VLA CASA Bandpass Slope-CASA4.5.2: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (99 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
== Overview == | == Overview == | ||
For the standard VLA flux calibrators, CASA includes | For the standard VLA flux density calibrators 3C138, 3C147, 3C286 and 3C48, CASA includes spatial and spectral models that are applied during calibration. The models account for the source characteristics, resulting in calibration solutions that represent the instrumental and atmospheric corrections. These VLA standard calibrators, however, exhibit a negative spectral index and are relatively weak at high frequencies. | ||
Although the standard VLA flux density calibrators are usually still bright enough for absolute flux density calibration, a good bandpass determination—which is very important for spectral line observations—requires large signal-to-noise ratios derived from either a long integration time or a very strong source (see the [https://science.nrao.edu/facilities/vla/docs/manuals/obsguide/modes/line#section-8 Spectral Line Guide for Observing]). Observations of non-standard, but strong, bandpass calibrators are therefore common at high frequencies. Unfortunately, such sources are likely variable and no ''a priori'' flux density model is available. In particular, these sources exhibit an unknown and maybe variable spectral slope, which, if not accounted for, will create an error in the bandpass calibration. This tutorial describes how to model a spectral slope and how to correct the bandpass solution for this effect. | |||
Data | Data used in this guide are taken in wide 3-bit mode for the protostar G192.16-3.84 in Ka-band with basebands centered at 29 and 36.5 GHz. Each baseband has over 4 GHz of bandwidth comprising thirty-two 128-MHz spectral windows. | ||
If you are new to CASA, or with VLA data reduction in CASA, it is '''strongly''' recommended that you start with the [[Getting Started in CASA]] guide, the [https://casaguides.nrao.edu/index.php?title=VLA_high_frequency_Spectral_Line_tutorial_-_IRC%2B10216 IRC+10216 spectral line tutorial], or the [[VLA Continuum Tutorial 3C391]] before proceeding with this tutorial. | |||
== Obtaining the Data == | == Obtaining the Data == | ||
As this tutorial concerns bandpass | As this tutorial concerns bandpass calibration, all sources other than the flux density and bandpass calibrator scans were removed from the measurement set (MS). All pre-calibration steps including flagging, antenna position offsets, requantizer gains, opacity corrections, and gain-elevation curves were applied. The original data (<tt>TVER0004.sb14459364.eb14492359.56295.26287841435</tt>) can be obtained through the [https://archive.nrao.edu NRAO archive] and has a raw size of 57.04 GB. | ||
The trimmed measurement set can be downloaded directly from [http://casa.nrao.edu/Data/EVLA/G192/G192-BP.ms.tar.gz http://casa.nrao.edu/Data/EVLA/G192/G192-BP.ms.tar.gz] (dataset size: 3.4 GB) | The trimmed measurement set can be downloaded directly from [http://casa.nrao.edu/Data/EVLA/G192/G192-BP.ms.tar.gz http://casa.nrao.edu/Data/EVLA/G192/G192-BP.ms.tar.gz] (dataset size: 3.4 GB) | ||
| Line 29: | Line 27: | ||
== Starting CASA == | == Starting CASA == | ||
To start CASA, type: | |||
<source lang="bash"> | <source lang="bash"> | ||
| Line 35: | Line 33: | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
This will run a script | This will run a script initializing CASA and setting paths appropriately. The script will also create two files called ''ipython-<unique-stamp>.log'' (which contains a record of all the text you enter at the CASA prompt) as well as ''casapy-<unique-stamp>.log'' (which will contain all the messages that are printed to the CASA logger window). It is recommended that you keep your log files intact—you may need them to remind you of the last step you completed in your data reduction. (It is also a good idea to include your log files when submitting a help desk ticket). | ||
Once CASA has started, a logger window will appear. | Once CASA has started, a logger window will appear. Note that you can rescale this window or change the font size (under the '''View''' menu option) as desired. | ||
== Examining the Measurement Set (MS) == | == Examining the Measurement Set (MS) == | ||
| Line 47: | Line 45: | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
This will write the output to a file called <tt>G192_listobs.txt</tt>, which we can print to the terminal using | This will write the output to a file called <tt>G192_listobs.txt</tt>, which we can print to the terminal using various Unix/Linux commands such as <tt>cat</tt>, <tt>less</tt>, or <tt>more</tt>: | ||
<source lang="python"> | <source lang="python"> | ||
| Line 78: | Line 76: | ||
2 EVLA_KA#A1C1#4 128 TOPO 34732.000 1000.000 128000.0 34795.5000 10 RR LL | 2 EVLA_KA#A1C1#4 128 TOPO 34732.000 1000.000 128000.0 34795.5000 10 RR LL | ||
3 EVLA_KA#A1C1#5 128 TOPO 34860.000 1000.000 128000.0 34923.5000 10 RR LL | 3 EVLA_KA#A1C1#5 128 TOPO 34860.000 1000.000 128000.0 34923.5000 10 RR LL | ||
<snip> | |||
13 EVLA_KA#A1C1#15 128 TOPO 36140.000 1000.000 128000.0 36203.5000 10 RR LL | 13 EVLA_KA#A1C1#15 128 TOPO 36140.000 1000.000 128000.0 36203.5000 10 RR LL | ||
14 EVLA_KA#A1C1#16 128 TOPO 36268.000 1000.000 128000.0 36331.5000 10 RR LL | 14 EVLA_KA#A1C1#16 128 TOPO 36268.000 1000.000 128000.0 36331.5000 10 RR LL | ||
| Line 93: | Line 85: | ||
17 EVLA_KA#A2C2#19 128 TOPO 36604.000 1000.000 128000.0 36667.5000 11 RR LL | 17 EVLA_KA#A2C2#19 128 TOPO 36604.000 1000.000 128000.0 36667.5000 11 RR LL | ||
18 EVLA_KA#A2C2#20 128 TOPO 36732.000 1000.000 128000.0 36795.5000 11 RR LL | 18 EVLA_KA#A2C2#20 128 TOPO 36732.000 1000.000 128000.0 36795.5000 11 RR LL | ||
<snip> | |||
29 EVLA_KA#A2C2#31 128 TOPO 38140.000 1000.000 128000.0 38203.5000 11 RR LL | 29 EVLA_KA#A2C2#31 128 TOPO 38140.000 1000.000 128000.0 38203.5000 11 RR LL | ||
30 EVLA_KA#A2C2#32 128 TOPO 38268.000 1000.000 128000.0 38331.5000 11 RR LL | 30 EVLA_KA#A2C2#32 128 TOPO 38268.000 1000.000 128000.0 38331.5000 11 RR LL | ||
| Line 109: | Line 94: | ||
33 EVLA_KA#B1D1#35 128 TOPO 27104.000 1000.000 128000.0 27167.5000 13 RR LL | 33 EVLA_KA#B1D1#35 128 TOPO 27104.000 1000.000 128000.0 27167.5000 13 RR LL | ||
34 EVLA_KA#B1D1#36 128 TOPO 27232.000 1000.000 128000.0 27295.5000 13 RR LL | 34 EVLA_KA#B1D1#36 128 TOPO 27232.000 1000.000 128000.0 27295.5000 13 RR LL | ||
<snip> | |||
45 EVLA_KA#B1D1#47 128 TOPO 28640.000 1000.000 128000.0 28703.5000 13 RR LL | 45 EVLA_KA#B1D1#47 128 TOPO 28640.000 1000.000 128000.0 28703.5000 13 RR LL | ||
46 EVLA_KA#B1D1#48 128 TOPO 28768.000 1000.000 128000.0 28831.5000 13 RR LL | 46 EVLA_KA#B1D1#48 128 TOPO 28768.000 1000.000 128000.0 28831.5000 13 RR LL | ||
| Line 125: | Line 103: | ||
49 EVLA_KA#B2D2#51 128 TOPO 29104.000 1000.000 128000.0 29167.5000 14 RR LL | 49 EVLA_KA#B2D2#51 128 TOPO 29104.000 1000.000 128000.0 29167.5000 14 RR LL | ||
