PPdisk simdata (CASA 3.3): Difference between revisions
From CASA Guides
Jump to navigationJump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (22 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Simulations Intro}} | {{Simulations Intro}} | ||
[[Category: Simulations]] | [[Category: Simulations]] | ||
''Old version: [[PPdisk simdata (CASA 3.2)]].'' | ''Old version: [[PPdisk simdata (CASA 3.2)]].'' | ||
| Line 11: | Line 9: | ||
*[ftp://ftp.cv.nrao.edu/NRAO-staff/rindebet/input50pc_672GHz.fits This fits file] is a model of a protoplanetary disk from S. Wolf (If you use it for anything more than learning CASA, please cite [http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2005ApJ...619.1114W Wolf & D'Angelo 2005]). | *[ftp://ftp.cv.nrao.edu/NRAO-staff/rindebet/input50pc_672GHz.fits This fits file] is a model of a protoplanetary disk from S. Wolf (If you use it for anything more than learning CASA, please cite [http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2005ApJ...619.1114W Wolf & D'Angelo 2005]). | ||
* | *sim_observe and sim_analyze version for CASA 3.3 | ||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
====Explanation of the script==== | ====Explanation of the script==== | ||
=====Set | =====Set sim_observe as current task and reset all parameters===== | ||
<source lang="python"> | |||
# Setting everything in simdata to original defaults | |||
default("sim_observe") | |||
</source> | |||
=====Image coordinate system can be verified===== | =====Image coordinate system can be verified===== | ||
<source lang="python"> | |||
# This reports image header parameters in the Log Messages window | |||
imhead("input50pc_672GHz.fits") | |||
</source> | |||
=====Image center can be identified===== | =====Image center can be identified===== | ||
<source lang="python"> | |||
# These are tools found in the CASA toolkit | |||
# They are very useful, but the interface is not as straightforward as the tasks | |||
# You can find the tool reference manual here: http://casa.nrao.edu/docs/CasaRef/CasaRef.html | |||
# The following command is used to open an image (this is part of the image analysis toolkit) | |||
# Whenever data are being viewed/manipulated by tools, what is being operated on needs to be explicitly opened | |||
# and closed (i.e. an image, a table, etc.) | |||
ia.open("input50pc_672GHz.fits") | |||
# Out[9]: True | |||
# | |||
# Reports the length of each axis in the opened image | |||
ia.shape() | |||
# Out[11]: [257L, 257L, 1L, 1L] | |||
# | |||
# This command converts from pixel (our source file) to world coordinates (something usable by simdata) | |||
ia.toworld([128.5,128.5]) | |||
# Out[12]: | |||
#{'numeric': array([ 4.71239120e+00, -4.01423802e-01, 1.00000000e+00, | |||
# 6.72000001e+11])} | |||
# | |||
# Formats the coordinate just converted into hms | |||
qa.formxxx("4.71239120rad",format='hms',prec=5) | |||
# Out[13]: '18:00:00.03052' | |||
# | |||
# Formats one of the other coordinates into dms | |||
qa.formxxx("-0.401423802rad",format='dms',prec=5) | |||
# Out[14]: '-022.59.59.602743' | |||
# | |||
# Final housekeeping by closing the image tool | |||
# The image tool will now be detached from the image | |||
ia.close() | |||
</source> | |||
=====Brightness scale can be viewed with 'imstat' task===== | =====Brightness scale can be viewed with 'imstat' task===== | ||
<source lang="python"> | |||
# Default parameters are adequate for this | |||
imstat("input50pc_672GHz.fits") | |||
# ... | |||
# 'max': array([ 6.52469971e-05]), | |||
# ... | |||
# that's 0.0652 mJy/pixel. | |||
</source> | |||
=====Let's call our project psim2===== | =====Let's call our project psim2===== | ||
<source lang="python"> | |||
# This defines the root prefix for any output files from simdata | |||
project = "psim2" | |||
</source> | |||
=====We'll leave the sky model the way it is: simdata will create psim2.skymodel CASA image since this model is a fits file, and most but not all of CASA routines can operate directly on fits===== | =====We'll leave the sky model the way it is: simdata will create psim2.skymodel CASA image since this model is a fits file, and most but not all of CASA routines can operate directly on fits===== | ||
<source lang="python"> | |||
skymodel = "input50pc_672GHz.fits" | |||
</source> | |||
