AntennaeBand7 for CASA 3.3: Difference between revisions
m moved AntennaeBand7 to AntennaeBand7 for CASA 3.3 |
|||
| (23 intermediate revisions by 7 users not shown) | |||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
==Science Target Overview== | ==Science Target Overview== | ||
[[File:604px-Antennae_galaxies_xl.jpg|200px|thumb|right|Fig. 1. HST image of Antennae. White contours correspond to the CO(1-0) intensity map in Wilson et al. (2000 | [[File:604px-Antennae_galaxies_xl.jpg|200px|thumb|right|'''Fig. 1.''' HST image of the Antennae. White contours correspond to the CO(1-0) intensity map in Wilson et al. (2000; see also Fig. 2). (Credit: NASA, ESA, and the Hubble Heritage Team STScI/AURA-ESA/Hubble Collaboration). Acknowledgement: B. Whitmore ( Space Telescope Science Institute) and James Long (ESA/Hubble)]] | ||
[[File:Wilson00-antennaeco1-0.jpg|200px|thumb|right|Fig. 2. Caltech millimeter array CO(1-0) integrated intensity map from Wilson et al. (2000). ]] | [[File:Wilson00-antennaeco1-0.jpg|200px|thumb|right|'''Fig. 2.''' Caltech millimeter array (OVRO) CO(1-0) integrated intensity map from Wilson et al. (2000). ]] | ||
The Antennae are a nearby (22 Mpc) pair of merging galaxies, NGC 4038 (RA 12h 01m 53.0s, Dec −18° 52′ 10″) in the north and NGC 4039 (RA 12h 01m 53.6s, Dec −18° 53′ 11″) in the south. These two spiral galaxies started to interact only a few hundred million years ago, making the Antennae one of the nearest and youngest examples of a major galaxy merger. The yellow bright components to the south and north of the image center of Figure 1 correspond to the nuclei of the original galaxies and are composed mostly of old stars. Dust filaments, which appear brown in the image, pervade the region between the two nuclei and | The Antennae are a nearby (22 Mpc, Schweizer et al. 2008) pair of merging galaxies, NGC 4038 (RA 12h 01m 53.0s, Dec −18° 52′ 10″) in the north and NGC 4039 (RA 12h 01m 53.6s, Dec −18° 53′ 11″) in the south. These two spiral galaxies started to interact only a few hundred million years ago (Mihos et al. 1993), making the Antennae one of the nearest and youngest examples of a major galaxy merger. The yellow bright components to the south and north of the image center of Figure 1 correspond to the nuclei of the original galaxies and are composed mostly of old stars. Dust filaments, which appear brown in the image, pervade the region between the two nuclei, and star-forming regions surrounded by HII regions (blue) can be seen throughout the system. [http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2000ApJ...542..120W Wilson et al. (2000)] used OVRO to map CO(1-0) emission, a tracer of the bulk molecular gas distribution, with a resolution of 3.15″ x 4.91″ (Figures 1 and 2). Molecular emission is detected throughout the system and is particularly bright in the "interaction region" between the two nuclei, where it appears concentrated in five supergiant molecular complexes (see Figure 2). | ||
