Simulating Observations in CASA v3.0.1: Difference between revisions
| Line 79: | Line 79: | ||
| rowspan=2; style="border-bottom:1px solid black;" | [[File:M51-ATZ2-p1.image.png|200px]] | | rowspan=2; style="border-bottom:1px solid black;" | [[File:M51-ATZ2-p1.image.png|200px]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
!style="border-bottom:1px solid black;"| [[M51 at z = 0.1|simdata version]] [[M51 at z = 0.1 | !style="border-bottom:1px solid black;"| [[M51 at z = 0.1|simdata version]] [[M51 at z = 0.1 and z = 0.3|simdata2 version]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Protoplanetary Disk | | Protoplanetary Disk | ||
| rowspan=2; stype="border-bottom:1px solid black;" | [[File:Psim2.analysis.png|200px]] | | rowspan=2; stype="border-bottom:1px solid black;" | [[File:Psim2.analysis.png|200px]] | ||
Revision as of 15:18, 24 May 2010
Simulation capability in CASA follows the usual two-layered structure: there is a beginner-level python task interface called simdata, which calls methods in the sm C++ tool. The task interface turns a model of the sky (2 to 4 dimensions including frequency and Stokes) into the visibilities that would be measured with ALMA, (E)VLA, CARMA, SMA, ATCA, PdB, etc. The task also can produce a cleaned image of the model visibilities, compare that image with your input convolved with the synthesized beam, and calculate a fidelity image. simdata can add thermal noise (from receiver, atmosphere, and ground) to the visibilities.
The sm tool has methods that can be used to add phase delay variations, gain fluctuations and drift, cross-polarization, and (coming soon) bandpass and pointing errors to your simulated data. sm also has more flexibility in adding thermal noise than simdata, for example for new observatories that are unknown to simdata.
New for 3.0.2: Two task interfaces will be present, the old simdata and a new simdata2. We recommend using simdata2 -- simdata is being retained because it has had more extensive testing, and simdata2 is very new, but in the future simdata will be removed.
CASA simulation uses the aatm atmospheric model, a thin wrapper of Juan Pardo's ATM library, to accurately calculate all atmospheric corruption terms (noise, phase delay) accurately as a function of frequency and site characteristics.
Part of CASA's simulation routines are generic ephemeris and geodesy calculations available in python - see simutil.py.
Because simdata is still actively being developed, documentation may lag reality, please email rindebet at nrao.edu with any questions - It's my job to help you use this software. In particular, you may find that some of the presentations and graphics below show parameter inputs that are slightly different from the latest version of CASA.
Steps to simulation
|