50 EVLA_KA#B2D2#52 128 TOPO 29232.000 1000.000 128000.0 29295.5000 14 RR LL | 50 EVLA_KA#B2D2#52 128 TOPO 29232.000 1000.000 128000.0 29295.5000 14 RR LL | ||
<snip> | |||
61 EVLA_KA#B2D2#63 128 TOPO 30640.000 1000.000 128000.0 30703.5000 14 RR LL | 61 EVLA_KA#B2D2#63 128 TOPO 30640.000 1000.000 128000.0 30703.5000 14 RR LL | ||
62 EVLA_KA#B2D2#64 128 TOPO 30768.000 1000.000 128000.0 30831.5000 14 RR LL | 62 EVLA_KA#B2D2#64 128 TOPO 30768.000 1000.000 128000.0 30831.5000 14 RR LL | ||
| Line 143: | Line 114: | ||
0 3C147 1 - - | 0 3C147 1 - - | ||
0 3C147 2 - - | 0 3C147 2 - - | ||
<snip> | |||
0 3C147 61 - - | 0 3C147 61 - - | ||
0 3C147 62 - - | 0 3C147 62 - - | ||
| Line 207: | Line 123: | ||
1 3c84-J0319+413 1 - - | 1 3c84-J0319+413 1 - - | ||
1 3c84-J0319+413 2 - - | 1 3c84-J0319+413 2 - - | ||
<snip> | |||
1 3c84-J0319+413 61 - - | 1 3c84-J0319+413 61 - - | ||
1 3c84-J0319+413 62 - - | 1 3c84-J0319+413 62 - - | ||
1 3c84-J0319+413 63 - - | 1 3c84-J0319+413 63 - - | ||
<snip> | |||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
This small MS contains only scans on the flux density calibrator 3C147 (field 0) and the bandpass calibrator 3C84 (field 1). Both fields have 64 spectral windows (spws); each spw is comprised of 128 channels, each channel being 1 MHz wide, for a total bandwidth of 128 MHz / spw. | |||
== Setting the Model of the Flux Density Calibrator == | |||
== Setting the | |||
To start, we insert the spectral (using the 'Perley-Butler 2013' standard) and spatial (3C147_A.im for Ka-band) models for the flux density calibrator 3C147 (field 0) with the {{setjy}} task: | |||
<source lang="python"> | <source lang="python"> | ||
# In CASA: model for the flux calibrator | # In CASA: model for the flux density calibrator | ||
setjy(vis='G192-BP.ms', field='0', scalebychan=True, \ | setjy(vis='G192-BP.ms', field='0', scalebychan=True, \ | ||
standard='Perley-Butler 2013', model='3C147_A.im') | standard='Perley-Butler 2013', model='3C147_A.im') | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
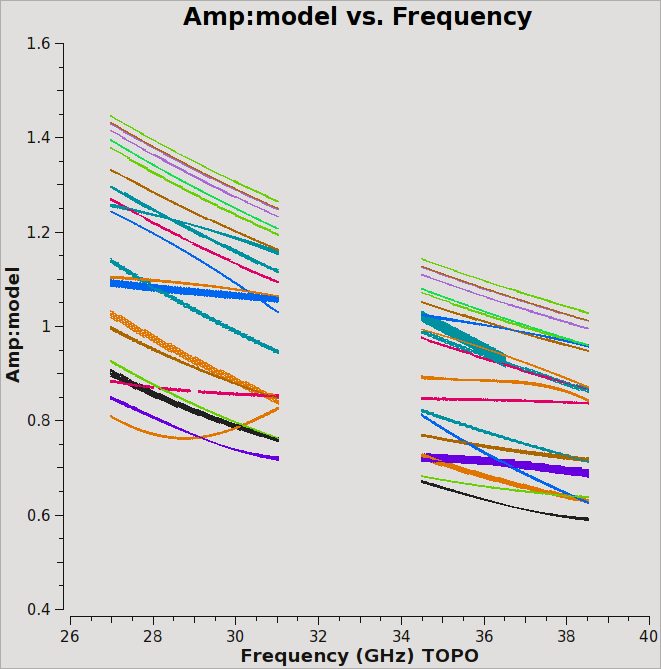
[[Image:ScreenshotPlotG192-setjy-4.5.png|200px|thumb|right|plotms of model amp vs freq for 3C147]] | [[Image:ScreenshotPlotG192-setjy-4.5.png|200px|thumb|right|Figure 1: plotms of model amp vs freq for 3C147]] | ||
* <tt>scalebychan=True</tt>: | * <tt>scalebychan=True</tt>: If ''scalebychan=False'' {{setjy}} would use a single value per spectral window. | ||
Inspecting the logger report shows that 3C147 has amplitudes ranging from ~1.0-1.47 Jy across all spws. | |||
We can plot the model data using {{plotms}}: | We can plot the model data using {{plotms}} (Figure 1): | ||
<source lang="python"> | <source lang="python"> | ||
# In CASA | # In CASA | ||
plotms(vis='G192-BP.ms', field='0', antenna=' | plotms(vis='G192-BP.ms', field='0', antenna='ea03', \ | ||
xaxis='freq', yaxis='amp', ydatacolumn='model') | xaxis='freq', yaxis='amp', ydatacolumn='model',coloraxis='ant2') | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
This plot shows baselines to antenna ea03. Since we provided both a spectral and a spatial model for this well resolved calibrator, each baseline has a somewhat different behavior. | |||
== Calibrating delays and initial bandpass solutions == | == Calibrating delays and initial bandpass solutions == | ||
As a first step, we use an antenna that is near the center of the array and has | As a first step, we need to specify a reference antenna for all phase calibrations. It is desirable to use an antenna that is near the center of the array and has the least amount of calibrator data flagged. The array can be mapped with {{plotants}}: | ||
<source lang="python"> | <source lang="python"> | ||
# In CASA: | # In CASA: plotting antenna locations | ||
plotants(vis='G192-BP.ms') | plotants(vis='G192-BP.ms') | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
Although the plot is a bit crowded (Figure 2), a zooming in (with the magnifying glass icon) shows that ea05 is located close to the center. It also has a comparably small number of flags and we will use this antenna as our reference. | |||
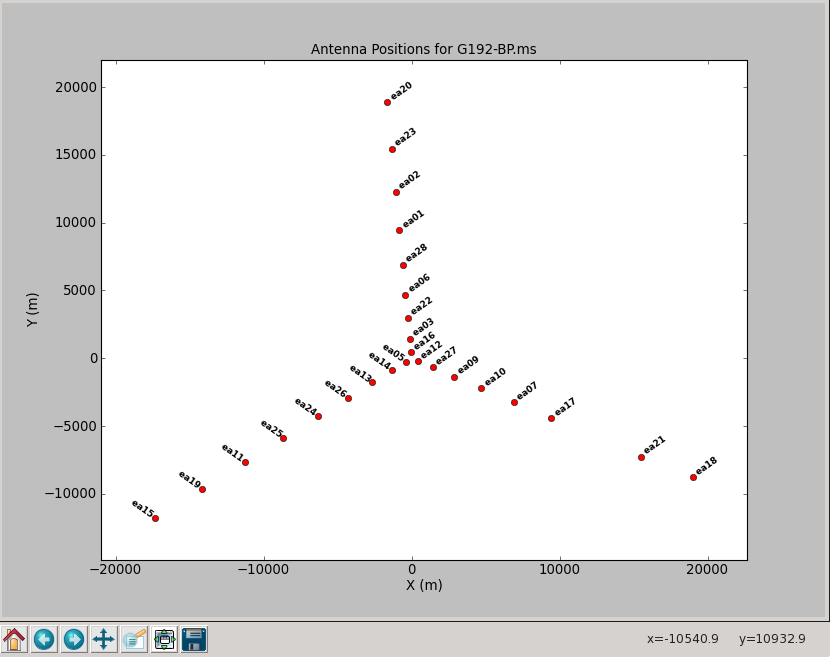
[[Image:plotG192_plotants.png|200px|thumb|right|plotants plotter | |||
[[Image:plotG192_plotants.png|200px|thumb|right|Figure 2: plotants plotter]] | |||
We start with a phase-only, time-dependent calibration solution for the bandpass calibrator. Solutions for each integration will remove most of the decorrelation of the signal. For best results, we will derive the phase variations from a narrow range of channels (60~68) near the centers of each spws: | |||
<source lang="python"> | <source lang="python"> | ||
# In CASA: phase only calibration | # In CASA: phase only calibration | ||
| Line 348: | Line 179: | ||
gaintype='G', refant='ea05', calmode='p', \ | gaintype='G', refant='ea05', calmode='p', \ | ||
solint='int', minsnr=3) | solint='int', minsnr=3) | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
| Line 355: | Line 185: | ||
* <tt>minsnr=3</tt> : Apply a minimum signal-to-noise cutoff. Solutions with less than this value will be flagged. | * <tt>minsnr=3</tt> : Apply a minimum signal-to-noise cutoff. Solutions with less than this value will be flagged. | ||
* <tt>gaintable</tt> is not set here as we have already applied pre-calibrations. | * <tt>gaintable</tt> is not set here as we have already applied pre-calibrations. | ||
Plot the phase solutions (using full phase range | |||
Plot the phase solutions (using full phase range -180 to 180 instead of autorange): | |||
<source lang="python"> | <source lang="python"> | ||
| Line 363: | Line 194: | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
Click on the Next button to navigate through the antennas. Click on the Quit button to exit the viewer. | |||
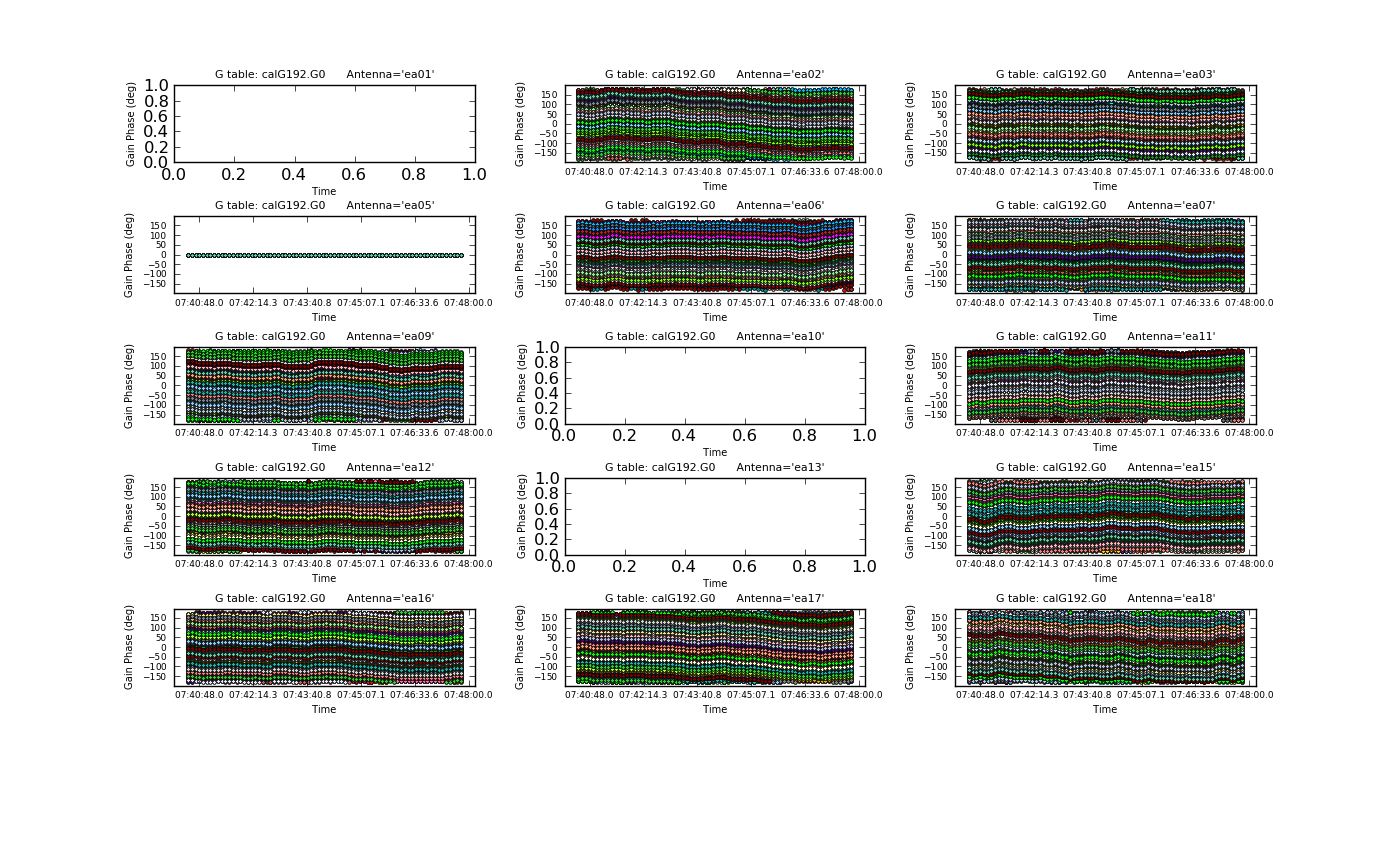
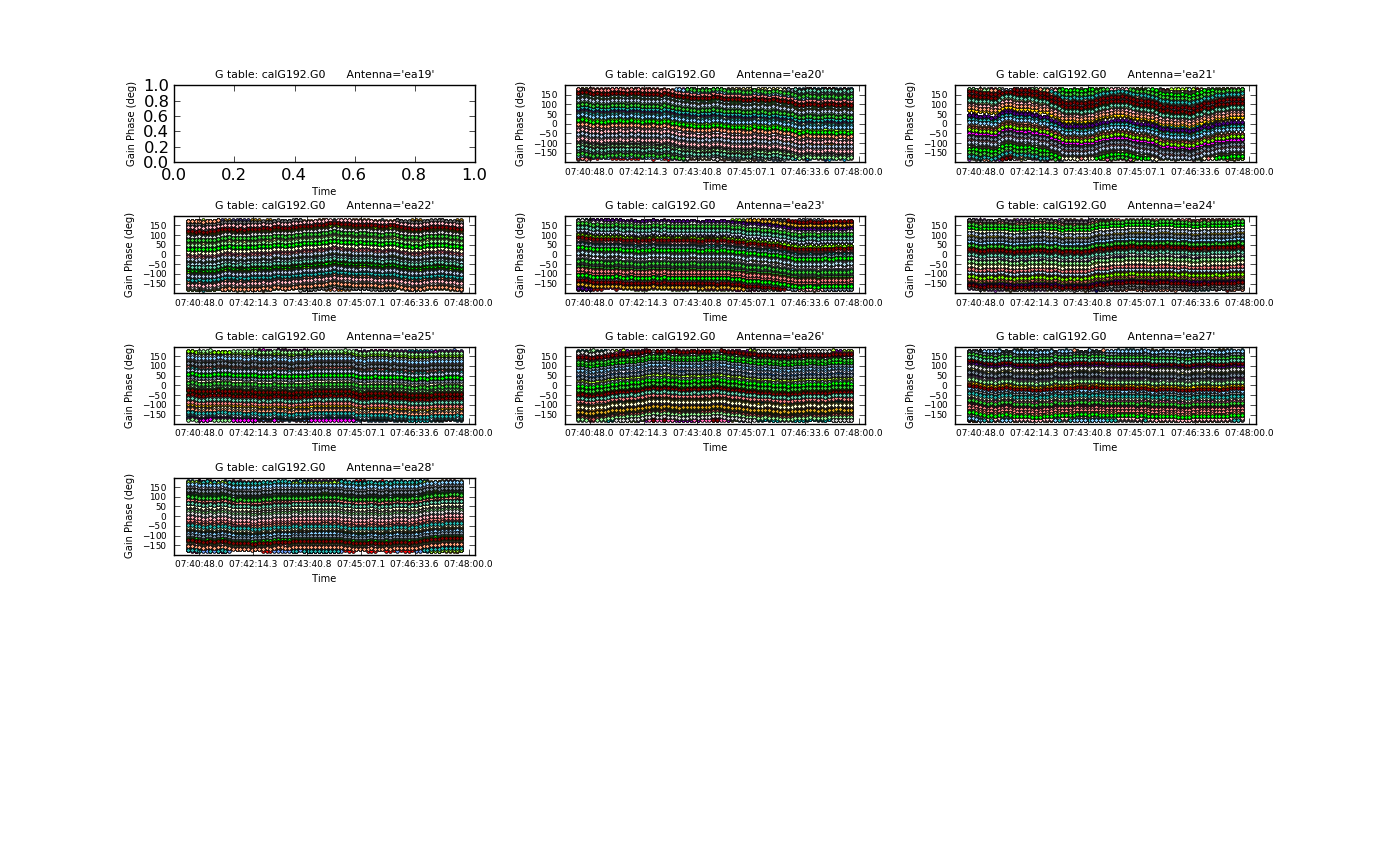
We will now produce multipanel plots of the phase solutions, writing the plots to output files as well as on the screen (Figures 3a & 3b). The output files generated are PNG files and can be viewed within CASA by executing an external viewer program, e.g., <tt>!xv plotG192_plotcal_G0p1.png</tt>; or by running an image viewing application such as xv, Preview, Gimp, Photoshop, etc., external to CASA at the OS level. <!-- (Note that the hardcopy only shows the first page): --> | |||
<source lang="python"> | <source lang="python"> | ||
# In CASA | # In CASA | ||
| Line 380: | Line 210: | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
We can now solve for the residual delays | {| | ||
| [[Image:plotG192_plotcal_G0p1_4.0.png|200px|thumb|left|Figure 3a: plotcal G0 phase ant 0~15]] | |||
| [[Image:plotG192_plotcal_G0p2_4.0.png|200px|thumb|center|Figure 3b: plotcal G0 phase ant 16~26]] | |||
|} | |||
<!-- | |||
NOTE: When you are done plotting and want to use the calibration table in another task (e.g., for subsequent calibration or viewing with plotms), use the Quit button on the GUI to dismiss the plotter and free-up the lock on the calibration table. You should see a message in your terminal window saying "Resetting plotcal" which means you are good to go! | |||