==ALMA Data Overview== | ==ALMA Data Overview== | ||
[[File:antennae_foralmaCO3_2_north_withSV.png|200px|thumb|right|Coverage of the "Northern Mosaic" carried out for ALMA Science Verification overlaid on an HST image. Circles show individual pointings, which were observed in rapid succession during each of the "Northern" observations.]] | [[File:antennae_foralmaCO3_2_north_withSV.png|200px|thumb|right|'''Fig. 3''' Coverage of the "Northern Mosaic" carried out for ALMA Science Verification overlaid on an HST image. Circles show individual pointings, which were observed in rapid succession during each of the "Northern" observations.]] | ||
[[File:antennae_foralmaCO3_2_withSV.png|200px|thumb|right|Coverage of the "Southern Mosaic" carried out for ALMA Science Verification overlaid on an HST image. Circles show individual pointings, which were observed in rapid succession during each of the "Southern" observations.]] | [[File:antennae_foralmaCO3_2_withSV.png|200px|thumb|right|'''fig 4.''' Coverage of the "Southern Mosaic" carried out for ALMA Science Verification overlaid on an HST image. Circles show individual pointings, which were observed in rapid succession during each of the "Southern" observations.]] | ||
This CASA Guide steps through reduction and imaging of ALMA Science Verification data targeting the CO 3-2 line in the Antennae galaxy. These data were obtained using the ALMA Band 7 receiver and observed in 10 separate blocks, each typically | This CASA Guide steps through the reduction and imaging of ALMA Science Verification data targeting the CO 3-2 line in the Antennae galaxy. These data were obtained using the ALMA Band 7 receiver and observed in 10 separate blocks, each typically ~1 hour long, during May and June 2011. Each block observed one of two mosaic patterns, which we will refer to as the "Northern" and "Southern" mosaics. Figures 3 and 4 show the coverage of these two mosaics on an optical image of the Antennae. Within an individual observing block, the observations progress through individual pointings of the mosaic in rapid succession. One field was offset from the main body of the galaxy in each mosaic for calibration purposes. | ||
The ten individual data sets | The observations are broken down into ten individual data sets, as follows: | ||
Northern mosaic (covering the nucleus of NGC 4038): | Northern mosaic (covering the nucleus of NGC 4038): | ||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
*uid://A002/X2181fb/X49 | *uid://A002/X2181fb/X49 | ||
Southern mosaic (covering the nucleus of NGC 4039 and | Southern mosaic (covering the nucleus of NGC 4039 and part of the interaction region): | ||
*uid://A002/X1ff7b0/X1c8 | *uid://A002/X1ff7b0/X1c8 | ||
