set to check contains the fields, spectral windows and observing times that we expected:
# In CASA
listobs('ngc3256_line.ms')
There are now only four spectral windows left:
2011-05-24 07:41:21 INFO listobs 0 128 TOPO 113211.988 15625 2000000 113204.175 XX YY 2011-05-24 07:41:21 INFO listobs 1 128 TOPO 111450.813 15625 2000000 111443 XX YY 2011-05-24 07:41:21 INFO listobs 2 128 TOPO 101506.187 15625 2000000 101514 XX YY 2011-05-24 07:41:21 INFO listobs 3 128 TOPO 103050.863 15625 2000000 103058.675 XX YY
and eight antennas have been used in total:
2011-05-24 07:41:21 INFO listobs Antennas: 8: 2011-05-24 07:41:21 INFO listobs ID Name Station Diam. Long. Lat. 2011-05-24 07:41:21 INFO listobs 0 DV04 J505 12.0 m -067.45.18.0 -22.53.22.8 2011-05-24 07:41:21 INFO listobs 1 DV06 T704 12.0 m -067.45.16.2 -22.53.22.1 2011-05-24 07:41:21 INFO listobs 2 DV07 J510 12.0 m -067.45.17.8 -22.53.23.5 2011-05-24 07:41:21 INFO listobs 3 DV08 T703 12.0 m -067.45.16.2 -22.53.23.9 2011-05-24 07:41:21 INFO listobs 4 DV09 N602 12.0 m -067.45.17.4 -22.53.22.3 2011-05-24 07:41:21 INFO listobs 5 PM02 T701 12.0 m -067.45.18.8 -22.53.22.2 2011-05-24 07:41:21 INFO listobs 6 PM03 J504 12.0 m -067.45.17.0 -22.53.23.0 2011-05-24 07:41:21 INFO listobs 7 DV10 N606 12.0 m -067.45.17.1 -22.53.23.6
Additional Data Inspection
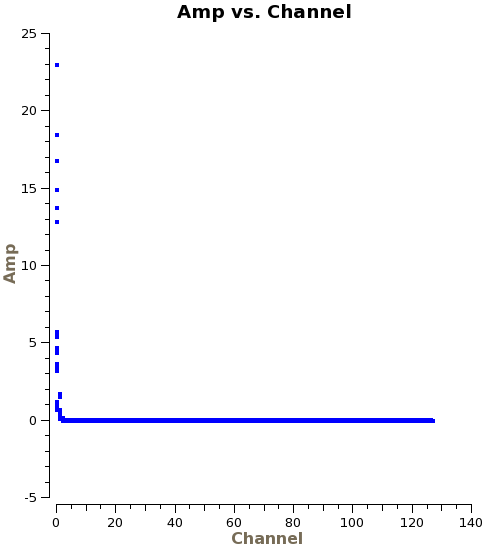
Now that the data are concatenated into one dataset, we will do some additional inspection with plotms. First we will plot amplitude versus channel, averaging over time and baselines in order to speed up the plotting process.
# In CASA
plotms(vis='ngc3256_line.ms', xaxis='channel', yaxis='amp',
averagedata=T, avgbaseline=T, avgtime='1e8', avgscan=T)
From this plot we see that the edge channels have abnormally high amplitudes. We will use flagdata to remove the edge channels from both sides of the bandpass:
# In CASA
flagdata(vis='ngc3256_line.ms', flagbackup=T, spw=['*:0~16','*:125~127'])
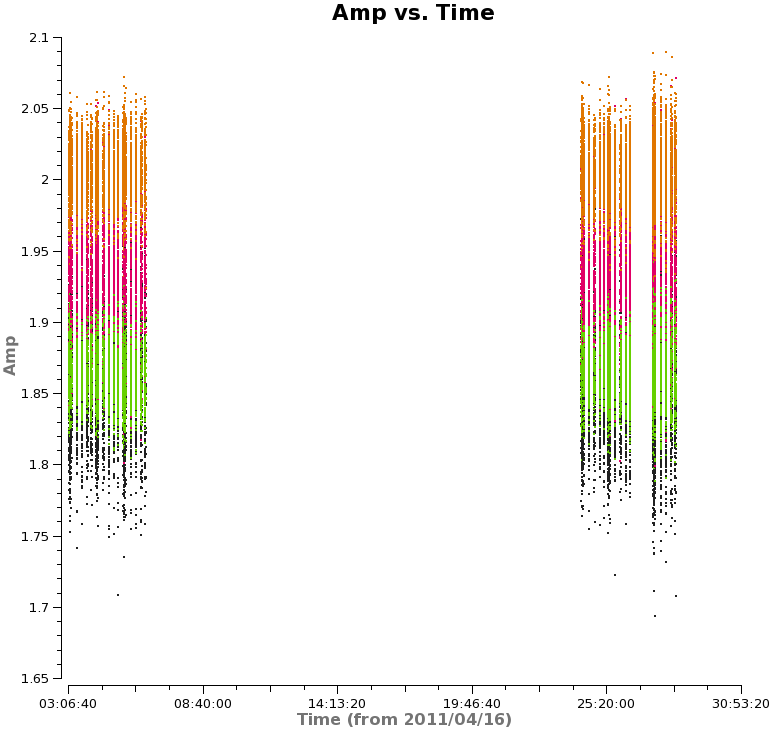
Next, we will look at amplitude versus time, averaging over all channels and colorizing by field. Since the observations take place over two days, you will need to zoom in to examine the data in more detail. In particular, note the difference in Titan's amplitude between the two days and the change in amplitude during the second day. The plot on the right shows a zoom-in on the first day of observations, only showing spw 1 in this case. Scans on Titan are colored red, NGC3256 is orange, and the calibrator 1037-295 is colored black. If you select other spws, you can see some outlying points, which will be flagged later on.