--> | |||
We can now solve for the residual delays using the parameter ''gaintype='K' ''option in {{gaincal}}. Note that this currently does not do a global fringe-fitting solution for delays, but instead does a baseline-based delay solution per spw for all baselines to the reference antenna, treating these as antenna-based delays. In most cases, with high enough S/N to get baseline-based delay solutions, this will suffice. We avoid the edge channels of each spectral window by selecting channels 5~122: | |||
<source lang="python"> | <source lang="python"> | ||
# In CASA: residual delays | # In CASA: residual delays | ||
| Line 389: | Line 229: | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
Note that we have also pre-applied our initial phase table | Note that we have also pre-applied our initial phase table <tt>calG192.G0</tt>. | ||
Alternatively, you can also derive a delay across all spws of a baseband. If this is desired, use parameter ''combine='spw''' in {{gaincal}} and run the task for each baseband separately. The solutions from the second and following runs can be appended to the same calibration table via parameter ''append=T''. | |||
[[Image:plotG192_plotcal_delays.png|200px|thumb|right|Figure 4: plotcal K0 delay vs. antenna]] | |||
Now plot the delays, in nanoseconds, as a function of antenna index (you will get one for each spw and polarization): | |||
<source lang="python"> | <source lang="python"> | ||
# In CASA | # In CASA | ||
| Line 395: | Line 242: | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
The delays range from around -5 to 4 nanoseconds. | The delays range from around -5 to 4 nanoseconds (Figure 4). | ||
Now solve for the antenna bandpasses using the previously generated tables <tt>calG192.G0</tt> and <tt>calG192.K0</tt>: | |||
<source lang="python"> | <source lang="python"> | ||
# In CASA: antenna bandpasses | # In CASA: antenna bandpasses | ||
| Line 405: | Line 253: | ||
bandtype='B', solint='inf') | bandtype='B', solint='inf') | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
'''WARNING''': You must set <tt>solnorm=False</tt> here or later on you will find some offsets | '''WARNING''': You must set <tt>solnorm=False</tt> here or later on you will find some offsets | ||
among spws due to the way the amplitude scaling adjusts weights internally during solving. | among spws due to the way the amplitude scaling adjusts weights internally during solving. | ||
You will see in the terminal some reports of solutions failing due to "Insufficient unflagged antennas" | You will see in the terminal window some reports of solutions failing due to "Insufficient unflagged antennas"—note that these are for bad channels that have been pre-flagged. | ||
Plot the resulting bandpasses in amplitude and phase. Note that the first panel with ea01 is empty as it is completely flagged. Proceed to ea06 to see the plots as shown in Figures 5a, 5b, 6a, and 6b: | |||
<source lang="python"> | <source lang="python"> | ||
# In CASA | # In CASA | ||
| Line 431: | Line 279: | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
{| | |||
| [[Image:plotG192_plotcal_B0a1_4.0.png|200px|thumb|left|Figure 5a: plotcal B0 bandpass amp ant ea06 spw 0-31]] | |||
| [[Image:plotG192_plotcal_B0a2_4.0.png|200px|thumb|center|Figure 5b: plotcal B0 bandpass amp ant ea06 spw 32-63]] | |||
| [[Image:plotG192_plotcal_B0p1_4.0.png|200px|thumb|center|Figure 6a: plotcal B0 bandpass phase ant ea06 spw 0-31]] | |||
| [[Image:plotG192_plotcal_B0p2_4.0.png|200px|thumb|right|Figure 6b: plotcal B0 bandpass phase ant ea06 spw 32-63]] | |||
|} | |||
== Bootstrapping the bandpass calibrator spectrum == | == Bootstrapping the bandpass calibrator spectrum == | ||
Since there is no | Since there is no ''a priori'' spectral information for our chosen bandpass calibrator of 3C84, we need to bootstrap to find its spectral index, then recalibrate with this information in order to avoid folding the intrinsic spectral shape of 3C84 into our calibration. | ||
First, we again do a phase-only calibration solution, this time for both the bandpass and the flux density calibrator. This will correct for decorrelation of the signals. We again use the channel range 60~68 and apply the bandpass and delay calibration tables: | |||
<source lang="python"> | |||
# In CASA: flux and bandpass calibrators gain | |||
gaincal(vis='G192-BP.ms', caltable='calG192.G1p', field='0,1', \ | |||
gaintable=['calG192.K0', 'calG192.B0'], \ | |||
gaintype='G', refant='ea05', calmode='p', solint='int', minsnr=3) | |||
</source> | |||
Now we are ready to solve for both phase and gain for each scan: | |||
<source lang="python"> | <source lang="python"> | ||
# In CASA: flux and bandpass calibrators gain | # In CASA: flux and bandpass calibrators gain | ||
gaincal(vis='G192-BP.ms', caltable='calG192.G1', field='0,1', \ | gaincal(vis='G192-BP.ms', caltable='calG192.G1', field='0,1', \ | ||
gaintable=['calG192.K0', 'calG192.B0'], \ | gaintable=['calG192.K0', 'calG192.B0','calG192.G1p'], \ | ||
gaintype='G', refant='ea05', calmode='ap', solint=' | gaintype='G', refant='ea05', calmode='ap', solint='inf', minsnr=3) | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
<!-- | |||
Let's have a look at the phase and amplitude solutions, iterating over antenna. We will look at the flux density calibrator (3C147) and bandpass calibrator (3C84) individually since they're widely separated in time: | |||
<source lang="python"> | <source lang="python"> | ||
# In CASA | # In CASA | ||
| Line 465: | Line 329: | ||
The solutions all look reasonable and relatively constant with time. | The solutions all look reasonable and relatively constant with time. | ||
--> | |||
With gain solutions for the flux density and bandpass calibrators, we can now use {{fluxscale}} to scale the gain amplitudes of the bandpass calibrator using those of the flux density calibrator: | |||
<source lang="python"> | <source lang="python"> | ||
# In CASA: bandpass calibrator gain amplitudes scaling | # In CASA: bandpass calibrator gain amplitudes scaling | ||
| Line 473: | Line 340: | ||
transfer='1', listfile='3C84.fluxinfo', fitorder=1) | transfer='1', listfile='3C84.fluxinfo', fitorder=1) | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
* <tt>flux1 = fluxscale(...)</tt>: | * <tt>flux1 = fluxscale(...)</tt>: we allow {{fluxscale}} to use the variable <tt>flux1</tt> for the Python dictionary that is returned, which has information about the flux scaling. You can inspect the dictionary flux1 by typing "print flux1" at the CASA command line. | ||
* <tt>fluxtable='calG192.F1'</tt>: this is the output scaled gain table. | * <tt>fluxtable='calG192.F1'</tt>: this is the output scaled gain table. Since we are only using this to find the spectral index of 3C84, we won't be using this table. | ||