*uid://A002/X207fe4/X1f7 | *uid://A002/X207fe4/X1f7 | ||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
*uid://A002/X215db8/X18 | *uid://A002/X215db8/X18 | ||
The observations | The observations used two basebands, each associated with one spectral window (see the [https://almascience.nrao.edu/call-for-proposals/technical-guide ALMA Technical Handbook] for a discussion of the distinction between basebands and spectral windows). The baseband in the lower sideband (LSB) is centered on the CO (3-2) transition, and the baseband in the upper sideband (USB) is used to measure continuum emission. This guide will focus on the reduction of the LSB CO (3-2) data. Each sideband was observed in both a high spectral resolution "Frequency Domain Mode" (FDM) and a lower spectral resolution "Time Domain Mode" (TDM). We will focus on reducing the FDM data, which have an effective total bandwidth of 1.875 GHz (1634 km/s) divided over 3840 channels. The channel width in FDM mode is 488.28 kHz (0.426 km/s); because the data are automatically Hanning smoothed, the actual spectral resolution is twice this. The TDM mode data were observed and used mainly for calibration purposes; we will not directly analyze them in this CASA Guide, though we will use calibration products (system temperature measurements) derived from these data. | ||
When these observations were taken, the ALMA antennas were in a configuration that is intermediate between the Cycle 0 "Extended" and "Compact" configurations. We expect this configuration to yield an angular resolution of about 1 arcsecond near 345 GHz. | When these observations were taken, the ALMA antennas were in a configuration that is intermediate between the Cycle 0 "Extended" and "Compact" configurations. We expect this configuration to yield an angular resolution of about 1 arcsecond near 345 GHz. | ||
We thank | Using the data for publication: | ||
The following statement should be included in the acknowledgment of papers using the datasets listed above: | |||
“The Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA), an international astronomy facility, is a partnership of Europe, North America and East Asia in cooperation with the Republic of Chile. This paper makes use of the following ALMA Science Verification data: ADS/JAO.ALMA#2011.0.00003.SV” | |||
We thank the following people for suggesting NGC4038/9 for ALMA Science Verification: Francois Boulanger, Nicole Nesvadba, Cinthya Herrera. We particularly thank Christine Wilson and Junko Ueda for providing both the suggestions and the OVRO (CO(1-0): Wilson et al. 2000) and SMA (CO(3-2): Ueda et al., submitted) data for verification purposes. | |||
==Obtaining the Data== | ==Obtaining the Data== | ||
| Line 42: | Line 46: | ||
[http://almascience.nrao.edu/almadata/sciver/AntennaeBand7 North America] | [http://almascience.nrao.edu/almadata/sciver/AntennaeBand7 North America] | ||