=====We need to decide where to point the telescope. The image is 2/3 arcsec in size, so we only need one pointing. We could put that in a text file ourself, or let simdata create the ascii pointing file for us.===== | =====We need to decide where to point the telescope. The image is 2/3 arcsec in size, so we only need one pointing. We could put that in a text file ourself, or let simdata create the ascii pointing file for us.===== | ||
<source lang="python"> | |||
setpointings = True | |||
direction = "J2000 18h00m00.031s -22d59m59.6s" | |||
mapsize = "0.76arcsec" | |||
</source> | |||
=====The default pointingspacing is fine: we'll only fit one pointing in the small mapsize the default calculation maptype hexagonal is ok too since only one will fit anyway.===== | =====The default pointingspacing is fine: we'll only fit one pointing in the small mapsize the default calculation maptype hexagonal is ok too since only one will fit anyway.===== | ||
=====We do want to calculate visibilities in a measurement set: let's do a 20 min snapshot observation using out20 configuration:===== | =====We do want to calculate visibilities in a measurement set: let's do a 20 min snapshot observation using the "out20" ALMA antenna configuration:===== | ||
<source lang="python"> | |||
observe = True | |||
totaltime = "1200s" | |||
</source> | |||
=====Use appropriate antenna configurations based on desired angular resolution (configuration 20 - alma.out20.cfg in this case - is the largest "compact" configuration)===== | |||
<source lang="python"> | |||
# It might be helpful to confirm the alma.out20.cfg file exists in the path defined below | |||
# If you have a problem, this might be the first thing to check, if you haven't already | |||
repodir=os.getenv("CASAPATH").split(' ')[0] | |||
antennalist = repodir+"/data/alma/simmos/alma.out20.cfg" | |||
sim_observe() | |||
</source> | |||
===== | ===== Deconvolve the visibilities back into an image===== | ||
<source lang="python"> | |||
default ("sim_analyze") | |||
project = "psim2" | |||
image = True | |||
# Prior image to use in clean | |||
modelimage = "input50pc_672GHz.fits" | |||
vis = project+".alma.out20.ms" | |||
imsize = [192, 192] | |||
</source> | |||
=====Specify number of iteration of cleaning task with proper threshold and weighting===== | =====Specify number of iteration of cleaning task with proper threshold and weighting===== | ||
<source lang="python"> | |||
niter = 10000 | |||
threshold = "1e-7Jy" | |||
weighting = "natural" | |||
</source> | |||
=====We'd like to calculate a difference and fidelity image, and see some diagnostics:===== | =====We'd like to calculate a difference and fidelity image, and see some diagnostics:===== | ||
<source lang="python"> | |||
analyze = True | |||
</source> | |||
=====And see the array but not the UV coverage:===== | =====And see the array but not the UV coverage:===== | ||
<source lang="python"> | |||
showuv = False | |||
showresidual = True | |||
showconvolved = True | |||
</source> | |||
=====Plot both to the screen and the png files with lots of messages:===== | =====Plot both to the screen and the png files with lots of messages:===== | ||
<source lang="python"> | |||
graphics = "both" | |||
verbose = True | |||
overwrite = True | |||
</source> | |||
===Run simdata=== | ===Run simdata=== | ||
<source lang="python"> | |||
# This commands CASA to execute sim_analyze | |||
sim_analyze() | |||
</source> | |||
<br> | <br> | ||
*Output results: | *Output results: | ||
| Line 87: | Line 148: | ||
{| style="border:1px solid #3366FF; " cellspacing=2 | {| style="border:1px solid #3366FF; " cellspacing=2 | ||
|Input:<br> [[File:Psim2.skymodel.png|300px]] | |Input:<br> [[File:Psim2.skymodel.png|300px]] | ||
|Predict:<br> [[File:Psim2. | |Predict:<br> [[File:Psim2.alma.out20.observe.png|300px]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
|Image:<br> [[File:Psim2.image.png|300px]] | |Image:<br> [[File:Psim2.alma.out20.image.png|300px]] | ||
|Analyze:<br> [[File:Psim2.analysis.png|300px]] | |Analyze:<br> [[File:Psim2.analysis.png|300px]] | ||
|} | |} | ||
{{Simulations Intro}} | {{Simulations Intro}} | ||
{{Checked 3.3.0}} | |||
Latest revision as of 15:17, 22 November 2011
↵ Simulating Observations in CASA
Old version: PPdisk simdata (CASA 3.2).
To create a script of the Python code on this page see Extracting scripts from these tutorials.
Protoplanetary disk
- This fits file is a model of a protoplanetary disk from S. Wolf (If you use it for anything more than learning CASA, please cite Wolf & D'Angelo 2005).