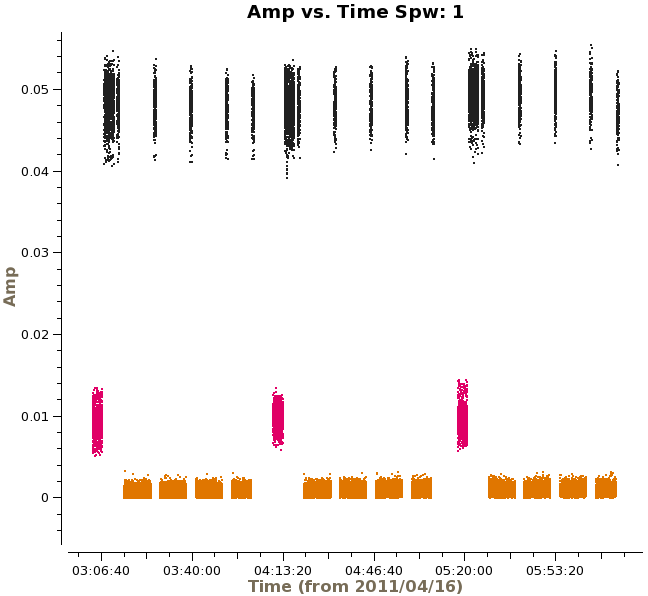
# In CASA
plotms(vis='ngc3256_line.ms', xaxis='time', yaxis='amp',
averagedata=T, avgchannel='128', coloraxis='field',
iteraxis='spw')
Titan is our primary flux calibrator. However, for the second day of observations, Titan had moved too close to Saturn, and Saturn's rings moved into the primary beam. Another way to see this is to plot amplitude versus uv-distance and colorize by scan:
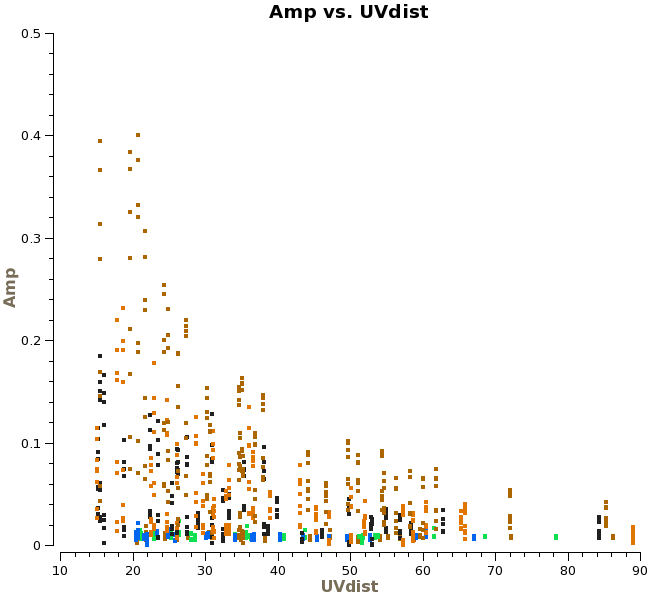
# In CASA
plotms(vis='ngc3256_line.ms', xaxis='uvdist', yaxis='amp', field='1',
averagedata=T, avgchannel='128', avgtime='1e8', coloraxis='scan')
If you use the "Mark a region" and "Locate" tools in plotms, you will see the signature of a bright, resolved source during the latter three (last day's) scans. We will therefore need to flag the Titan scans for the second day:
# In CASA
flagdata(vis = 'ngc3256_line.ms', flagbackup = T,
timerange='>2011/04/16/12:00:00', field='Titan')
We also find that during the first day, the Titan observations in spw 2 and 3 are also affected by Saturn. These spectral windows are at lower frequencies and therefore correspond to slightly larger primary beams. This results in Saturn just being picked up in spw 2 and 3, but not in spw 0 and 1. We do not flag these data here, but have to take this effect into account when we do the flux calibration later.
Next, we will fix the position of Titan in the combined dataset. Recall that the position of the Titan field is currently set to 00:00:00.0000 +00.00.00.0000. The following procedure will replace this with the actual mean position observed by the telescopes and, at the same time, it will recalculate the uvw coordinates.
First initialize the CASA script with:
# In CASA
execfile(casadef.python_library_directory+'/recipes/fixplanets.py')
Now fix the position of Titan:
# In CASA
fixplanets('ngc3256_line.ms', 'Titan', True)
The third parameter in fixplanets, set to True, indicates that the uvw-coordinates for Titan are recalculated. Note that for Cycle 0 data, the coordinates of ephemeris objects will be treated correctly in the data.
Now check to see that the coordinates for Titan have been corrected:
2011-05-31 19:19:41 INFO listobs ID Code Name RA Decl Epoch SrcId nVis 2011-05-31 19:19:41 INFO listobs 0 none 1037-295 10:37:16.0790 -29.34.02.8130 J2000 0 61440 2011-05-31 19:19:41 INFO listobs 1 none Titan 12:51:24.5886 -02.31.59.7035 J2000 1 25344 2011-05-31 19:19:41 INFO listobs 2 none NGC3256 10:27:51.6000 -43.54.18.0000 J2000 2 239616
Continue to inspect the data with plotms, plotting different axes and colorizing by the different parameters. Don't forget to average the data if possible to speed the plotting process. You will find the following:
- Baselines with DV07 have very high amplitudes in spw 3, correlation YY
- Baselines with DV08 have very low amplitudes in spw 3, correlation YY, but only for the last observation
- Baselines with PM03 have low amplitudes at 2011/04/17/02:15:00 for spw 0
- Baselines with PM03 have low amplitudes at 2011/04/16/04:15:15 for spw 2 and 3
- For the second day, the baseline DV10-PM03 is corrupted
The times to insert in flagdata can be obtained using plotms Tools Hover/Display. Instead of using the following flagdata commands, you can also flag by hand in plotms. To do this, select your bad data by clicking on the 'Mark Regions" button, then on 'Flag".
We flag the bad data with the following commands:
# In CASA
flagdata(vis='ngc3256_line.ms', flagbackup=T, spw='3',
correlation='YY', mode='manualflag', selectdata=T,
antenna='DV07', timerange='')
# In CASA
flagdata(vis='ngc3256_line.ms', flagbackup=T, spw='3',
correlation='YY', mode='manualflag', selectdata=T,
antenna='DV08', timerange='>2011/04/17/03:00:00')
# In CASA
flagdata(vis='ngc3256_line.ms', flagbackup=T, spw='0',
correlation='', mode='manualflag', selectdata=T,
antenna='PM03', timerange='2011/04/17/02:15:00~02:15:50')
# In CASA
flagdata(vis='ngc3256_line.ms', flagbackup=T, spw='2,3',
correlation='', mode='manualflag', selectdata=T,
antenna='PM03', timerange='2011/04/16/04:13:50~04:18:00')
# In CASA
flagdata(vis='ngc3256_line.ms', flagbackup=T, spw='',
correlation='', mode='manualflag', selectdata=T,
antenna='PM03&DV10', timerange='>2011/04/16/15:00:00')
Bandpass Calibration
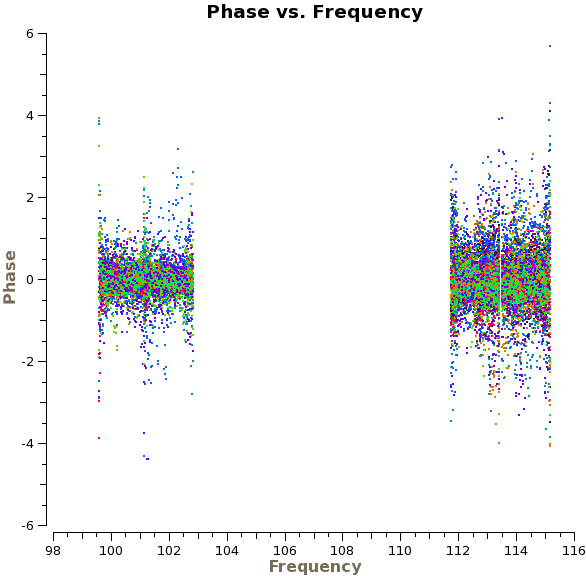
We are now ready to begin the bandpass calibration. First, we will inspect the bandpass calibrator by plotting the phase as a function of frequency and time. For the first plot we use avgscan=T and avgtime='1E6' to average in time over all scans, and we specify coloraxis='baseline' to colorize by baseline. For the second, we use spw='0:30~90' and avgchannel='128' to average over the central 61 channels of the first spectral window. For both plots we will iterate on antenna, so you will need to use the green arrows at the bottom of the plotms GUI to view different antennas.