[http://almascience.eso.org/almadata/sciver/AntennaeBand7 Europe] | [http://almascience.eso.org/almadata/sciver/AntennaeBand7 Europe] | ||
[http://almascience.nao.ac.jp/almadata/sciver/AntennaeBand7 East Asia] | [http://almascience.nao.ac.jp/almadata/sciver/AntennaeBand7 East Asia] | ||
Here you will find three gzipped tar files which, after unpacking, will create three directories: | Here you will find three gzipped tar files which, after unpacking, will create three directories: | ||
*'''Antennae_Band7_UnCalibratedMSandTablesForReduction''' - Here we provide you with "starter" datasets, where we have taken the raw data in ALMA Science Data Model (ASDM) format and converted them to CASA Measurement Sets (MS). We did this using the {{importasdm}} task in CASA. Along with the raw data, we provide | *'''Antennae_Band7_UnCalibratedMSandTablesForReduction''' - Here we provide you with "starter" datasets, where we have taken the raw data in ALMA Science Data Model (ASDM) format and converted them to CASA Measurement Sets (MS). We did this using the {{importasdm}} task in CASA. Along with the raw data, we provide tables that are needed to calibrate the data, but that cannot currently be generated inside of CASA (for Early Science, these tables will either be pre-applied or supplied with the data). | ||
*'''Antennae_Band7_CalibratedData''' - The fully-calibrated u-v data, ready for imaging. | *'''Antennae_Band7_CalibratedData''' - The fully-calibrated u-v data, ready for imaging. | ||
| Line 55: | Line 61: | ||
To see which files you will need, read on below. The downloads to your local computer will take some time, so you may wish to begin them now. | To see which files you will need, read on below. The downloads to your local computer will take some time, so you may wish to begin them now. | ||
'''NOTE: CASA 3. | '''NOTE: CASA 3.3 or later is required to follow this guide.''' For more information on obtaining the latest version of CASA, see [http://casa.nrao.edu/ http://casa.nrao.edu]. | ||
==Antennae Band 7 Data Reduction Tutorial== | ==Antennae Band 7 Data Reduction Tutorial== | ||
This tutorial has been split into parts | This tutorial has been split into two parts - calibration and imaging: | ||
1) '''[[Antennae Band7 - Calibration]]''' : This section of the tutorial steps you through inspection and calibration of the basic visibility (u-v) data. To complete this part, you will need the data in the first directory: Antennae_Band7_UnCalibratedMSandTablesForReduction. | 1) '''[[Antennae Band7 - Calibration]]''' : This section of the tutorial steps you through inspection and calibration of the basic visibility (u-v) data. To complete this part, you will need the data in the first directory: Antennae_Band7_UnCalibratedMSandTablesForReduction. | ||
| Line 75: | Line 81: | ||