- sim_observe and sim_analyze version for CASA 3.3
Explanation of the script
Set sim_observe as current task and reset all parameters
# Setting everything in simdata to original defaults
default("sim_observe")
Image coordinate system can be verified
# This reports image header parameters in the Log Messages window
imhead("input50pc_672GHz.fits")
Image center can be identified
# These are tools found in the CASA toolkit
# They are very useful, but the interface is not as straightforward as the tasks
# You can find the tool reference manual here: http://casa.nrao.edu/docs/CasaRef/CasaRef.html
# The following command is used to open an image (this is part of the image analysis toolkit)
# Whenever data are being viewed/manipulated by tools, what is being operated on needs to be explicitly opened
# and closed (i.e. an image, a table, etc.)
ia.open("input50pc_672GHz.fits")
# Out[9]: True
#
# Reports the length of each axis in the opened image
ia.shape()
# Out[11]: [257L, 257L, 1L, 1L]
#
# This command converts from pixel (our source file) to world coordinates (something usable by simdata)
ia.toworld([128.5,128.5])
# Out[12]:
#{'numeric': array([ 4.71239120e+00, -4.01423802e-01, 1.00000000e+00,
# 6.72000001e+11])}
#
# Formats the coordinate just converted into hms
qa.formxxx("4.71239120rad",format='hms',prec=5)
# Out[13]: '18:00:00.03052'
#
# Formats one of the other coordinates into dms
qa.formxxx("-0.401423802rad",format='dms',prec=5)
# Out[14]: '-022.59.59.602743'
#
# Final housekeeping by closing the image tool
# The image tool will now be detached from the image
ia.close()
Brightness scale can be viewed with 'imstat' task
# Default parameters are adequate for this
imstat("input50pc_672GHz.fits")
# ...
# 'max': array([ 6.52469971e-05]),
# ...
# that's 0.0652 mJy/pixel.
Let's call our project psim2
# This defines the root prefix for any output files from simdata
project = "psim2"
We'll leave the sky model the way it is: simdata will create psim2.skymodel CASA image since this model is a fits file, and most but not all of CASA routines can operate directly on fits