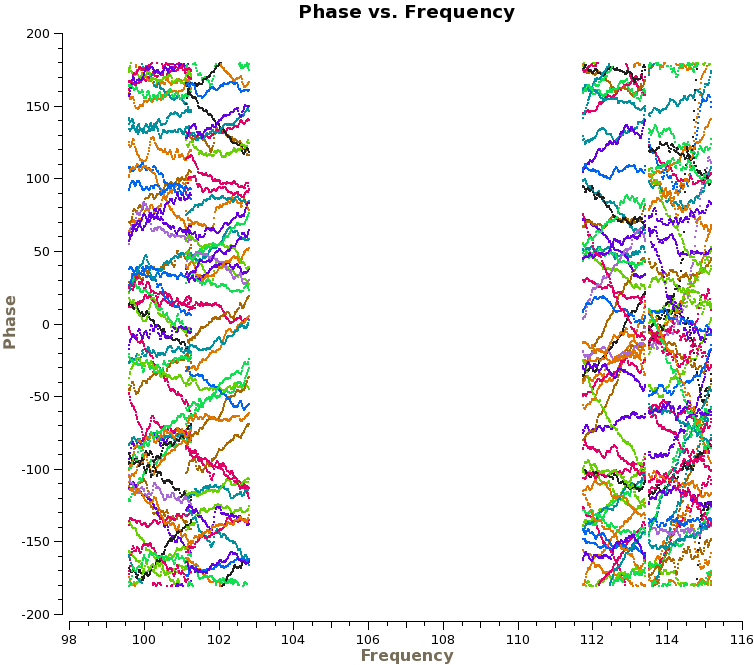
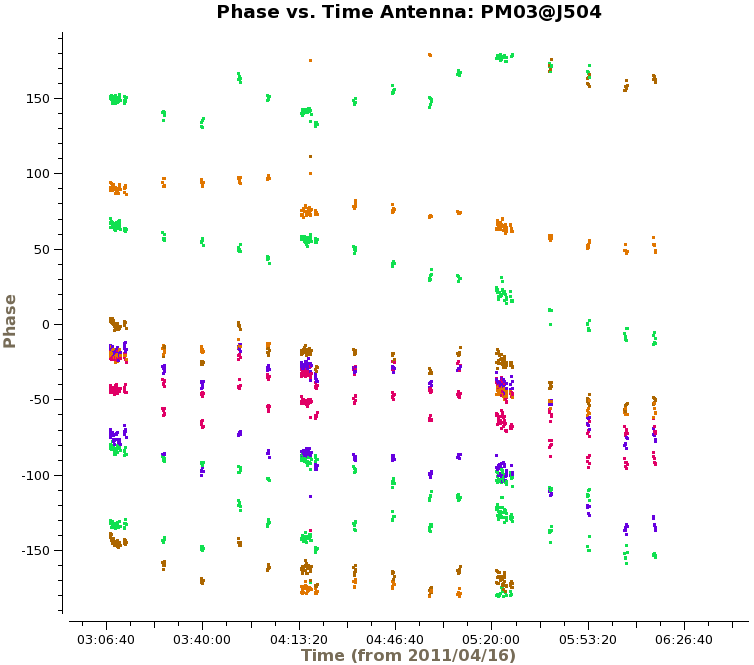
# In CASA
plotms(vis='ngc3256_line.ms', xaxis='freq', yaxis='phase', selectdata=True,
field='1037*', avgtime='1E6', avgscan=T, coloraxis='baseline', iteraxis='antenna')
# In CASA
plotms(vis='ngc3256_line.ms', xaxis='time', yaxis='phase', selectdata=True,
field='1037*', spw='0:30~90', avgchannel='128', avgscan=T,
coloraxis='baseline', iteraxis='antenna')
The top plot on the right shows the time-averaged phase as a function of frequency for the calibrator 1037-295, with all baselines shown at once (i.e., without iteraxis='antenna') for presentation purposes. We see that the phase variations across the spectral windows are modest, typically ~30 degrees. The second plot shows how the phase varies as function of time. For clarity, we only show baselines with one antenna and only for the first day of observations. There are clearly phase variations on short time scales that we wish to correct for before calculating the bandpass solutions.
Hence, we run gaincal on the bandpass calibrator to determine phase-only gain solutions. We will use solint='int' for the solution interval, which means that one gain solution will be determined for every integration time. This short integration time is possible because the bandpass calibrator is a very bright point source, so we have very high signal-to-noise and a perfect model. This will correct for any phase variations in the bandpass calibrator as a function of time, a step which will prevent decorrelation of the vector-averaged bandpass solutions. We will then apply these solutions on-the-fly when we run bandpass.
We will use the average of channels 40 to 80 to increase our signal-to-noise in the determination of the antenna-based phase solutions. Averaging over a subset of channels near the center of the bandpass is acceptable when the phase variation as a function of channel is small, which it is here. For our reference antenna, we choose DV04. We call the output calibration table "cal-ngc3256.G1".
# In CASA
gaincal(vis='ngc3256_line.ms', caltable='cal-ngc3256.G1', spw='*:40~80', field='1037*',
selectdata=T, solint='int', refant='DV04', calmode='p')
We then check the time variations of the phase solutions with plotcal. We will plot the XX and YY polarization products separately and make different subplots for each of the spectral windows. This is done by setting the "iteration" parameter to "spw" and specifying subplot=221. By setting the parameter "figfile" to a non-blank value, it will also generate png files of the plots.
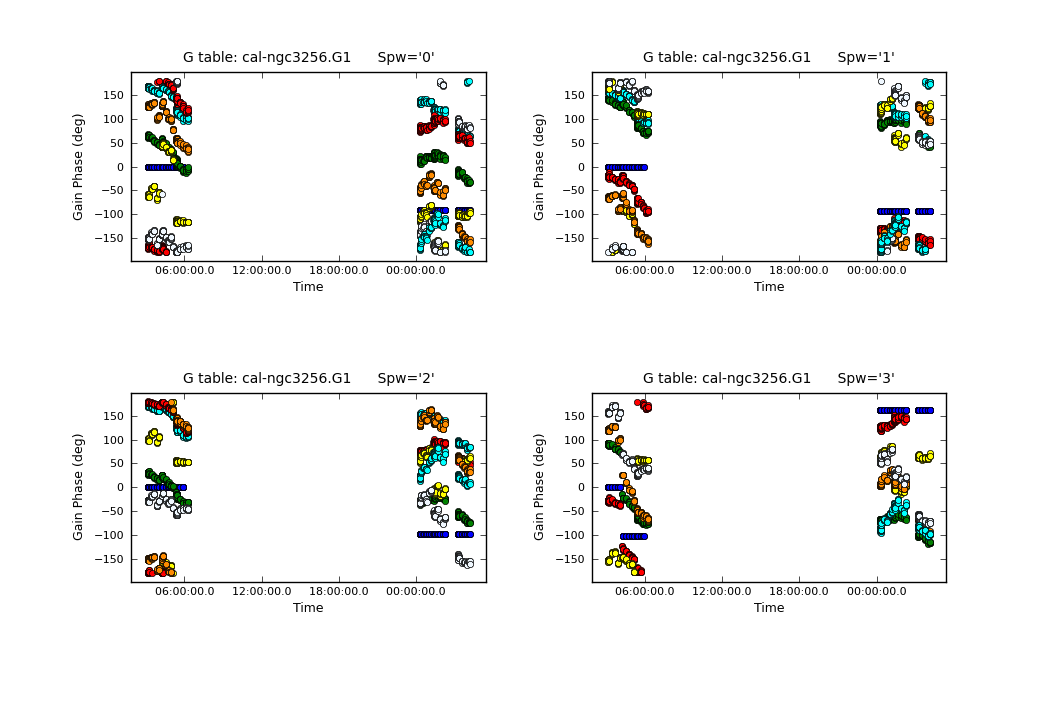
# In CASA
plotcal(caltable = 'cal-ngc3256.G1', xaxis = 'time', yaxis = 'phase',
poln='X', plotsymbol='o', plotrange = [0,0,-180,180], iteration = 'spw',
figfile='cal-phase_vs_time_XX.G1.png', subplot = 221)
# In CASA
plotcal(caltable = 'cal-ngc3256.G1', xaxis = 'time', yaxis = 'phase',
poln='Y', plotsymbol='o', plotrange = [0,0,-180,180], iteration = 'spw',
figfile='cal-phase_vs_time_YY.G1.png', subplot = 221)
If you examine the solutions closely, you may notice some phase jumps. (For example: Correlation XX, spw 3, antenna DV09). These jumps occur between the individual observing blocks and will thus not affect the science data. Other than that, the solutions look reasonable.