* <tt>listfile='3C84.fluxinfo'</tt>: an output file that contains the derived flux values and fit information. | * <tt>listfile='3C84.fluxinfo'</tt>: an output file that contains the derived flux values and fit information. | ||
* <tt>fitorder=1</tt>: only find a spectral index, ignoring curvature in the spectrum. | * <tt>fitorder=1</tt>: only find a spectral index, ignoring curvature in the spectrum. | ||
* <tt>reference='0'</tt>: the reference field ''from'' which the flux scaling is transferred (here: the flux density calibrator 3C147, field 0) | |||
* <tt>transfer='1'</tt>: the target field ''to'' which the flux scaling is transferred (here: the bandpass calibrator 3C84, field 1) | |||
The last line in the file (and displayed in the logger) shows: | The last line in the file (and displayed in the logger) shows: | ||
<pre style="background-color: #fffacd;"> | <pre style="background-color: #fffacd;"> | ||
Fitted spectrum for 3c84-J0319+413 with fitorder=1: Flux density = 29. | Fitted spectrum for 3c84-J0319+413 with fitorder=1: Flux density = 29.0282 +/- 0.0308648 (freq=32.5128 GHz) spidx=-0.538758 +/- 0.00882913 | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
[[Image:PlotG192-3C84-fluxspec-4.5.png|200px|thumb|right|3C84 flux values returned by fluxscale | [[Image:PlotG192-3C84-fluxspec-4.5.png|200px|thumb|right|Figure 7: 3C84 flux values returned by fluxscale]] | ||
Using the information in the returned <tt> | Using the information in the returned <tt>flux1</tt> dictionary, we can plot the derived spectrum (Figure 7): | ||
<source lang="python"> | <source lang="python"> | ||
# In CASA | # In CASA | ||
| Line 495: | Line 364: | ||
thisspw = str(i) | thisspw = str(i) | ||
spw_str.append(thisspw) | spw_str.append(thisspw) | ||
</source> | |||
(Note that in order to close indented python loops, conditions etc. you will have to press ''Enter'' again to execute the indented commands and to return to the CASA prompt.) | |||
<source lang="python"> | |||
# In CASA | |||
bootstrapped_fluxes = [] | bootstrapped_fluxes = [] | ||
for j in spw_str: | for j in spw_str: | ||
| Line 503: | Line 377: | ||
else: | else: | ||
bootstrapped_fluxes.append(thisflux) | bootstrapped_fluxes.append(thisflux) | ||
</source> | |||
<source lang="python"> | |||
# In CASA - this section creates the plot seen in Figure 7 | |||
pl.clf() | pl.clf() | ||
pl.plot(freq, bootstrapped_fluxes, 'bo') | pl.plot(freq, bootstrapped_fluxes, 'bo') | ||
| Line 512: | Line 390: | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
We can use the model from {{fluxscale}} to fill the MODEL column with 3C84's spectral information using {{setjy}}. With ''standard='fluxscale''', we can directly use the <tt>flux1</tt> Python dictionary as input via ''fluxdict'': | |||
[[Image:ScreenshotPlotG192-setjy-bp-4.5.png|200px|thumb|right|Figure 8: plotms of model amp vs freq for 3C84]] | |||
<source lang="python"> | <source lang="python"> | ||
# In CASA: spectral information | # In CASA: spectral information | ||
| Line 520: | Line 400: | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
Check with plotms that the data have been appropriately filled (Figure 8): | |||
<source lang="python"> | <source lang="python"> | ||
# In CASA | # In CASA | ||
| Line 529: | Line 408: | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
Next, we redo the previous calibration using this new model information. Although the commands are the same as issued earlier, keep in mind that the model values for the bandpass calibrator have changed and, therefore, the results of these calibration calculations will differ: | |||
<source lang="python"> | <source lang="python"> | ||
# In CASA: phase only recalibration | # In CASA: phase only recalibration | ||
| Line 553: | Line 428: | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
Finally, we inspect these solutions (Figures 9a, 9b, 10a, and 10b): | |||
<source lang="python"> | <source lang="python"> | ||
# In CASA | # In CASA - Figure 9a | ||
plotcal(caltable='calG192.B0.b', xaxis='freq', yaxis='amp', \ | plotcal(caltable='calG192.B0.b', xaxis='freq', yaxis='amp', \ | ||
spw='0~31', iteration='antenna') | spw='0~31', iteration='antenna') | ||
# | # Figure 9b | ||
plotcal(caltable='calG192.B0.b', xaxis='freq', yaxis='amp', \ | plotcal(caltable='calG192.B0.b', xaxis='freq', yaxis='amp', \ | ||
spw='32~63', iteration='antenna') | spw='32~63', iteration='antenna') | ||
# | # Figure 10a | ||
plotcal(caltable='calG192.B0.b', xaxis='freq', yaxis='phase', \ | plotcal(caltable='calG192.B0.b', xaxis='freq', yaxis='phase', \ | ||
iteration='antenna', spw='0~31', \ | iteration='antenna', spw='0~31', \ | ||
plotrange=[-1,-1,-180,180]) | plotrange=[-1,-1,-180,180]) | ||
# | # Figure 10b | ||
plotcal(caltable='calG192.B0.b', xaxis='freq', yaxis='phase', \ | plotcal(caltable='calG192.B0.b', xaxis='freq', yaxis='phase', \ | ||
iteration='antenna', spw='32~63', \ | iteration='antenna', spw='32~63', \ | ||
| Line 571: | Line 447: | ||
</source> | </source> | ||
They look virtually unchanged from the previous solutions | {| | ||
| [[Image:plotG192_plotcal_B0a1.b_4.1.png|200px|thumb|left|Figure 9a: plotcal B0 bootstrapped bandpass amp ant ea06 spw 0-31]] | |||
| [[Image:plotG192_plotcal_B0a2.b_4.1.png|200px|thumb|center|Figure 9b: plotcal B0 bootstrapped bandpass amp ant ea06 spw 32-63]] | |||
| [[Image:plotG192_plotcal_B0p1.b_4.1.png|200px|thumb|center|Figure 10a: plotcal B0 bootstrapped bandpass phase ant ea06 spw 0-31]] | |||
| [[Image:plotG192_plotcal_B0p2.b_4.1.png|200px|thumb|right|Figure 10b: plotcal B0 bootstrapped bandpass phase ant ea06 spw 32-63]] | |||
|} | |||
They look virtually unchanged from the previous solutions with the exception that the amplitude scaling is corrected for the spectrum of 3C84. We have the final version of our delay and bandpass calibration tables, '''calG192.K0.b''' and '''calG192.B0.b''', which can be used for all subsequent calibration steps. | |||
{{Checked 4.5.2}} | {{Checked 4.5.2}} | ||
<!-- | |||
-- Original: Miriam Hartman (full G192 guide) | -- Original: Miriam Hartman (full G192 guide) <br /> | ||
-- Topical Guide: Juergen Ott 2016/04/14 | -- Modifications: Jose Salcido (4.5.2. 2016/04/14) <br /> | ||
-- Topical Guide: Juergen Ott (4.5.2, 2016/04/14) <br /> | |||
-- Edits to Guide: Tony Perreault (4.5.2, 2016/05/18) <br /> | |||
--> | |||
Latest revision as of 14:41, 14 June 2016
This CASA Guide is for CASA version 4.5.2
Overview
For the standard VLA flux density calibrators 3C138, 3C147, 3C286 and 3C48, CASA includes spatial and spectral models that are applied during calibration. The models account for the source characteristics, resulting in calibration solutions that represent the instrumental and atmospheric corrections. These VLA standard calibrators, however, exhibit a negative spectral index and are relatively weak at high frequencies.