skymodel = "input50pc_672GHz.fits"
We need to decide where to point the telescope. The image is 2/3 arcsec in size, so we only need one pointing. We could put that in a text file ourself, or let simdata create the ascii pointing file for us.
setpointings = True
direction = "J2000 18h00m00.031s -22d59m59.6s"
mapsize = "0.76arcsec"
The default pointingspacing is fine: we'll only fit one pointing in the small mapsize the default calculation maptype hexagonal is ok too since only one will fit anyway.
We do want to calculate visibilities in a measurement set: let's do a 20 min snapshot observation using the "out20" ALMA antenna configuration:
observe = True
totaltime = "1200s"
Use appropriate antenna configurations based on desired angular resolution (configuration 20 - alma.out20.cfg in this case - is the largest "compact" configuration)
# It might be helpful to confirm the alma.out20.cfg file exists in the path defined below
# If you have a problem, this might be the first thing to check, if you haven't already
repodir=os.getenv("CASAPATH").split(' ')[0]
antennalist = repodir+"/data/alma/simmos/alma.out20.cfg"
sim_observe()
Deconvolve the visibilities back into an image
default ("sim_analyze")
project = "psim2"
image = True
# Prior image to use in clean
modelimage = "input50pc_672GHz.fits"
vis = project+".alma.out20.ms"
imsize = [192, 192]
Specify number of iteration of cleaning task with proper threshold and weighting
niter = 10000
threshold = "1e-7Jy"
weighting = "natural"
We'd like to calculate a difference and fidelity image, and see some diagnostics:
analyze = True
And see the array but not the UV coverage:
showuv = False
showresidual = True
showconvolved = True
Plot both to the screen and the png files with lots of messages:
graphics = "both"
verbose = True
overwrite = True
Run simdata
# This commands CASA to execute sim_analyze
sim_analyze()
- Output results:
Input: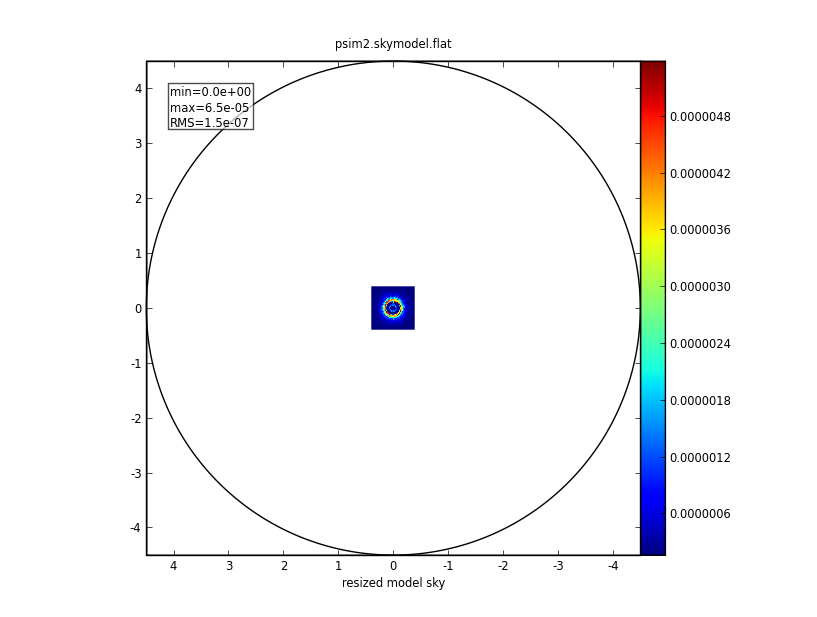
|
Predict:
|
Image: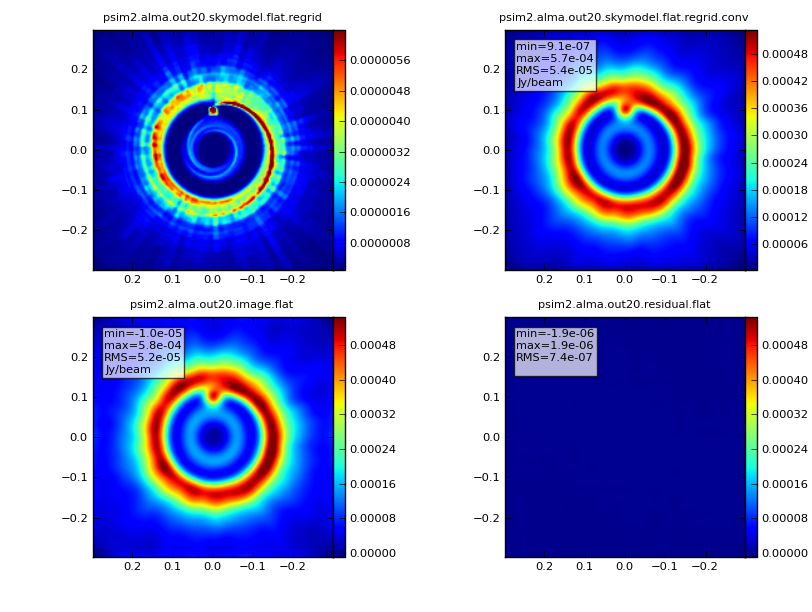
|
Analyze: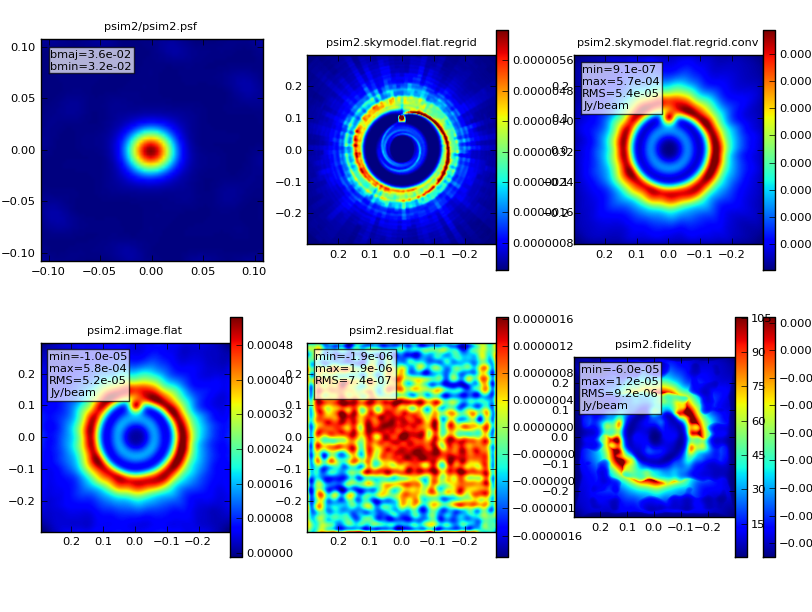
|
↵ Simulating Observations in CASA
Last checked on CASA Version 3.3.0.