Importing Data into CASA: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
The second way to download your data is easier for the user, but may place a large burden on the archive and delay your data's arrival. Simply select "CASA MS" format on the "Download Archive Data Files" page of the archive. You'll probably want to still create a tar file, and you may or may not want to apply telescope flags. | The second way to download your data is easier for the user, but may place a large burden on the archive and delay your data's arrival. Simply select "CASA MS" format on the "Download Archive Data Files" page of the archive. You'll probably want to still create a tar file, and you may or may not want to apply telescope flags. The flagging steps included in this "Apply flags generated during observing" command is currently in flux, so you may want to exercise caution here. Wait for your email from the archive stating that the data set has been copied, download it, un-tar it, and voila! You have a measurement set ready for use in CASA. | ||
Revision as of 21:58, 6 June 2010
To manipulate your data in CASA, it will have to be in measurement set format. But how do you get it into a measurement set?
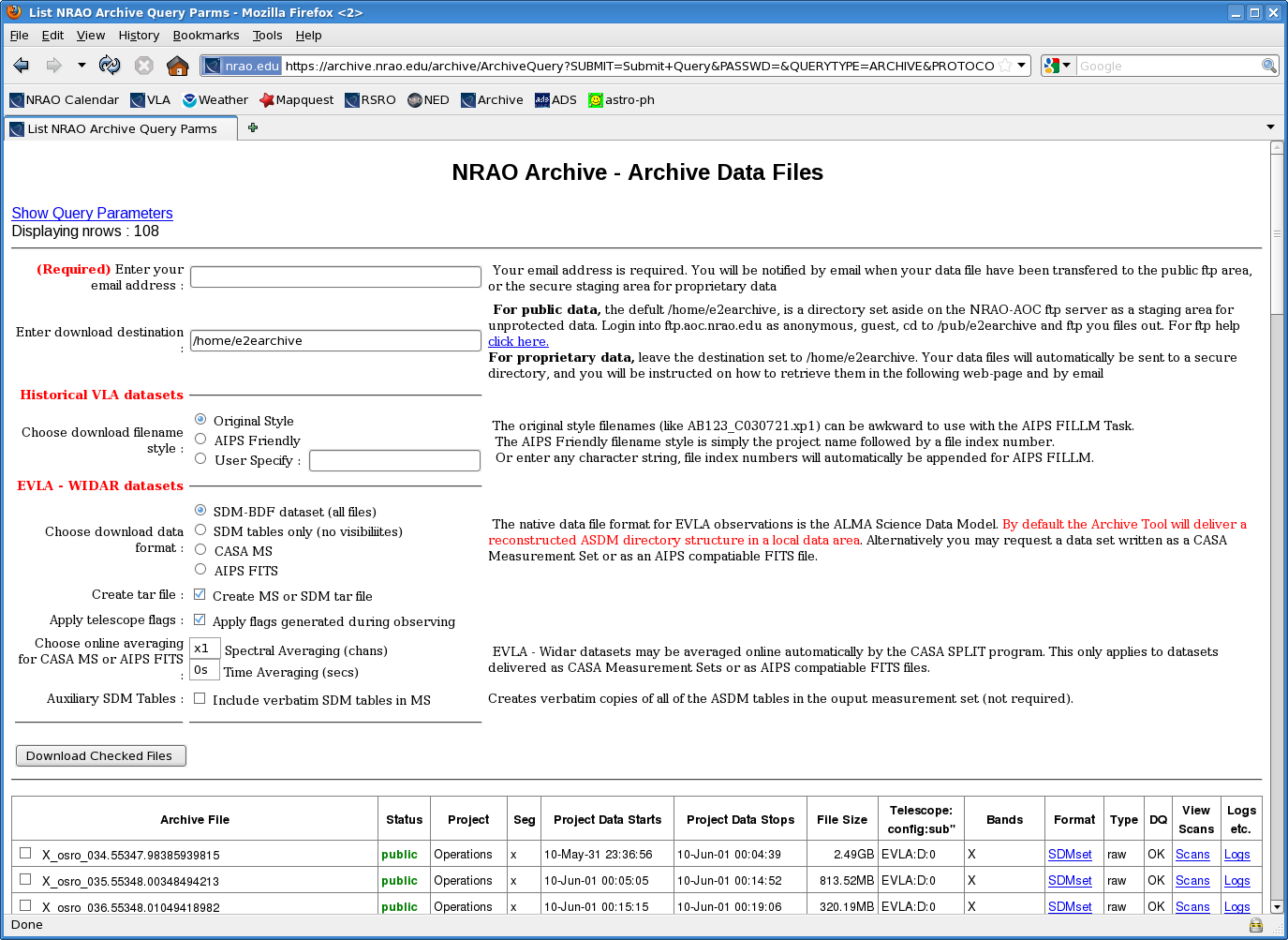
- For EVLA Data: Go to the NRAO archive and find the data set you'd like to download. Navigate to the "Download Archive Data Files" page, which will look something like this:
Note that there are quite a few format options for EVLA-WIDAR datasets. The most fundamental data format is the science data model (SDM). This is the fastest way to get your data from the archive, places the least burden on the archive, and gives you---the user---most control. If you decide to download the data in SDM format, select "SDM-BDF dataset (all files)" and "Create MS or SDM tar file". Whether or not you select "Apply flags generated during observing" is irrelevant at this point---you will decide which flags to apply. Click on "Download Checked Files" and wait for an email that says your data has been copied. Download the data into your working directory. Unpack the tar ball with a tar -xvf. Fire up CASA in your working directory.