Now that we have a first measurement of the phase variations as a function of time, we can determine the bandpass solutions with bandpass. We will apply the phase calibration table on-the-fly with the parameter "gaintable". Now that the phases are corrected, the data can be time-averaged over longer intervals to maximise SNR in each individual channel. We determine bandpass solutions for both days separately because we find that for some antennas, the response across the bandwidth has changed slightly in between the two sessions. We first calculate the bandpass solution for the first day. Do not worry about the message "Insufficient unflagged antennas", which relates to the flagged edge channels.
# In CASA
bandpass(vis = 'ngc3256_line.ms', caltable = 'cal-ngc3256.B1',
gaintable = 'cal-ngc3256.G1', timerange='<2011/04/16/15:00:00',
field = '1037*', minblperant=3, minsnr=2, solint='inf', combine='scan',
bandtype='B', fillgaps=1, refant = 'DV04', solnorm = T)
- caltable = 'cal-ngc3256.B1': Output bandpass calibration table
- gaintable = 'cal-ngc3256.G1': Gain calibration table to apply
- minblperant=3: Minimum number of baselines required per antenna for each solve
- minsnr=2: Minimum SNR for solutions
- solint='inf': This setting, combined with the default combine='scan', sets the solution interval to the entire observation
- combine='scan': The solutions cross scans
- timerange='<2011/04/16/15:00:00': Only determine solutions for the first day
- bandtype='B': The default type of bandpass solution, which does a channel by channel solution for each specified spw
- fillgaps=1: Interpolate channel gaps 1 channel wide
- solnorm=T: Normalize the bandpass amplitudes and phases of the corrections to unity
And then append the solutions (append=True) for the second day:
# In CASA
bandpass(vis = 'ngc3256_line.ms', caltable = 'cal-ngc3256.B1',
gaintable = 'cal-ngc3256.G1', timerange='>2011/04/16/15:00:00',
field = '1037*', minblperant=3, minsnr=2, solint='inf', combine='scan',
bandtype='B', fillgaps=1, refant = 'DV04', solnorm = T, append=True)
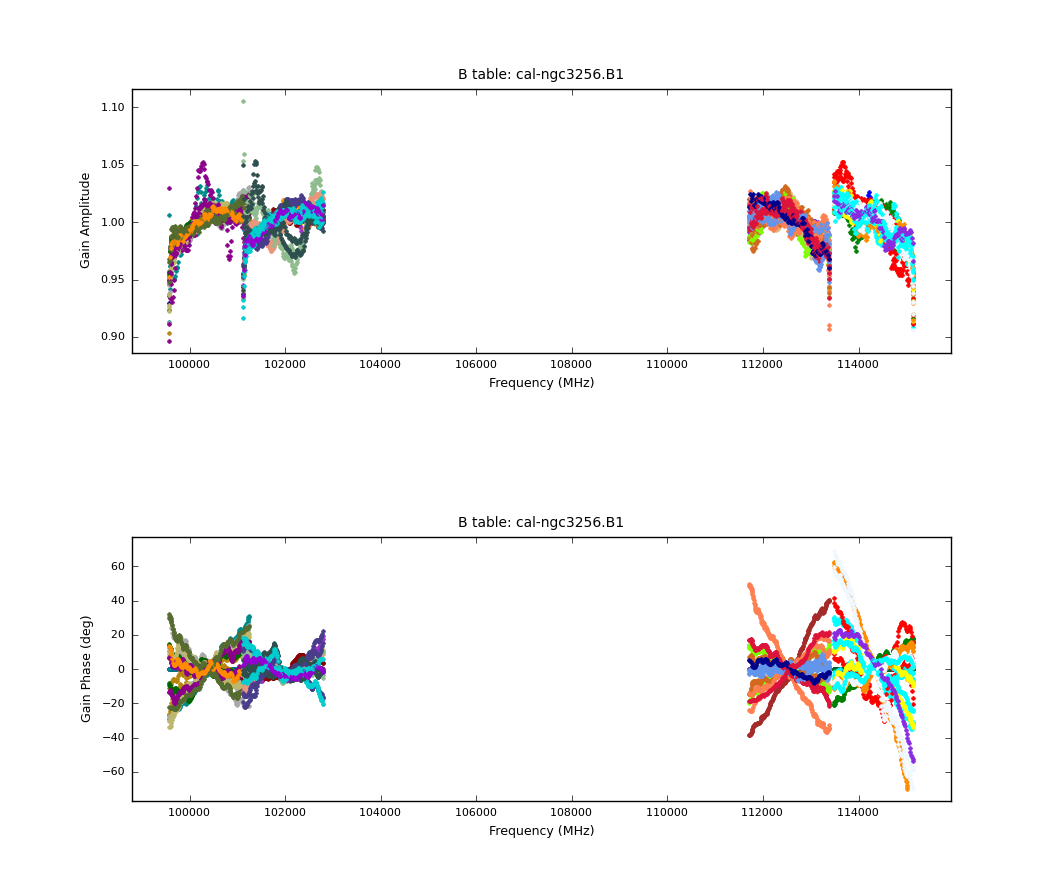
We then plot the bandpass solutions with the following commands:
# In CASA
plotcal(caltable = 'cal-ngc3256.B1', xaxis='freq', yaxis='phase', spw='',
subplot=212, overplot=False, plotrange = [0,0,-70,70],
plotsymbol='.', timerange='')
# In CASA
plotcal(caltable = 'cal-ngc3256.B1', xaxis='freq', yaxis='amp', spw='',
subplot=211, overplot=False,
figfile='bandpass.B1.png', plotsymbol='.', timerange='')
The solutions seem reasonable, so we will now apply them on-the-fly during gain calibration.