simdata pdf presentation explaining the same things as below: File:Tutorial.dec2009.pdf 1. Install CASA simdata inputs look like this (v3.0.2; click to enlarge): the links below describe the various sections of inputs 2. Input Model - Preparing a patch of sky for simdata to pseudoobserve. 3. Antenna List - how to specify the positions and diameters of your antennas or stations. 4. Specifying Observation - how to set up what/when/how you want to observe, and the output image details 5. Corrupting Observation - (Optional) For added realism, corrupt your visibilities with thermal and phase noise. 6. Deconvolve Image (Optional) Go back from the calculated visibilities to a synthesis image |
simdata2 1. Install CASA simdata2 inputs look like this (v3.0.2; click to enlarge): The subtasks are modular i.e. as long as you follow a few conventions about filenames, you can run each bit independently and optionally. For example, you can modify the sky model, then predict ACA visibilities, then run again and predict ATCA 12m visibilities and image and analyze both measurement sets together. You can run once to predict, run interactive clean yourself, and as long as you called your image $project.image, run simdata2 just to calculate a difference image and analyze the results. 2. Modify Model - relabel (scale) the spectral and spatial coordinates and brightness of the sky model image. 3. Set Pointings - calculate a mosaic of pointings and save in a text file. You could also make the text file yourself. 4. Predict - Calculate visibilities for a specified array on a specified day 5. Corrupting Observation - Corrupt the measurement set with thermal noise, phase noise, cross-polarization, etc. 6. Image A subset of clean to re-image the visibilities 7. Analyze Calculate and display the difference between output and input, and fidelity image. |
These links need to be incorporated into the next section below:
- Sample Model Images
- Simulation Recipes - a nearby galaxy with ALMA, a protoplanetary disk with SMA, etc
Tutorials, Recipes, and Example images
| Simulated ALMA Observation of M51 at z = 0.1 and z = 0.3: annotated tutorial | 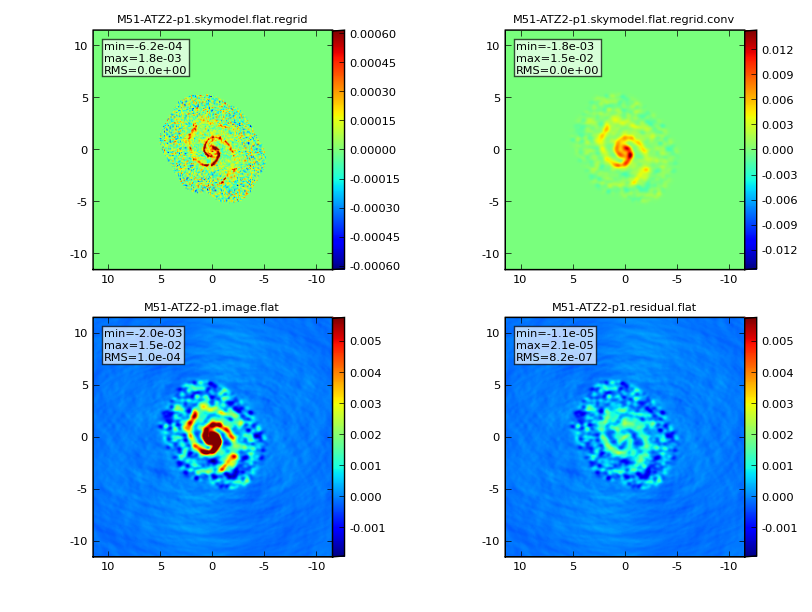
|
| simdata version simdata2 version | |
|---|---|
| Protoplanetary Disk | 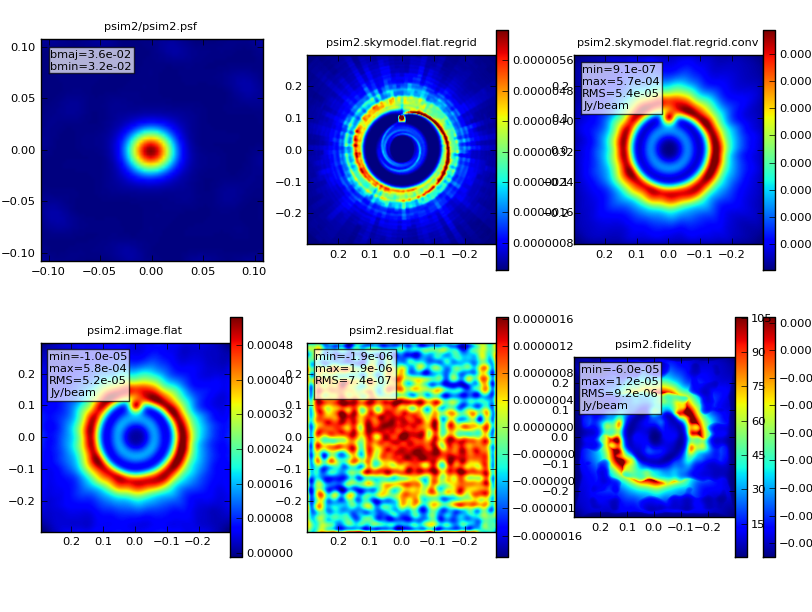
|
| File:Ppdisk.simdata.txt simdata script File:Ppdisk.simdata2.txt |
Technical and Planning
I always welcome input on developing the CASA simulator, and these links are meetings, technical documents, and planning discussions. Much of it won't make sense to a new user of CASA::simdata, but may be of interest to those wanting to delve deeper:
- Simulation Library This will become a library of use cases and examples illustrating different science and observation setups. It is in early stages as of Jan 2010, and we're actively seeking volunteers to turn their simulation projects into use cases.
- Jan 2010 workshop Including slides and discussion of how simdata and Simulator work "under the hood" and plans for development