Although the standard VLA flux density calibrators are usually still bright enough for absolute flux density calibration, a good bandpass determination—which is very important for spectral line observations—requires large signal-to-noise ratios derived from either a long integration time or a very strong source (see the Spectral Line Guide for Observing). Observations of non-standard, but strong, bandpass calibrators are therefore common at high frequencies. Unfortunately, such sources are likely variable and no a priori flux density model is available. In particular, these sources exhibit an unknown and maybe variable spectral slope, which, if not accounted for, will create an error in the bandpass calibration. This tutorial describes how to model a spectral slope and how to correct the bandpass solution for this effect.
Data used in this guide are taken in wide 3-bit mode for the protostar G192.16-3.84 in Ka-band with basebands centered at 29 and 36.5 GHz. Each baseband has over 4 GHz of bandwidth comprising thirty-two 128-MHz spectral windows.
If you are new to CASA, or with VLA data reduction in CASA, it is strongly recommended that you start with the Getting Started in CASA guide, the IRC+10216 spectral line tutorial, or the VLA Continuum Tutorial 3C391 before proceeding with this tutorial.
Obtaining the Data
As this tutorial concerns bandpass calibration, all sources other than the flux density and bandpass calibrator scans were removed from the measurement set (MS). All pre-calibration steps including flagging, antenna position offsets, requantizer gains, opacity corrections, and gain-elevation curves were applied. The original data (TVER0004.sb14459364.eb14492359.56295.26287841435) can be obtained through the NRAO archive and has a raw size of 57.04 GB.
The trimmed measurement set can be downloaded directly from http://casa.nrao.edu/Data/EVLA/G192/G192-BP.ms.tar.gz (dataset size: 3.4 GB)
Your first step will be to unzip and untar the file in a terminal (before you start CASA):
tar -xzvf G192-BP.ms.tar.gz
Starting CASA
To start CASA, type:
casa
This will run a script initializing CASA and setting paths appropriately. The script will also create two files called ipython-<unique-stamp>.log (which contains a record of all the text you enter at the CASA prompt) as well as casapy-<unique-stamp>.log (which will contain all the messages that are printed to the CASA logger window). It is recommended that you keep your log files intact—you may need them to remind you of the last step you completed in your data reduction. (It is also a good idea to include your log files when submitting a help desk ticket).
Once CASA has started, a logger window will appear. Note that you can rescale this window or change the font size (under the View menu option) as desired.
Examining the Measurement Set (MS)
We use listobs to summarize our MS:
# In CASA: listobs on the initial data set
listobs('G192-BP.ms', listfile='G192_listobs.txt')
This will write the output to a file called G192_listobs.txt, which we can print to the terminal using various Unix/Linux commands such as cat, less, or more:
# In CASA
cat G192_listobs.txt
================================================================================
MeasurementSet Name: /lustre/aoc/sciops/jott/casa/topicalguide/bandpass/new/G192-BP.ms MS Version 2
================================================================================
Observer: Dr. Debra Shepherd Project: uid://evla/pdb/7303457
Observation: EVLA
Data records: 1769355 Total elapsed time = 4563 seconds
Observed from 03-Jan-2013/06:31:48.0 to 03-Jan-2013/07:47:51.0 (UTC)
ObservationID = 0 ArrayID = 0
Date Timerange (UTC) Scan FldId FieldName nRows SpwIds Average Interval(s) ScanIntent
03-Jan-2013/06:31:48.0 - 06:36:42.0 6 0 3C147 704865 [0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57,58,59,60,61,62,63] [6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 5.94, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6] [CALIBRATE_FLUX#UNSPECIFIED,OBSERVE_TARGET#UNSPECIFIED]
07:40:27.0 - 07:47:51.0 64 1 3c84-J0319+413 1064490 [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30, 31, 32, 33, 34, 35, 36, 37, 38, 39, 40, 41, 42, 43, 44, 45, 46, 47, 48, 49, 50, 51, 52, 53, 54, 55, 56, 57, 58, 59, 60, 61, 62, 63] [6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6] [CALIBRATE_BANDPASS#UNSPECIFIED,OBSERVE_TARGET#UNSPECIFIED]
(nRows = Total number of rows per scan)
Fields: 2
ID Code Name RA Decl Epoch SrcId nRows
0 E 3C147 05:42:36.137916 +49.51.07.23356 J2000 0 704865
1 F 3c84-J0319+413 03:19:48.160102 +41.30.42.10305 J2000 1 1064490
Spectral Windows: (64 unique spectral windows and 1 unique polarization setups)
SpwID Name #Chans Frame Ch0(MHz) ChanWid(kHz) TotBW(kHz) CtrFreq(MHz) BBC Num Corrs
0 EVLA_KA#A1C1#2 128 TOPO 34476.000 1000.000 128000.0 34539.5000 10 RR LL
1 EVLA_KA#A1C1#3 128 TOPO 34604.000 1000.000 128000.0 34667.5000 10 RR LL
2 EVLA_KA#A1C1#4 128 TOPO 34732.000 1000.000 128000.0 34795.5000 10 RR LL
3 EVLA_KA#A1C1#5 128 TOPO 34860.000 1000.000 128000.0 34923.5000 10 RR LL
<snip>
13 EVLA_KA#A1C1#15 128 TOPO 36140.000 1000.000 128000.0 36203.5000 10 RR LL
14 EVLA_KA#A1C1#16 128 TOPO 36268.000 1000.000 128000.0 36331.5000 10 RR LL
15 EVLA_KA#A1C1#17 128 TOPO 36396.000 1000.000 128000.0 36459.5000 10 RR LL
16 EVLA_KA#A2C2#18 128 TOPO 36476.000 1000.000 128000.0 36539.5000 11 RR LL
17 EVLA_KA#A2C2#19 128 TOPO 36604.000 1000.000 128000.0 36667.5000 11 RR LL
18 EVLA_KA#A2C2#20 128 TOPO 36732.000 1000.000 128000.0 36795.5000 11 RR LL
<snip>
29 EVLA_KA#A2C2#31 128 TOPO 38140.000 1000.000 128000.0 38203.5000 11 RR LL
30 EVLA_KA#A2C2#32 128 TOPO 38268.000 1000.000 128000.0 38331.5000 11 RR LL
31 EVLA_KA#A2C2#33 128 TOPO 38396.000 1000.000 128000.0 38459.5000 11 RR LL
32 EVLA_KA#B1D1#34 128 TOPO 26976.000 1000.000 128000.0 27039.5000 13 RR LL
33 EVLA_KA#B1D1#35 128 TOPO 27104.000 1000.000 128000.0 27167.5000 13 RR LL
34 EVLA_KA#B1D1#36 128 TOPO 27232.000 1000.000 128000.0 27295.5000 13 RR LL
<snip>
45 EVLA_KA#B1D1#47 128 TOPO 28640.000 1000.000 128000.0 28703.5000 13 RR LL
46 EVLA_KA#B1D1#48 128 TOPO 28768.000 1000.000 128000.0 28831.5000 13 RR LL
47 EVLA_KA#B1D1#49 128 TOPO 28896.000 1000.000 128000.0 28959.5000 13 RR LL
48 EVLA_KA#B2D2#50 128 TOPO 28976.000 1000.000 128000.0 29039.5000 14 RR LL
49 EVLA_KA#B2D2#51 128 TOPO 29104.000 1000.000 128000.0 29167.5000 14 RR LL
50 EVLA_KA#B2D2#52 128 TOPO 29232.000 1000.000 128000.0 29295.5000 14 RR LL
<snip>
61 EVLA_KA#B2D2#63 128 TOPO 30640.000 1000.000 128000.0 30703.5000 14 RR LL
62 EVLA_KA#B2D2#64 128 TOPO 30768.000 1000.000 128000.0 30831.5000 14 RR LL
63 EVLA_KA#B2D2#65 128 TOPO 30896.000 1000.000 128000.0 30959.5000 14 RR LL
Sources: 128
ID Name SpwId RestFreq(MHz) SysVel(km/s)
0 3C147 0 - -
0 3C147 1 - -
0 3C147 2 - -
<snip>
0 3C147 61 - -
0 3C147 62 - -
0 3C147 63 - -
1 3c84-J0319+413 0 - -
1 3c84-J0319+413 1 - -
1 3c84-J0319+413 2 - -
<snip>
1 3c84-J0319+413 61 - -
1 3c84-J0319+413 62 - -
1 3c84-J0319+413 63 - -
<snip>
This small MS contains only scans on the flux density calibrator 3C147 (field 0) and the bandpass calibrator 3C84 (field 1). Both fields have 64 spectral windows (spws); each spw is comprised of 128 channels, each channel being 1 MHz wide, for a total bandwidth of 128 MHz / spw.