Gain Calibration
The first step is to set the flux density for Titan using the task setjy. We will use the Butler-JPL-Horizons 2010 model:
# In CASA
setjy(vis='ngc3256_line.ms', field='Titan', standard='Butler-JPL-Horizons 2010',
spw='0,1,2,3')
The flux density of Titan is 370 mJy at 114 GHz (spw 0) and drops to 288 mJy at 101 GHz (spw 2):
2011-05-24 08:35:08 INFO setjy Titan spwid= 0 [I=0.37, Q=0, U=0, V=0] Jy, (JPL-Butler Solar System Object) 2011-05-24 08:35:08 INFO setjy Titan spwid= 1 [I=0.3588, Q=0, U=0, V=0] Jy, (JPL-Butler Solar System Object) 2011-05-24 08:35:09 INFO setjy Titan spwid= 2 [I=0.2878, Q=0, U=0, V=0] Jy, (JPL-Butler Solar System Object) 2011-05-24 08:35:10 INFO setjy Titan spwid= 3 [I=0.2966, Q=0, U=0, V=0] Jy, (JPL-Butler Solar System Object)
Now we will do a new gain calibration, this time applying the bandpass calibration solutions on-the-fly. We solve for amplitude and phase simultaneously and determine average solutions per scan:
# In CASA
gaincal(vis = 'ngc3256_line.ms', caltable = 'cal-ngc3256.G2', spw =
'*:16~112', field = '1037*,Titan', minsnr=1.0,
solint= 'inf', selectdata=T, solnorm=False, refant = 'DV04',
gaintable = 'cal-ngc3256.B1', calmode = 'ap')
- caltable = 'cal-ngc3256.G2': the output gain calibration table
- minsnr=1.0: To reject solutions with a signal-to-noise less than 1.0
- calmode = 'ap': To solve for amplitude and phase
- spw='*:16~112': to select all spectral windows, but only the inner 75% of the channels of each
- solint='inf': Together with the default for the "combine" parameter, this setting will solve for one solution per scan
- solnorm=F: We do not want to normalize the solutions to unity since we wish to relate the measured amplitudes of the secondary calibrator (1037-295) to the flux calibrator (Titan)
- gaintable = ['cal-ngc3256.B1']: We apply the bandpass calibration on-the-fly
Now we will examine the amplitude and phase solutions as a function of time, iterating on spectral window and plotting the XX and YY correlations separately for clarity. Zoom in on the GUI to examine the plots in more detail. You can also use the "Mark Region" and "Locate" buttons on the toolbar to identify points. Use the field parameter to select which calibrator you want to plot the solutions for.
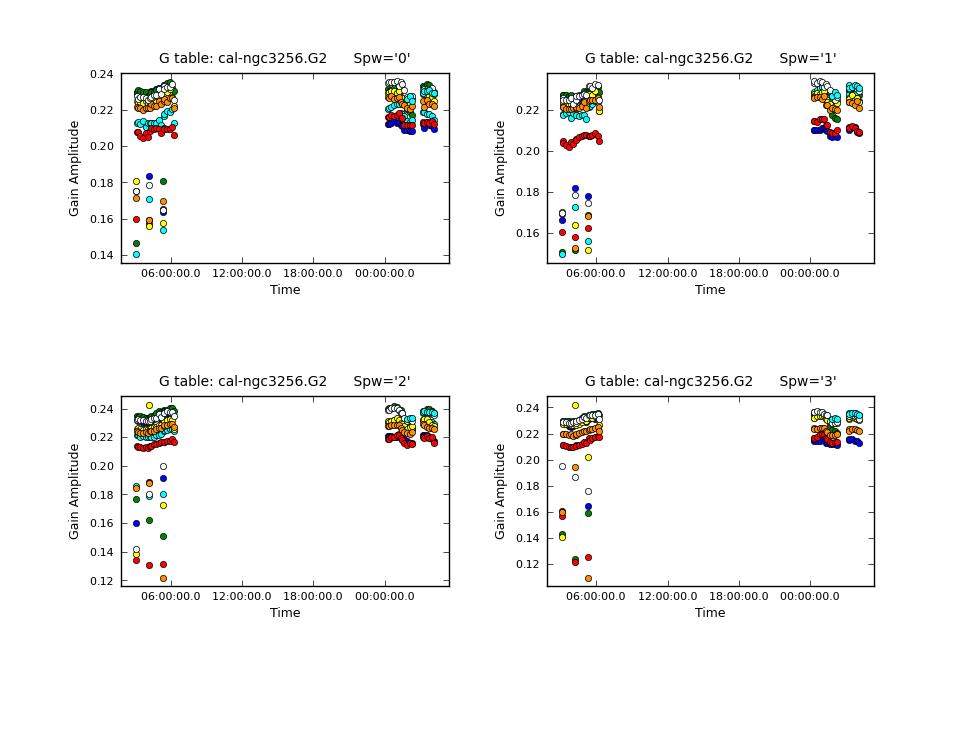
# In CASA
plotcal(caltable = 'cal-ngc3256.G2', xaxis = 'time', yaxis = 'phase',
poln='X', plotsymbol='o', plotrange = [0,0,-180,180], iteration= 'spw',
figfile='cal-phase_vs_time_XX.G2.png', subplot = 221)
# In CASA
plotcal(caltable = 'cal-ngc3256.G2', xaxis = 'time', yaxis = 'phase',
poln='Y', plotsymbol='o', plotrange = [0,0,-180,180], iteration= 'spw',
figfile='cal-phase_vs_time_YY.G2.png', subplot = 221)
# In CASA
plotcal(caltable = 'cal-ngc3256.G2', xaxis = 'time', yaxis = 'amp',
poln='X', plotsymbol='o', plotrange = [], iteration = 'spw',
figfile='cal-amp_vs_time_XX.G2.png', subplot = 221)
# In CASA
plotcal(caltable = 'cal-ngc3256.G2', xaxis = 'time', yaxis = 'amp',
poln='Y', plotsymbol='o', plotrange = [], iteration = 'spw',
figfile='cal-amp_vs_time_YY.G2.png', subplot = 221)
We find very stable amplitude solutions for the phase calibrator. The lower points for the first day are the solutions for Titan.
Finally, we will bootstrap the flux density of the secondary calibrator from that of Titan using the task fluxscale. The new flux table cal-ngc3256.G2.flux replaces the previous cal-ngc3256.G2 table in future application of the calibration to the data, i.e. the new flux table contains both cal-ngc3256.G2 and the newly acquired flux scaling. Unlike the gain calibration steps, this is not an incremental table.
# In CASA
fluxscale( vis="ngc3256_line.ms", caltable="cal-ngc3256.G2",
fluxtable="cal-ngc3256.G2.flux", reference="Titan",
transfer="1037*", refspwmap=[0,1,1,1])
Note that we previously flagged the Titan scans from the second day due to contamination from nearby Saturn's rings. We have therefore used the Titan scans from the first day alone to flux calibrate both days' observations. This would not always be an acceptable solution; however, in this case, examination of the measured amplitudes for the phase calibrator over both days indicate that the flux scale is relatively stable.
Also note that we have used refspwmap=[0,1,1,1]. This means that the 1037-295 observations in spw 2 and 3 are referenced to Titan observations observed in spw 1. We have to do this here because the Titan data in spw 2 and 3 are contaminated by Saturn, as explained above.
The logger produces the following output:
2011-05-31 21:32:31 INFO fluxscale Flux density for 1037-295 in SpW=0 is: 1.81638 +/- 0.0179226 (SNR = 101.346, nAnt= 7) 2011-05-31 21:32:31 INFO fluxscale Flux density for 1037-295 in SpW=1 is: 1.81967 +/- 0.0149109 (SNR = 122.037, nAnt= 7) 2011-05-31 21:32:31 INFO fluxscale Flux density for 1037-295 in SpW=2 (ref SpW=1) is: 1.90794 +/- 0.0155891 (SNR = 122.389, nAnt= 7) 2011-05-31 21:32:31 INFO fluxscale Flux density for 1037-295 in SpW=3 (ref SpW=1) is: 1.86595 +/- 0.0153365 (SNR = 121.668, nAnt= 6)
We find that the flux density of 1037-295 is ~1.8 Jy in the higher frequency spectral windows and ~1.9 Jy in the lower frequency spectral windows. This fluxes agree very well with the 3mm measurements from the ATCA and OVRO of a few years ago (see SMA calibrator list).