'''To learn how to extract executable Python scripts from the tutorial, see [[Extracting_scripts_from_these_tutorials]].''' | '''To learn how to extract executable Python scripts from the tutorial, see [[Extracting_scripts_from_these_tutorials]].''' | ||
Within the guides: | |||
<source lang="python"> | <source lang="python"> | ||
| Line 93: | Line 99: | ||
This color shows you background information about the data or other types of reference material | This color shows you background information about the data or other types of reference material | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
{{Checked 3.3.0}} | |||
Latest revision as of 16:08, 22 November 2011
NOTE: These guides are dynamic and will evolve as our understanding of how best to reduce ALMA data improves. Check back for updates periodically.
Science Target Overview
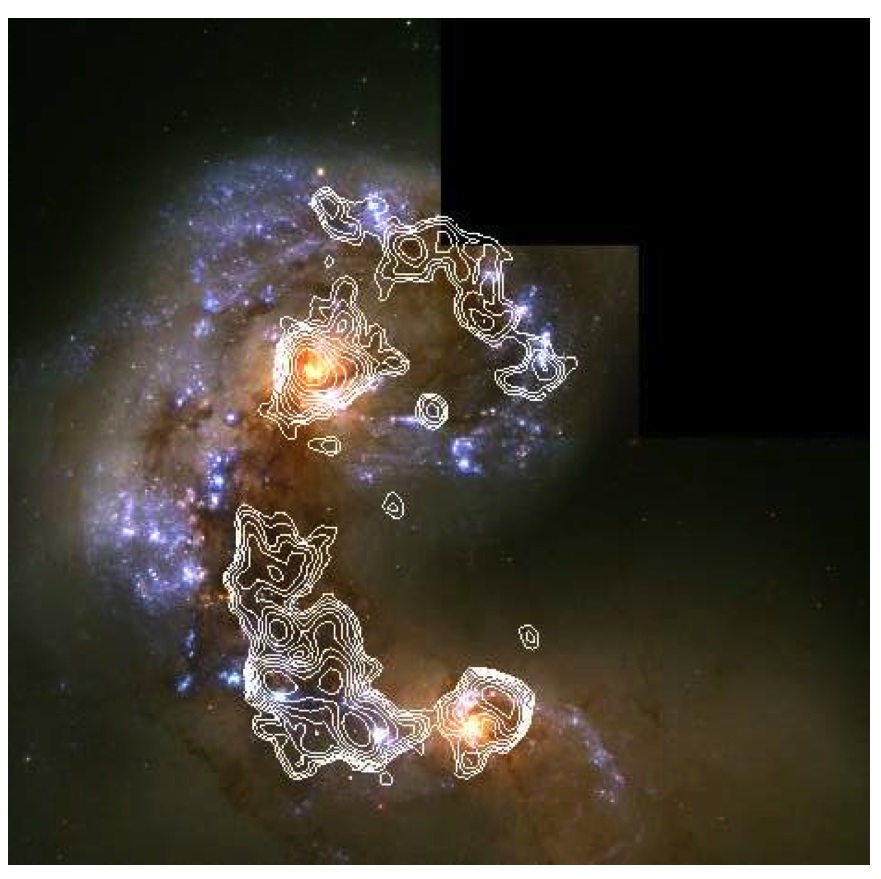
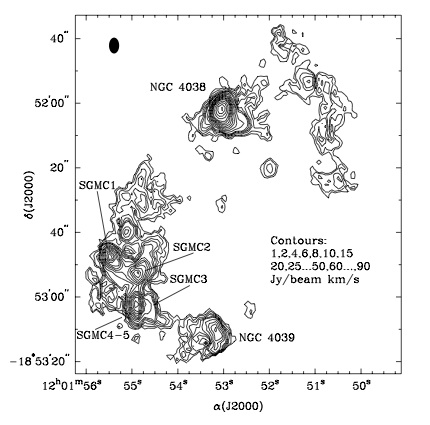
The Antennae are a nearby (22 Mpc, Schweizer et al. 2008) pair of merging galaxies, NGC 4038 (RA 12h 01m 53.0s, Dec −18° 52′ 10″) in the north and NGC 4039 (RA 12h 01m 53.6s, Dec −18° 53′ 11″) in the south. These two spiral galaxies started to interact only a few hundred million years ago (Mihos et al. 1993), making the Antennae one of the nearest and youngest examples of a major galaxy merger. The yellow bright components to the south and north of the image center of Figure 1 correspond to the nuclei of the original galaxies and are composed mostly of old stars. Dust filaments, which appear brown in the image, pervade the region between the two nuclei, and star-forming regions surrounded by HII regions (blue) can be seen throughout the system. Wilson et al. (2000) used OVRO to map CO(1-0) emission, a tracer of the bulk molecular gas distribution, with a resolution of 3.15″ x 4.91″ (Figures 1 and 2). Molecular emission is detected throughout the system and is particularly bright in the "interaction region" between the two nuclei, where it appears concentrated in five supergiant molecular complexes (see Figure 2).
ALMA Data Overview
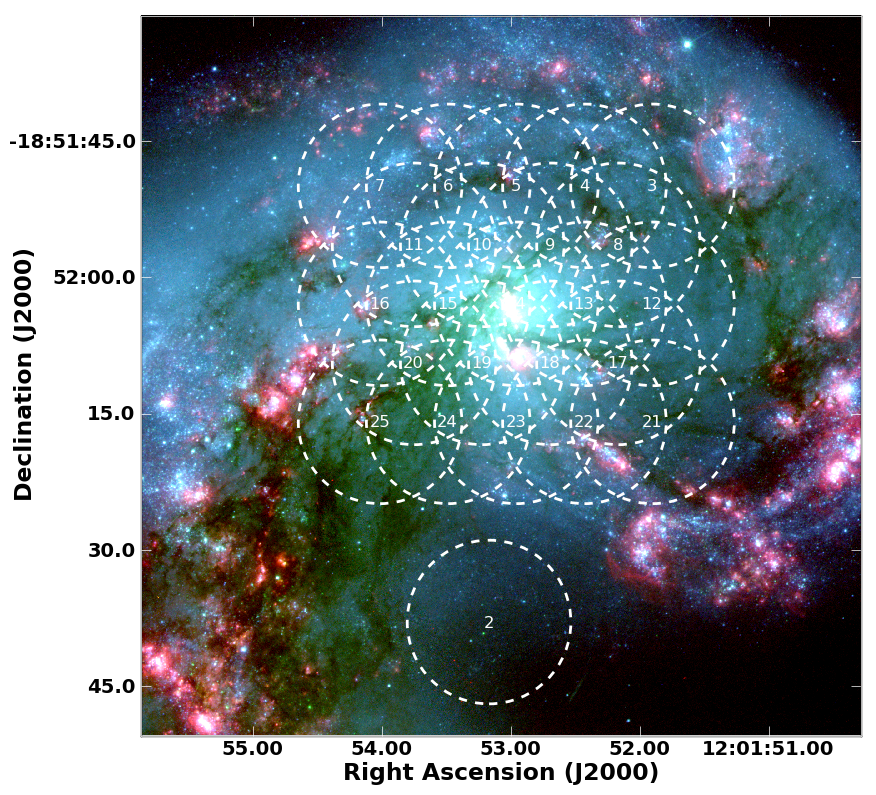
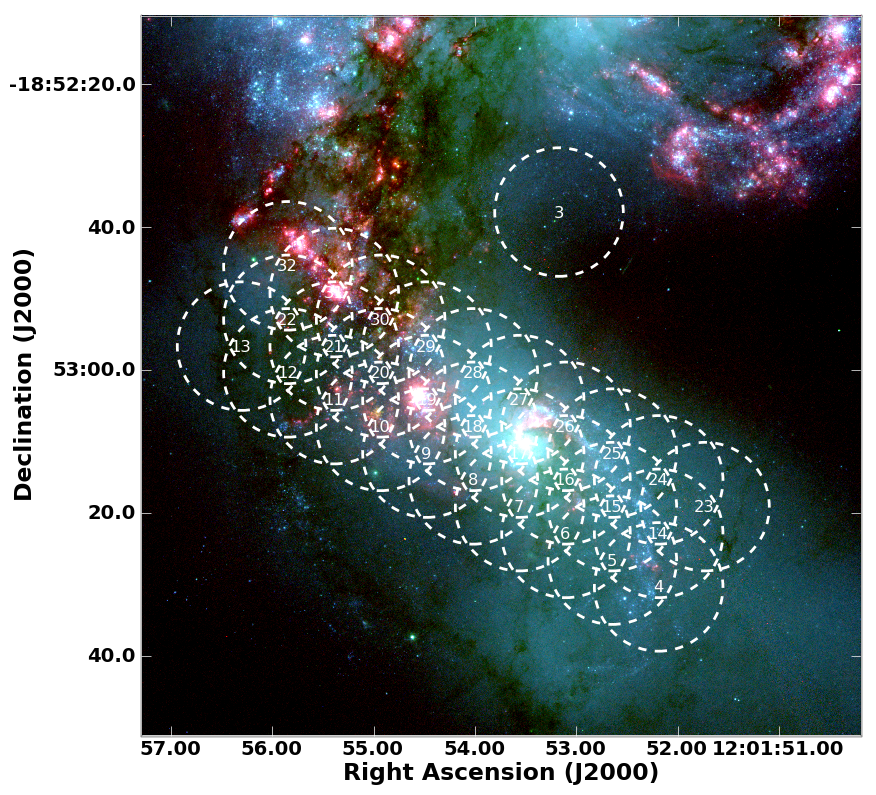
This CASA Guide steps through the reduction and imaging of ALMA Science Verification data targeting the CO 3-2 line in the Antennae galaxy. These data were obtained using the ALMA Band 7 receiver and observed in 10 separate blocks, each typically ~1 hour long, during May and June 2011. Each block observed one of two mosaic patterns, which we will refer to as the "Northern" and "Southern" mosaics. Figures 3 and 4 show the coverage of these two mosaics on an optical image of the Antennae. Within an individual observing block, the observations progress through individual pointings of the mosaic in rapid succession. One field was offset from the main body of the galaxy in each mosaic for calibration purposes.