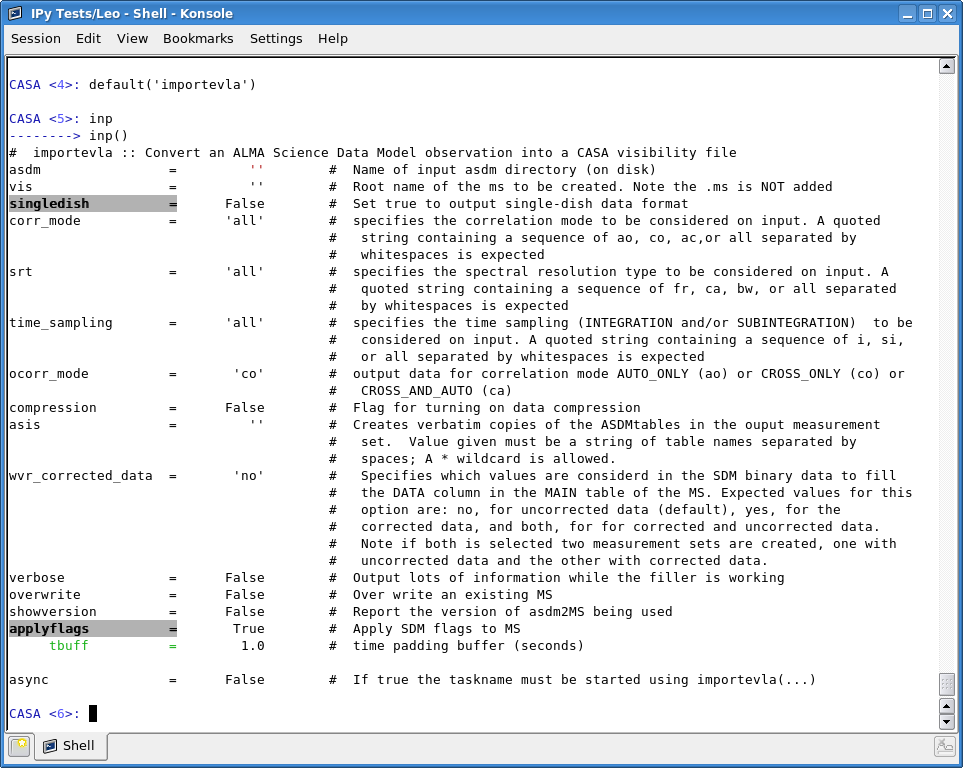
Now it's time to use the CASA task importevla to convert this SDM into a measurement set.
Set asdm to the name of the SDM directory you've just downloaded. Set ms to the name of the measurement set you'd like to create---make sure you add a ".ms" to the end of the name! Everything else should be fine left as defaults. Note that applyflags=True will apply the online flags, which are very basic. Antennas which are not on source will be flagged, but that is about all. You will still need to quack, flag for shadowing, flag antennas which are not fringing, etc. Type go, check the logger output periodically, and you should end up with a nice measurement set as output.
The second way to download your data is easier for the user, but may place a large burden on the archive and delay your data's arrival. Simply select "CASA MS" format on the "Download Archive Data Files" page of the archive. You'll probably want to still create a tar file, and you may or may not want to apply telescope flags. The flagging steps included in this "Apply flags generated during observing" command is currently in flux, so you may want to exercise caution here. Wait for your email from the archive stating that the data set has been copied, download it, un-tar it, and voila! You have a measurement set ready for use in CASA.
- For Historical VLA Data: Download the data from the archive as you normally would, selecting the naming style that is most convenient ("Original Style", "AIPS Friendly", or "User Specify"). Wait for the email to arrive from the archive saying your data has been copied, and download it into your working directory. Now fire up CASA.
You will use the CASA task importvla to import these historical data:
Set archivefiles to the name(s) of the files you just downloaded, and set vis to the name of the measurement set you'd like to produce (make sure you add a ".ms" to the end of the name!). Type go, check the logger output periodically, and you should end up with a nice measurement set as output.
--Laura Chomiuk 21:57, 6 June 2010 (UTC)