Applying the calibrations
Now we will use applycal to apply the bandpass and gaincal tables that we generated in the previous sections. First, we will apply the solutions from the secondary calibrator to the science target and the secondary calibrator itself. We want to use the solutions from the secondary calibrator for the science target because, as the phase calibrator, it was observed throughout the observations. Its flux scale has also now been bootstrapped to that of the flux calibrator, so it can serve as an amplitude and phase calibrator. The application of the solutions to the secondary calibrator itself is a way for us to check the quality of the calibration. Below, we will do the same for the flux calibrator (Titan), applying its amplitude and phase solutions to itself to check the calibration.
# In CASA
applycal( vis='ngc3256_line.ms', flagbackup=F, field='NGC*,1037*',
interp=['nearest','nearest'], gainfield = ['1037*', '1037*'],
gaintable=['cal-ngc3256.G2.flux', 'cal-ngc3256.B1'])
- gaintable=['cal-ngc3256.G2.flux', 'cal-ngc3256.B1']: We apply the gaincal table with the correct flux scaling and the bandpass table
- gainfield = ['1037*', '1037*']: We use the solutions from the secondary calibrator (1037-295) in both tables
- interp='nearest': We opt for interpolation mode "nearest"
- flagbackup=F: We do not back up the state of the flags before applying calibration
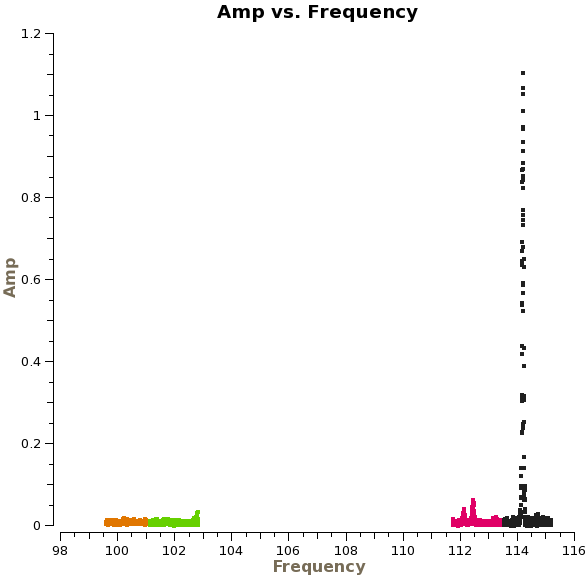
Let's now use plotms to examine the corrected amplitude of NGC3256 as a function of frequency:
# In CASA
plotms(vis='ngc3256_line.ms', xaxis='freq', yaxis='amp',
ydatacolumn='corrected', selectdata=True, field='NGC*',
averagedata=True, avgchannel='', avgtime='10000s',
avgscan=True, avgbaseline=T, coloraxis='spw')
Use the "Zoom" tool to zoom in on the different spectral windows. (Note that spw 2-3 are on the left). There are three emission lines in spectral windows 0-1. There is no emission in spw 2 and 3. Also note that there are still some high channels on the edge of spw 2-3. We will exclude these channels for our subsequent imaging.
It also makes sense to plot the corrected amplitudes and phases of 1037-295 as a function of time and frequency, to check that the phases are close to zero and the amplitudes are constant. The result of the amplitude versus time plot is shown to the right.
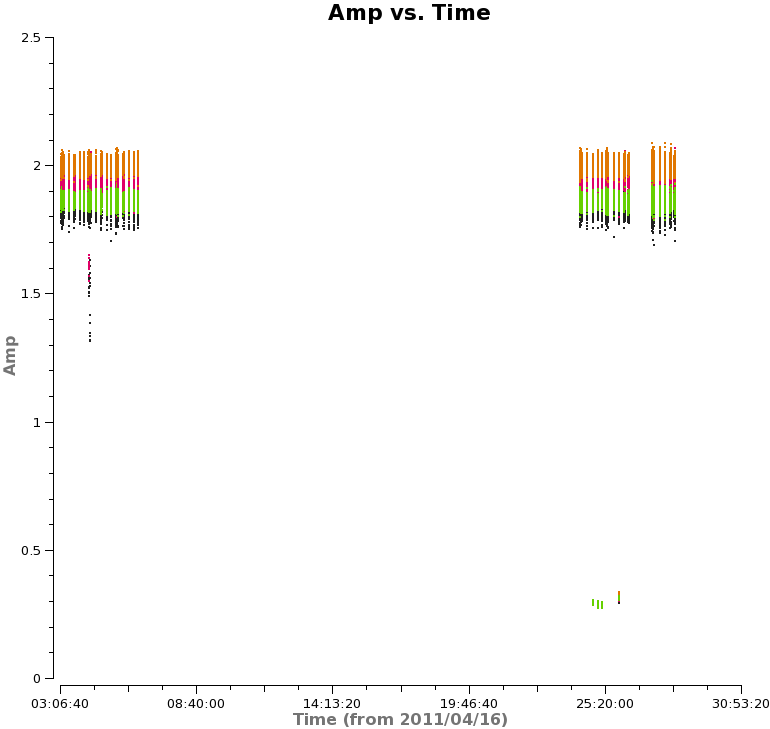
# In CASA
plotms(vis='ngc3256_line.ms', xaxis='time', yaxis='amp',
ydatacolumn='corrected', selectdata=True, field='1037*',
averagedata=True, avgchannel='128', avgtime='',
avgscan=False, avgbaseline=F, coloraxis='spw')
# In CASA
plotms(vis='ngc3256_line.ms', xaxis='freq', yaxis='phase',
ydatacolumn='corrected', selectdata=True, field='1037*',
averagedata=True, avgchannel='', avgtime='1e8',
avgscan=True, avgbaseline=F, coloraxis='baseline')
Based on the inspection of these plots, we identify some bad data and flag them:
# In CASA
flagdata(vis='ngc3256_line.ms', mode='manualflag',
timerange='2011/04/16/04:13:35~04:13:45', flagbackup = T)
tget(flagdata)
timerange='2011/04/16/05:21:13~05:21:19'
flagdata()
timerange='2011/04/16/04:16:40~04:16:49'
flagdata()
timerange='2011/04/16/04:14:00~04:17:10'; antenna='PM03'
flagdata()
timerange='2011/04/17/00:35:30~01:20:20'; antenna='DV04'; spw='3'
flagdata()
Note that in the above command sequence, we utilize the CASA function tget. This function retrieves the last input values for the function specified.
Now that we have flagged some of the calibrator data, we should redo the calibration steps above. We start with a clearcal to reinitialize the calibration columns in ngc3256_line.ms. Specifically, it will set the MODEL data column to unity, and it will set the CORRECTED data column equal to the original DATA column. After the clearcal, the commands are identical to what has been done above. (The improvements in the calibration are only minor, so in principle, one could carry on with making calibrator images and skip the following eight commands.)