Setting the Model of the Flux Density Calibrator
To start, we insert the spectral (using the 'Perley-Butler 2013' standard) and spatial (3C147_A.im for Ka-band) models for the flux density calibrator 3C147 (field 0) with the setjy task:
# In CASA: model for the flux density calibrator
setjy(vis='G192-BP.ms', field='0', scalebychan=True, \
standard='Perley-Butler 2013', model='3C147_A.im')
- scalebychan=True: If scalebychan=False setjy would use a single value per spectral window.
Inspecting the logger report shows that 3C147 has amplitudes ranging from ~1.0-1.47 Jy across all spws.
We can plot the model data using plotms (Figure 1):
# In CASA
plotms(vis='G192-BP.ms', field='0', antenna='ea03', \
xaxis='freq', yaxis='amp', ydatacolumn='model',coloraxis='ant2')
This plot shows baselines to antenna ea03. Since we provided both a spectral and a spatial model for this well resolved calibrator, each baseline has a somewhat different behavior.
Calibrating delays and initial bandpass solutions
As a first step, we need to specify a reference antenna for all phase calibrations. It is desirable to use an antenna that is near the center of the array and has the least amount of calibrator data flagged. The array can be mapped with plotants:
# In CASA: plotting antenna locations
plotants(vis='G192-BP.ms')
Although the plot is a bit crowded (Figure 2), a zooming in (with the magnifying glass icon) shows that ea05 is located close to the center. It also has a comparably small number of flags and we will use this antenna as our reference.
We start with a phase-only, time-dependent calibration solution for the bandpass calibrator. Solutions for each integration will remove most of the decorrelation of the signal. For best results, we will derive the phase variations from a narrow range of channels (60~68) near the centers of each spws:
# In CASA: phase only calibration
gaincal(vis='G192-BP.ms', caltable='calG192.G0', \
field='1', spw='*:60~68', \
gaintype='G', refant='ea05', calmode='p', \
solint='int', minsnr=3)
- refant='ea05' : Use ea05 as the reference antenna
- solint='int' : Do a per-integration solve (every 6 seconds, since we've time-averaged the data).
- minsnr=3 : Apply a minimum signal-to-noise cutoff. Solutions with less than this value will be flagged.
- gaintable is not set here as we have already applied pre-calibrations.
Plot the phase solutions (using full phase range -180 to 180 instead of autorange):
# In CASA
plotcal(caltable='calG192.G0', xaxis='time', yaxis='phase', \
iteration='antenna', plotrange=[-1,-1,-180,180])
Click on the Next button to navigate through the antennas. Click on the Quit button to exit the viewer.
We will now produce multipanel plots of the phase solutions, writing the plots to output files as well as on the screen (Figures 3a & 3b). The output files generated are PNG files and can be viewed within CASA by executing an external viewer program, e.g., !xv plotG192_plotcal_G0p1.png; or by running an image viewing application such as xv, Preview, Gimp, Photoshop, etc., external to CASA at the OS level.
# In CASA
plotcal(caltable='calG192.G0', xaxis='time', yaxis='phase', \
antenna='0~10,12~15', subplot=531, iteration='antenna', \
plotrange=[-1,-1,-180,180], fontsize=8.0, \
markersize=3.0, figfile='plotG192_plotcal_G0p1.png')
plotcal(caltable='calG192.G0', xaxis='time', yaxis='phase', \
antenna='16~26', subplot=531, iteration='antenna', \
plotrange=[-1,-1,-180,180], fontsize=8.0, \
markersize=3.0, figfile='plotG192_plotcal_G0p2.png')
 |
 |
We can now solve for the residual delays using the parameter gaintype='K' option in gaincal. Note that this currently does not do a global fringe-fitting solution for delays, but instead does a baseline-based delay solution per spw for all baselines to the reference antenna, treating these as antenna-based delays. In most cases, with high enough S/N to get baseline-based delay solutions, this will suffice. We avoid the edge channels of each spectral window by selecting channels 5~122:
# In CASA: residual delays
gaincal(vis='G192-BP.ms', caltable='calG192.K0', \
field='1', spw='*:5~122', gaintype='K', \
gaintable=['calG192.G0'],
refant='ea05', solint='inf', minsnr=3)
Note that we have also pre-applied our initial phase table calG192.G0.
Alternatively, you can also derive a delay across all spws of a baseband. If this is desired, use parameter combine='spw' in gaincal and run the task for each baseband separately. The solutions from the second and following runs can be appended to the same calibration table via parameter append=T.
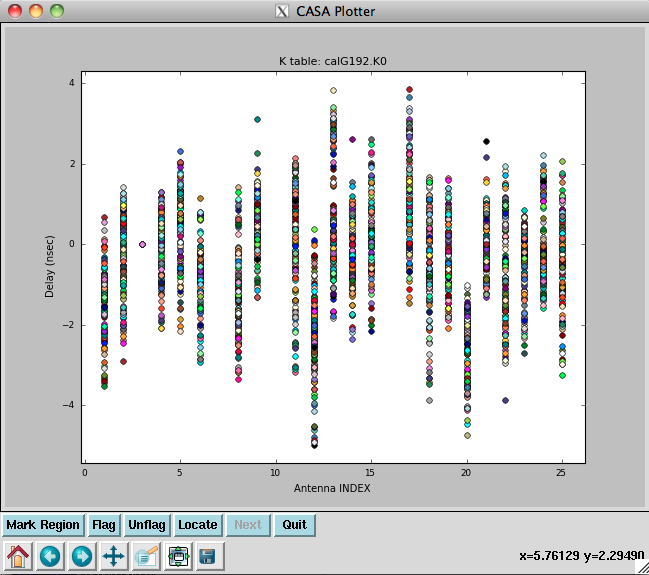
Now plot the delays, in nanoseconds, as a function of antenna index (you will get one for each spw and polarization):
# In CASA
plotcal(caltable='calG192.K0', xaxis='antenna', yaxis='delay')
The delays range from around -5 to 4 nanoseconds (Figure 4).
Now solve for the antenna bandpasses using the previously generated tables calG192.G0 and calG192.K0:
# In CASA: antenna bandpasses
bandpass(vis='G192-BP.ms', caltable='calG192.B0', \
gaintable=['calG192.G0', 'calG192.K0'], \
field='1', refant='ea05', solnorm=False, \
bandtype='B', solint='inf')
WARNING: You must set solnorm=False here or later on you will find some offsets among spws due to the way the amplitude scaling adjusts weights internally during solving.
You will see in the terminal window some reports of solutions failing due to "Insufficient unflagged antennas"—note that these are for bad channels that have been pre-flagged.