The observations are broken down into ten individual data sets, as follows:
Northern mosaic (covering the nucleus of NGC 4038):
- uid://A002/X1ff7b0/Xb
- uid://A002/X207fe4/X3a
- uid://A002/X207fe4/X3b9
- uid://A002/X2181fb/X49
Southern mosaic (covering the nucleus of NGC 4039 and part of the interaction region):
- uid://A002/X1ff7b0/X1c8
- uid://A002/X207fe4/X1f7
- uid://A002/X207fe4/X4d7
- uid://A002/X215db8/X1d5
- uid://A002/X215db8/X392
- uid://A002/X215db8/X18
The observations used two basebands, each associated with one spectral window (see the ALMA Technical Handbook for a discussion of the distinction between basebands and spectral windows). The baseband in the lower sideband (LSB) is centered on the CO (3-2) transition, and the baseband in the upper sideband (USB) is used to measure continuum emission. This guide will focus on the reduction of the LSB CO (3-2) data. Each sideband was observed in both a high spectral resolution "Frequency Domain Mode" (FDM) and a lower spectral resolution "Time Domain Mode" (TDM). We will focus on reducing the FDM data, which have an effective total bandwidth of 1.875 GHz (1634 km/s) divided over 3840 channels. The channel width in FDM mode is 488.28 kHz (0.426 km/s); because the data are automatically Hanning smoothed, the actual spectral resolution is twice this. The TDM mode data were observed and used mainly for calibration purposes; we will not directly analyze them in this CASA Guide, though we will use calibration products (system temperature measurements) derived from these data.
When these observations were taken, the ALMA antennas were in a configuration that is intermediate between the Cycle 0 "Extended" and "Compact" configurations. We expect this configuration to yield an angular resolution of about 1 arcsecond near 345 GHz.
Using the data for publication: The following statement should be included in the acknowledgment of papers using the datasets listed above: “The Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA), an international astronomy facility, is a partnership of Europe, North America and East Asia in cooperation with the Republic of Chile. This paper makes use of the following ALMA Science Verification data: ADS/JAO.ALMA#2011.0.00003.SV”
We thank the following people for suggesting NGC4038/9 for ALMA Science Verification: Francois Boulanger, Nicole Nesvadba, Cinthya Herrera. We particularly thank Christine Wilson and Junko Ueda for providing both the suggestions and the OVRO (CO(1-0): Wilson et al. 2000) and SMA (CO(3-2): Ueda et al., submitted) data for verification purposes.
Obtaining the Data
To download the data, click on the region closest to your location:
Here you will find three gzipped tar files which, after unpacking, will create three directories:
- Antennae_Band7_UnCalibratedMSandTablesForReduction - Here we provide you with "starter" datasets, where we have taken the raw data in ALMA Science Data Model (ASDM) format and converted them to CASA Measurement Sets (MS). We did this using the importasdm task in CASA. Along with the raw data, we provide tables that are needed to calibrate the data, but that cannot currently be generated inside of CASA (for Early Science, these tables will either be pre-applied or supplied with the data).
- Antennae_Band7_CalibratedData - The fully-calibrated u-v data, ready for imaging.
- Antennae_Band7_ReferenceImages - The final continuum and spectral line images.
To see which files you will need, read on below. The downloads to your local computer will take some time, so you may wish to begin them now.
NOTE: CASA 3.3 or later is required to follow this guide. For more information on obtaining the latest version of CASA, see http://casa.nrao.edu.
Antennae Band 7 Data Reduction Tutorial
This tutorial has been split into two parts - calibration and imaging:
1) Antennae Band7 - Calibration : This section of the tutorial steps you through inspection and calibration of the basic visibility (u-v) data. To complete this part, you will need the data in the first directory: Antennae_Band7_UnCalibratedMSandTablesForReduction.
2) Antennae Band7 - Imaging : This part of the tutorial focuses on constructing images from the calibrated visibility data. If you wish to skip calibration and proceed directly to this part of the tutorial, you will need the fully-calibrated visibility data in the Antennae_Band7_CalibratedData directory.
We also provide the final continuum and spectral line images in the Antennae_Band7_ReferenceImages directory.
For a similar tutorial on the reduction of ALMA Band 7 data on TW Hydra, and Band 3 on NGC 3256, see the casaguides TWHydraBand7 and NGC3256Band3.
How to Use A CASA Guide
For tips on using CASA and ways CASA can be run, see EVLA_Spectral_Line_Calibration_IRC+10216#How_to_Use_This_casaguide page.
To learn how to extract executable Python scripts from the tutorial, see Extracting_scripts_from_these_tutorials.
Within the guides:
# In CASA
Regions of this color are CASA commands (or definitions) that need to be cut and
pasted in sequence. Wait until one command is finished before pasting another.
Tabs matter in python, make sure that commands that span more than one line and
"for" loops keep their spacing. Sometimes (especially "for" loops) you may need to
explicitly hit enter twice to get the command going.
Information in this color shows excerpts from the CASA Logger output
This color shows you background information about the data or other types of reference material
Last checked on CASA Version 3.3.0.