# In CASA
clearcal('ngc3256_line.ms')
# In CASA
gaincal(vis='ngc3256_line.ms', caltable='cal-ngc3256.G1', spw='*:40~80', field='1037*',
selectdata=T, solint='int', refant='DV04', calmode='p')
# In CASA
bandpass(vis = 'ngc3256_line.ms', caltable = 'cal-ngc3256.B1',
gaintable = 'cal-ngc3256.G1', timerange='<2011/04/16/15:00:00',
field = '1037*', minblperant=3, minsnr=2, solint='inf', combine='scan',
bandtype='B', fillgaps=1, refant = 'DV04', solnorm = T)
# In CASA
bandpass(vis = 'ngc3256_line.ms', caltable = 'cal-ngc3256.B1',
gaintable = 'cal-ngc3256.G1', timerange='>2011/04/16/15:00:00',
field = '1037*', minblperant=3, minsnr=2, solint='inf', combine='scan',
bandtype='B', fillgaps=1, refant = 'DV04', solnorm = T, append=True)
# In CASA
setjy(vis='ngc3256_line.ms', field='Titan', standard='Butler-JPL-Horizons 2010',
spw='0,1,2,3')
# In CASA
gaincal(vis = 'ngc3256_line.ms', caltable = 'cal-ngc3256.G2', spw =
'*:16~112', field = '1037*,Titan', minsnr=1.0,
solint= 'inf', selectdata=T, solnorm=False, refant = 'DV04',
gaintable = 'cal-ngc3256.B1', calmode = 'ap')
# In CASA
fluxscale( vis="ngc3256_line.ms", caltable="cal-ngc3256.G2",
fluxtable="cal-ngc3256.G2.flux", reference="Titan",
transfer="1037*", refspwmap=[0,1,1,1])
# In CASA
applycal( vis='ngc3256_line.ms', flagbackup=F, field='NGC*,1037*',
interp=['nearest','nearest'], gainfield = ['1037*', '1037*'],
gaintable=['cal-ngc3256.G2.flux', 'cal-ngc3256.B1'])
Having redone the calibration, we will again look at amplitude and phase versus time to check that the amplitudes are stable and the phases are close to zero.
# In CASA
plotms(vis='ngc3256_line.ms', xaxis='time', yaxis='amp',
ydatacolumn='corrected', selectdata=True, field='1037*',
averagedata=True, avgchannel='128', avgtime='',
avgscan=False, avgbaseline=F, coloraxis='spw')
# In CASA
plotms(vis='ngc3256_line.ms', xaxis='freq', yaxis='phase',
ydatacolumn='corrected', selectdata=True, field='1037*',
averagedata=True, avgchannel='', avgtime='1e8',
avgscan=True, avgbaseline=F, coloraxis='baseline')
-
Corrected amplitude vs. time
-
Corrected phase vs. time
In the first plot we show amplitude vs time, colorized by spectral window. This shows very clearly that the amplitude is constant in time, but varies as a function of frequency, which is intrinsic to the source. The second plot shows that the phases are very flat across all spectral windows.
Imaging the Calibrators
At this point, we will image the secondary calibrator as a check of our calibration. We do this using the task clean, after first removing any previous versions of the images that may exist in our directory. This is an important precaution, since if the image already exists, CASA will clean it further instead of producing a new image. In this clean run, we choose to use Multi-Frequency Synthesis (mfs) with nterms=2, which implies that the algorithm determines the continuum map and the spectral index map simultaneously. This is required here, because we found with fluxscale that the flux of 1037-295 increases significantly toward lower frequencies. Therefore, assuming a 'flat' spectral index would not give a good result. Do not be alarmed to see this message: "Multi-term MFS imaging algorithm is new and under active development and testing". The method is working fine and has been tested.
# In CASA
os.system('rm -rf result-phasecal_cont*')
clean(vis='ngc3256_line.ms', imagename='result-phasecal_cont', field='1037*',
spw='*:20~120', selectdata=T, mode='mfs', niter=500,
gain=0.1, threshold='0.75mJy', psfmode='hogbom',
interactive=False, mask=[62, 62, 67, 67], imsize=128,
cell='1arcsec', weighting='briggs', robust=0.0, nterms=2)
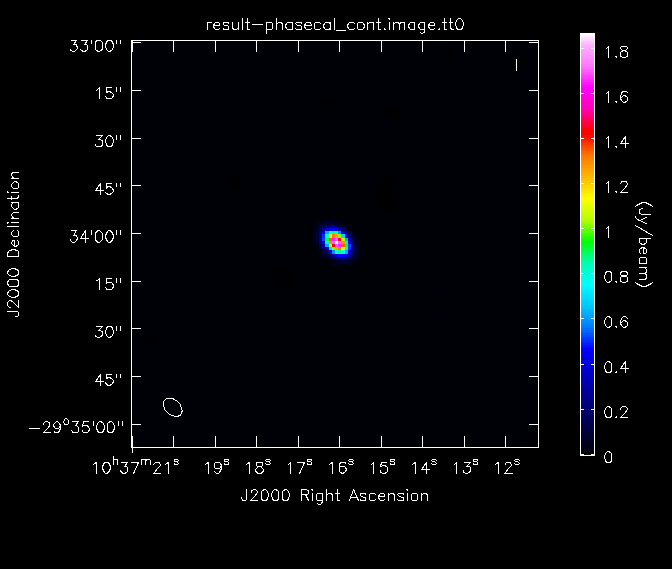
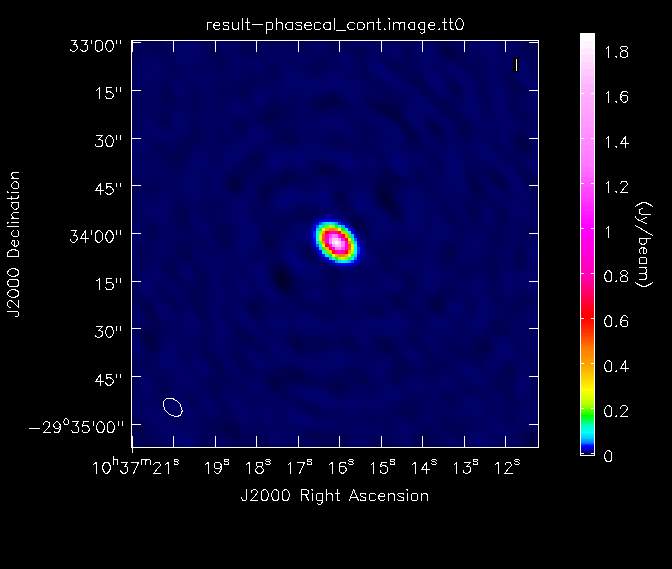
- imagename='result-phasecal_cont': the base name of the output images
- spw='*:20~120': We image all spectral windows, ignoring the outermost channels of each
- mode='mfs': Mult-Frequency Synthesis: the default mode, which produces one image from all the specified data combined
- nterms=2: The number of Taylor terms to be used to model the frequency dependence of the sky emission
- niter=500: Maximum number of clean iterations
- theshold='0.75mJy': Stop cleaning if the maximum residual is below this value. Here we choose a threshold equal to ~1.5 times the rms noise level
- psfmode='hogbom': The method used to calculate the PSF during minor clean cycles. Hogbom is a good choice for poorly-sampled uv-planes
- mask=[62, 62, 67, 67]: Limits the clean component placement to the region of the source. We know the source is compact so we do not need to worry about boxing interactively
- imsize=128, cell='1arcsec': Chosen to appropriately sample the resolution element and cover the primary beam
- weighting='briggs', robust=0.0: a weighting scheme that offers a good compromise between sensitivity and resolution
Note that using nterms=2 makes the clean task considerably slower than before. Once the imaging of the secondary calibrator is complete, we will generate some statistics on the image using the task imstat. Note that the output images from using a clean with nterms=2 now have a suffix .tt0 or .tt1, which is used to indicate the continuum map and spectral index map, respectively.
# In CASA
calstat=imstat(imagename='result-phasecal_cont.image.tt0', region='', box='85,8,120,120')
rms=(calstat['rms'][0])
print '>> rms in phase calibrator image: '+str(rms)
calstat=imstat(imagename='result-phasecal_cont.image.tt0', region='')
peak=(calstat['max'][0])
print '>> Peak in phase calibrator image: '+str(peak)
print '>> Dynamic range in phase calibrator image: '+str(peak/rms)
Here, we have used the "box" parameter in the first call of imstat to find the image rms in a region away from the strong central point source. The image dynamic range in the calibrator image is ~3100. We will then look at the image of the secondary calibrator with imview.