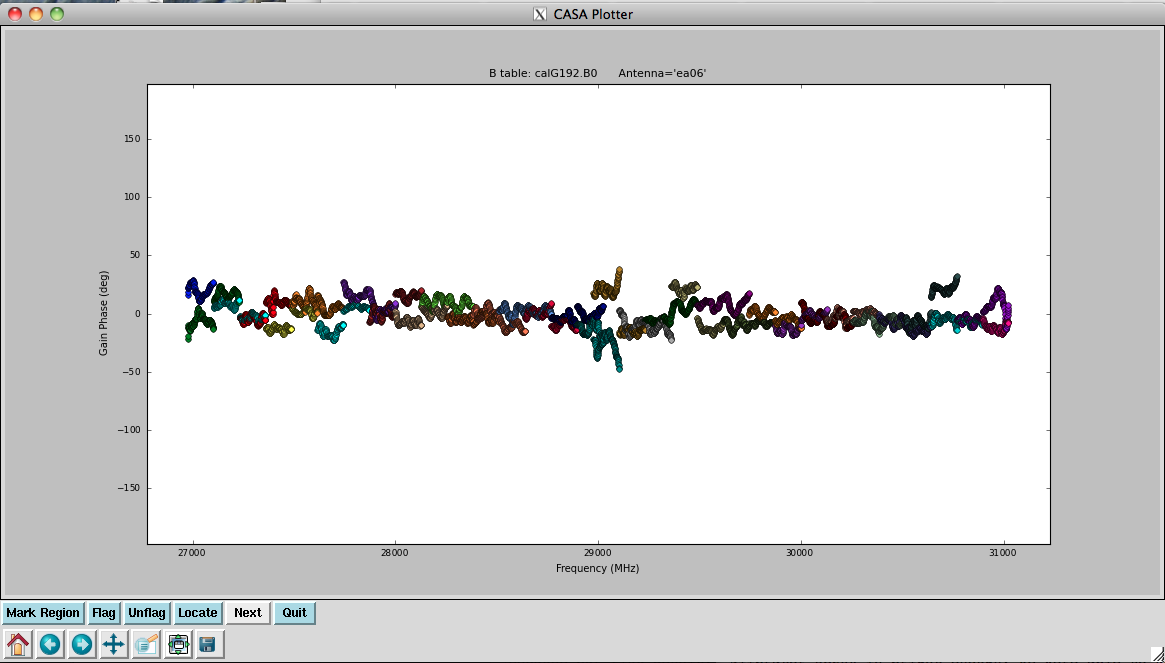
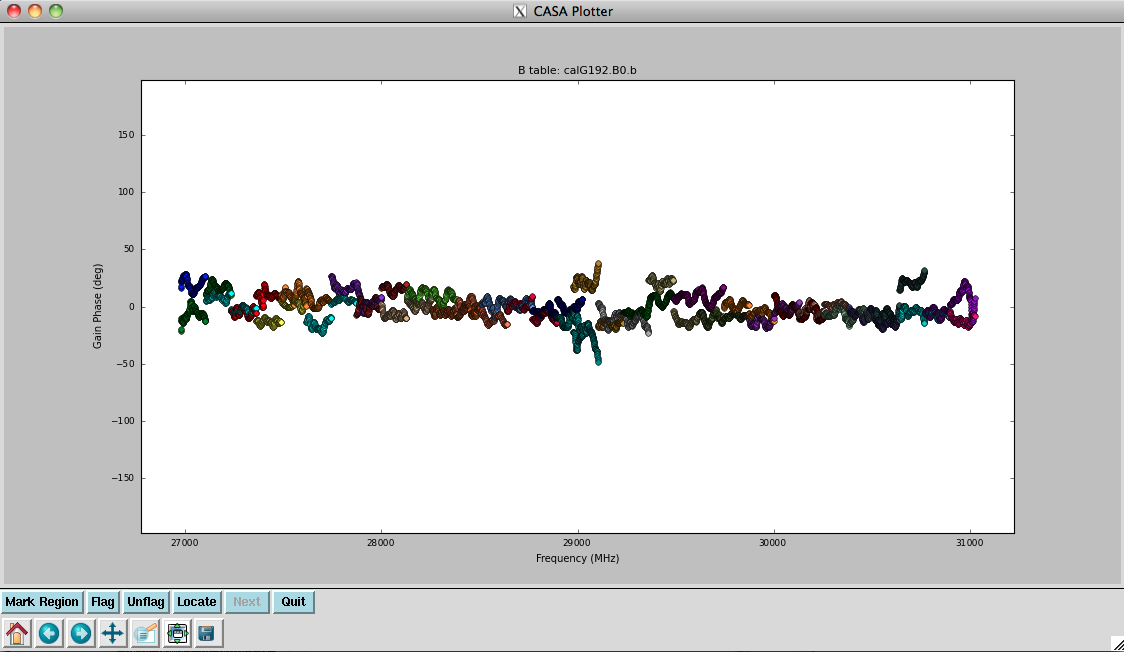
Plot the resulting bandpasses in amplitude and phase. Note that the first panel with ea01 is empty as it is completely flagged. Proceed to ea06 to see the plots as shown in Figures 5a, 5b, 6a, and 6b:
# In CASA
plotcal(caltable='calG192.B0', xaxis='freq', yaxis='amp', \
spw='0~31', iteration='antenna')
#
plotcal(caltable='calG192.B0', xaxis='freq', yaxis='amp', \
spw='32~63', iteration='antenna')
#
plotcal(caltable='calG192.B0', xaxis='freq', yaxis='phase', \
iteration='antenna', spw='0~31', \
plotrange=[-1,-1,-180,180])
#
plotcal(caltable='calG192.B0', xaxis='freq', yaxis='phase', \
iteration='antenna', spw='32~63', \
plotrange=[-1,-1,-180,180])
Bootstrapping the bandpass calibrator spectrum
Since there is no a priori spectral information for our chosen bandpass calibrator of 3C84, we need to bootstrap to find its spectral index, then recalibrate with this information in order to avoid folding the intrinsic spectral shape of 3C84 into our calibration.
First, we again do a phase-only calibration solution, this time for both the bandpass and the flux density calibrator. This will correct for decorrelation of the signals. We again use the channel range 60~68 and apply the bandpass and delay calibration tables:
# In CASA: flux and bandpass calibrators gain
gaincal(vis='G192-BP.ms', caltable='calG192.G1p', field='0,1', \
gaintable=['calG192.K0', 'calG192.B0'], \
gaintype='G', refant='ea05', calmode='p', solint='int', minsnr=3)
Now we are ready to solve for both phase and gain for each scan:
# In CASA: flux and bandpass calibrators gain
gaincal(vis='G192-BP.ms', caltable='calG192.G1', field='0,1', \
gaintable=['calG192.K0', 'calG192.B0','calG192.G1p'], \
gaintype='G', refant='ea05', calmode='ap', solint='inf', minsnr=3)
With gain solutions for the flux density and bandpass calibrators, we can now use fluxscale to scale the gain amplitudes of the bandpass calibrator using those of the flux density calibrator:
# In CASA: bandpass calibrator gain amplitudes scaling
flux1 = fluxscale(vis='G192-BP.ms', caltable='calG192.G1', \
fluxtable='calG192.F1', reference='0', \
transfer='1', listfile='3C84.fluxinfo', fitorder=1)
- flux1 = fluxscale(...): we allow fluxscale to use the variable flux1 for the Python dictionary that is returned, which has information about the flux scaling. You can inspect the dictionary flux1 by typing "print flux1" at the CASA command line.
- fluxtable='calG192.F1': this is the output scaled gain table. Since we are only using this to find the spectral index of 3C84, we won't be using this table.
- listfile='3C84.fluxinfo': an output file that contains the derived flux values and fit information.
- fitorder=1: only find a spectral index, ignoring curvature in the spectrum.
- reference='0': the reference field from which the flux scaling is transferred (here: the flux density calibrator 3C147, field 0)
- transfer='1': the target field to which the flux scaling is transferred (here: the bandpass calibrator 3C84, field 1)
The last line in the file (and displayed in the logger) shows:
Fitted spectrum for 3c84-J0319+413 with fitorder=1: Flux density = 29.0282 +/- 0.0308648 (freq=32.5128 GHz) spidx=-0.538758 +/- 0.00882913
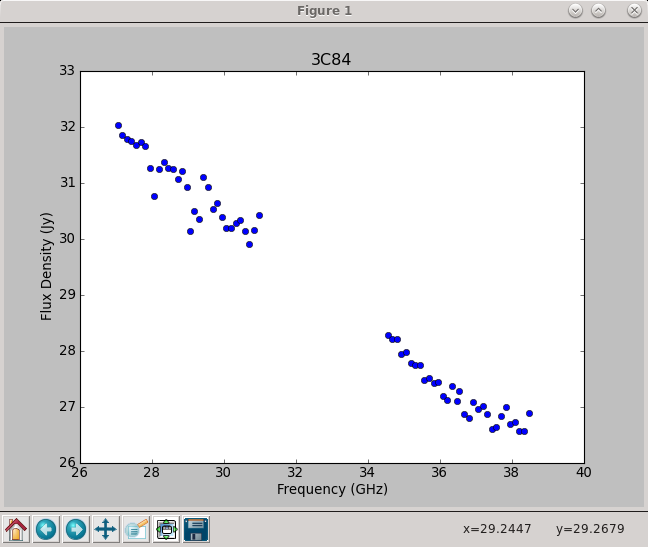
Using the information in the returned flux1 dictionary, we can plot the derived spectrum (Figure 7):
# In CASA
freq = flux1['freq'] / 1e9
spw_list = range(0,64)
spw_str = []
for i in spw_list:
thisspw = str(i)
spw_str.append(thisspw)
(Note that in order to close indented python loops, conditions etc. you will have to press Enter again to execute the indented commands and to return to the CASA prompt.)