# In CASA
imview(raster={'file': 'result-phasecal_cont.image.tt0', 'colorwedge':T,
'range':[-0.004, 0.250], 'scaling':-2.5, 'colormap':'Rainbow 2'},
out='result-phasecal_map.png', zoom=1)
This command rasters the image of the phase calibrator to the GUI and outputs the file phasecal_map.png. It uses the Rainbow 2 colomap scheme and includes a colorwedge on the plot. The "range" and "scaling" parameters have been chosen to bring out the weaker features in the map. The calibrator image looks pretty good, from which we conclude that the gain calibration has worked well and we will move on. If the image quality was not acceptable, we would need to flag some more data and redo the calibration to this point.
Now we will apply the calibration to the flux calibrator, Titan, using the time-dependent solutions we derived for Titan itself and the bandpass solutions from 1037*.
# In CASA
applycal(vis='ngc3256_line.ms', flagbackup=F, field='Titan',
interp=['nearest', 'nearest'], gainfield = ['Titan', '1037*'],
gaintable=['cal-ngc3256.G2.flux', 'cal-ngc3256.B1'])
Now we will image the flux calibrator (Titan). See the previous call to clean for a description of the various inputs. This time we will only use spectral windows 0 and 1 because we know that the Titan data in spectral windows 2 and 3 are corrupted by Saturn.
# In CASA
os.system('rm -rf result-ampcal_cont*')
clean(vis='ngc3256_line.ms', imagename='result-ampcal_cont',
field='Titan', spw='0:20~120,1:20~120', mode='mfs', niter=200,
threshold='5mJy', psfmode='hogbom', mask=[62, 62, 67, 67], imsize=128,
cell='1arcsec', weighting='briggs', robust=0.0)
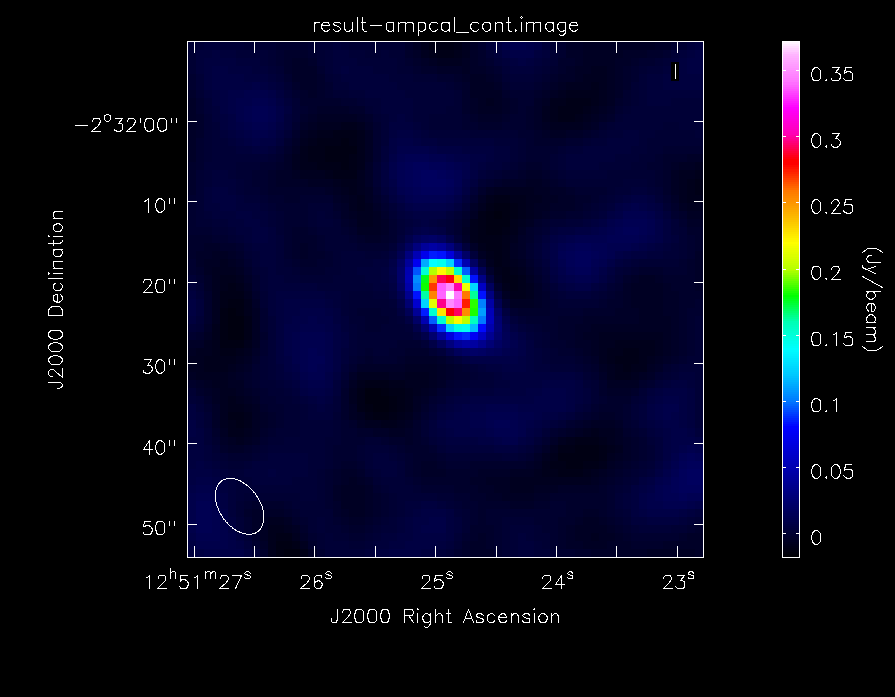
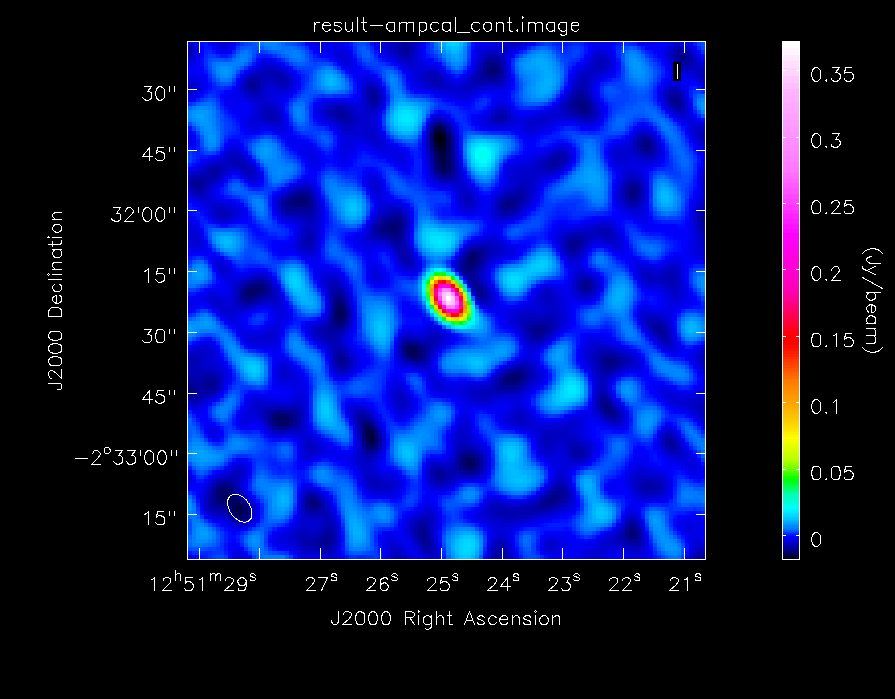
As before, we will generate some statistics on the image:
# In CASA
calstat=imstat(imagename="result-ampcal_cont.image",region="",box="85,8,120,120")
rms=(calstat['rms'][0])
print ">> rms in amp calibrator image: "+str(rms)
calstat=imstat(imagename="result-ampcal_cont.image",region="")
peak=(calstat['max'][0])
print ">> Peak in amp calibrator image: "+str(peak)
print ">> Dynamic range in amp calibrator image: "+str(peak/rms)
The dynamic range in this image is ~74. It's much less than the image of the secondary calibrator because less time was spent observing it (the total on-source time on Titan is only 9 minutes). We will then take a look at the image with imview, again choosing the data range and scaling parameter to bring out weak features in the map:
# In CASA
imview(raster={'file': 'result-ampcal_cont.image', 'colorwedge':T,
'range':[-0.02, 0.250], 'scaling':-1.5, 'colormap':'Rainbow 2'},
out='result-ampcal_map.png', zoom=1)
The image of Titan looks good, which further confirms the quality of the calibration. The last step is to split out the science target, since we no longer need the calibrator data. We run split with field='NGC*' to create ngc3256_line_target.ms:
# In CASA
os.system('rm -rf ngc3256_line_target.ms*')
split(vis='ngc3256_line.ms', outputvis='ngc3256_line_target.ms',
field='NGC*')
This concludes the Calibration section of this CASA Guide. To proceed to the Imaging section, click here: NGC3256 Band3 - Imaging. To go back to the main NGC3256 page, see: NGC3256Band3.