# In CASA
bootstrapped_fluxes = []
for j in spw_str:
thisflux = flux1['1'][j]['fluxd'][0]
if thisflux ==None:
continue
else:
bootstrapped_fluxes.append(thisflux)
# In CASA - this section creates the plot seen in Figure 7
pl.clf()
pl.plot(freq, bootstrapped_fluxes, 'bo')
pl.xlabel('Frequency (GHz)')
pl.ylabel('Flux Density (Jy)')
pl.title('3C84')
pl.show()
We can use the model from fluxscale to fill the MODEL column with 3C84's spectral information using setjy. With standard='fluxscale', we can directly use the flux1 Python dictionary as input via fluxdict:
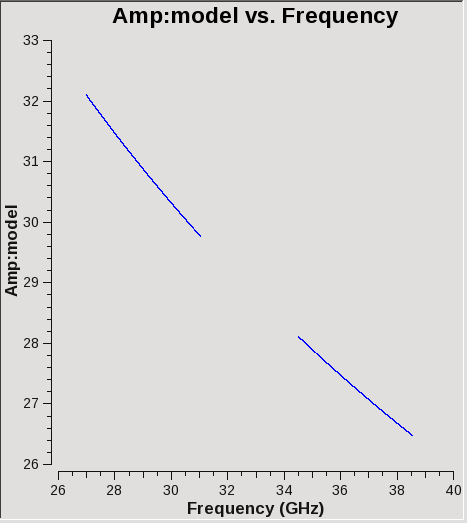
# In CASA: spectral information
setjy(vis='G192-BP.ms', field='1', scalebychan=True, \
standard = 'fluxscale', fluxdict=flux1)
Check with plotms that the data have been appropriately filled (Figure 8):
# In CASA
plotms(vis='G192-BP.ms', field='1', antenna='ea05&ea02', \
xaxis='freq', yaxis='amp', ydatacolumn='model')
Next, we redo the previous calibration using this new model information. Although the commands are the same as issued earlier, keep in mind that the model values for the bandpass calibrator have changed and, therefore, the results of these calibration calculations will differ:
# In CASA: phase only recalibration
gaincal(vis='G192-BP.ms', caltable='calG192.G0.b', \
field='1', spw='*:60~68', \
gaintype='G', refant='ea05', calmode='p', \
solint='int', minsnr=3)
# In CASA: residual delays recalibration
gaincal(vis='G192-BP.ms', caltable='calG192.K0.b', \
gaintable=['calG192.G0.b'], \
field='1', spw='*:5~122', gaintype='K', \
refant='ea05', solint='inf', minsnr=3)
# In CASA: antenna bandpasses recalibration
bandpass(vis='G192-BP.ms', caltable='calG192.B0.b', \
gaintable=['calG192.G0.b', 'calG192.K0.b'], \
field='1', refant='ea05', solnorm=False, \
bandtype='B', solint='inf')
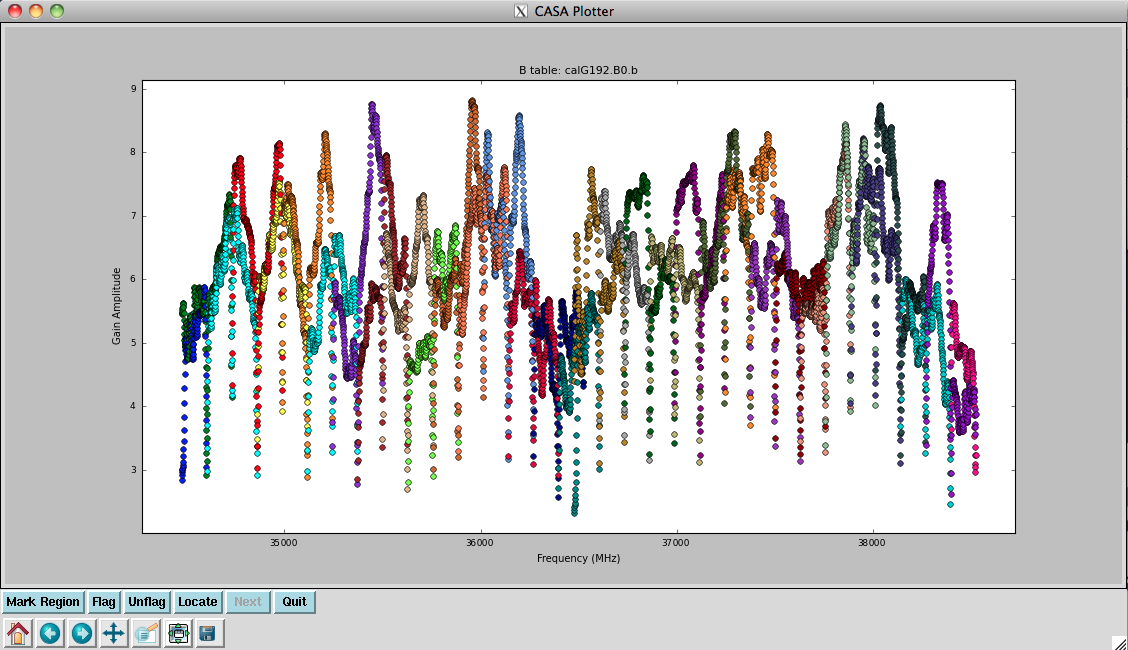
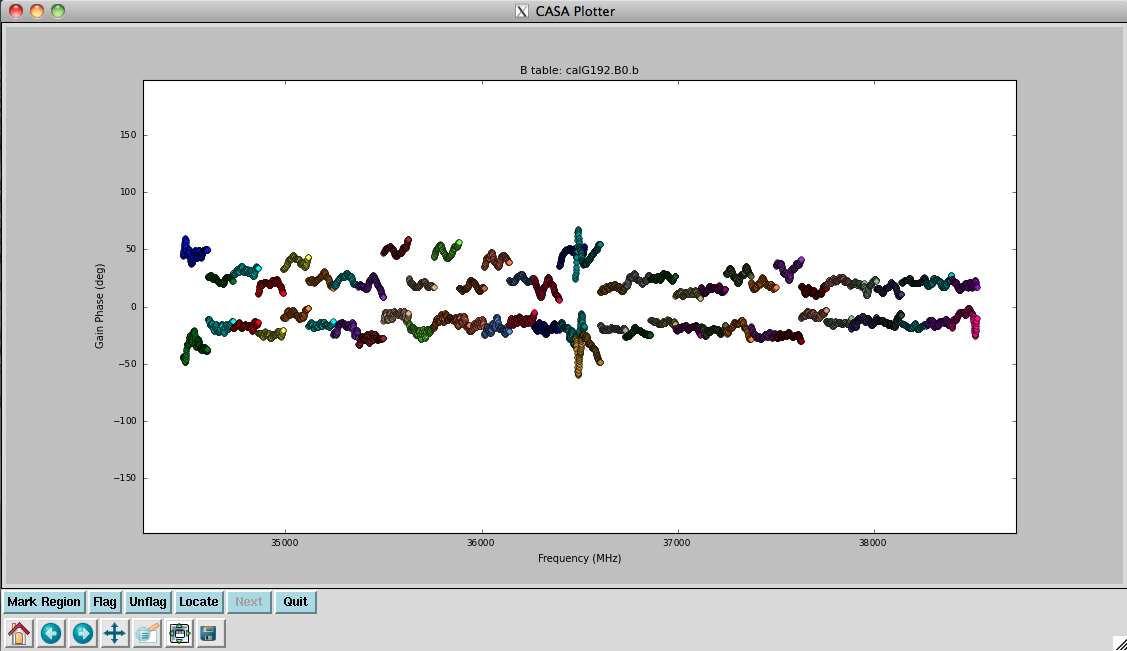
Finally, we inspect these solutions (Figures 9a, 9b, 10a, and 10b):
# In CASA - Figure 9a
plotcal(caltable='calG192.B0.b', xaxis='freq', yaxis='amp', \
spw='0~31', iteration='antenna')
# Figure 9b
plotcal(caltable='calG192.B0.b', xaxis='freq', yaxis='amp', \
spw='32~63', iteration='antenna')
# Figure 10a
plotcal(caltable='calG192.B0.b', xaxis='freq', yaxis='phase', \
iteration='antenna', spw='0~31', \
plotrange=[-1,-1,-180,180])
# Figure 10b
plotcal(caltable='calG192.B0.b', xaxis='freq', yaxis='phase', \
iteration='antenna', spw='32~63', \
plotrange=[-1,-1,-180,180])
They look virtually unchanged from the previous solutions with the exception that the amplitude scaling is corrected for the spectrum of 3C84. We have the final version of our delay and bandpass calibration tables, calG192.K0.b and calG192.B0.b, which can be used for all subsequent calibration steps.
Last checked on CASA Version 4.5.2